Abstract.
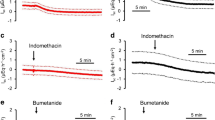
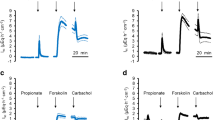
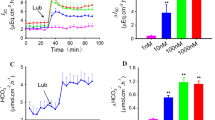
We investigated the effects of 1-ethyl-2-benzimidazolinone (1-EBIO) on ion transport in the mouse jejunum through the use of the short-circuit (I sc) current technique and the application of the patch-clamp technique to isolated jejunal crypts. In HCO3 – Ringer's, 1-EBIO stimulated a dose-dependent (EC50 964 µmol/l), bumetanide-sensitive increase in I sc consistent with stimulation of Cl– secretion. In contrast, in Cl–-free HCO3 – Ringer's containing glucose, 1-EBIO (500 µmol/l) did not increase the phloridzin (100 µmol/l) sensitive I sc, suggesting that electrogenic Na+ absorption was unaltered. Measurement of the membrane potential (V m) with the perforated-patch technique indicated that in isolated crypts, 1-EBIO caused a reversible hyperpolarization of V m and an increase in the change in V m associated with step changes in bath K+, consistent with an increase in K+ conductance. In on-cell patch experiments with KCl Ringer's in the patch pipette and crypts bathed with NaCl Ringer's, 1-EBIO (500 µmol/l) increased the open probability (NP o; 0.01±0.01 to 0.45±0.11, n=7) of an inwardly rectified intermediate conductance (g) channel. In inside-out patches with KCl Ringer's in the patch pipette and KCl Ringer's containing 100 nmol/l Ca2+ in the bath, the current-voltage relationship of the channel was inwardly rectified (g of 10 and 52 pS at –V p of 100 and –100 mV, respectively) and reversed at 0 mV (n=5). Replacement of bath K+ with Na+ shifted the reversal potential toward the equilibrium potential for K+. In the presence of 1-EBIO, reducing the bath Ca2+ from 200 nmol/l to nominally Ca2+-free conditions decreased NP o from 0.90±0.27 to 0.07±0.03 (n=3). We conclude that in the mouse jejunum, 1-EBIO does not stimulate electrogenic Na+ absorption. It does, however, stimulate secretion primarily through the activation of a basolateral, intermediate conductance Ca2+-sensitive K+ channel.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received after revision: 30 June 1999
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamilton, K., Meads, L. & Butt, A. 1-EBIO stimulates Cl– secretion by activating a basolateral K+ channel in the mouse jejunum. Pflügers Arch – Eur J Physiol 439, 158–166 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004249900137
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004249900137