Abstract
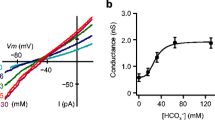
We have previously shown that a new type of K+ channel, present in the basolateral membrane of the colonic crypt base (blm), is necessary for cAMP-activated Cl− secretion. Under basal conditions, and when stimulated by carbachol (CCH) alone, this channel is absent. In the present patch clamp-study we examined the ion channels present in the blm under cell-attached and in cell-excised conditions. In cell-attached recordings with NaCl-type solution in the pipette we measured activity of a K+ channel of 16 ± 0.3 pS (n = 168). The activity of this channel was sharply increased by CCH (0.1 mmol/1, n = 26). Reduction of extracellular Ca2+ to 0.1 mmol/1 (n = 34) led to a reversible reduction of activity of this small channel (SKCa). It was also inactivated by forskolin (5 μmol/l, n = 38), whilst the K+ channel noise caused by the very small K+ channel increased. Activity of non-selective cation channels (NScat) was rarely observed immediately prior to the loss of attached basolateral patches and routinely in excised patches. The NScat, with a mean conductance of 49 ± 1.0 pS (n = 96), was Ca2+ activated and required > 10 μmol/l Ca2+ (cytosolic side = cs). It was reversibly inhibited by ATP (< 1 mmol/1, n = 13) and by 3′,5-dichloro-diphenylamine-2-carboxylate (10–100 μmol/l, n = 5). SKCa was also Ca2+ dependent in excised inside-out basolateral patches. Its activity stayed almost unaltered down to 1 μmol/l (cs) and then fell sharply to almost zero at 0.1 μmol/l Ca2+ (cs, n = 12). SKCa was inhibited by Ba2+ (n = 31) and was charybdotoxin sensitive (1 nmol/1) in outside-out basolateral patches (n = 3). Measurements of the Ca2+ activity ([Ca2+]i) in these cells using fura-2 indicated that forskolin and depolarization, induced by an increase in bath K+ concentration to 30 mmol/l, reduced [Ca2+]i markedly (n = 8–10). Hyperpolarization had the opposite effect. The present data indicate that the blm of these cells contains a small-conductance Ca2+-sensitive K+ channel. This channel is activated promptly by very small increments in [Ca2+]i and is inactivated by a fall in [Ca2+]i induced by forskolin.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad I, Korbmacher C, Segal AS, Cheung P, Boulpaep E, Barnstable CJ (1992) Mouse cortical collecting duct cells show non-selective cation channel activity and express a gene related to the cGMP-gated rod photoreceptor channel. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 10262–10266
Bleich M, Schlatter E, Greger R (1990) The luminal K+ channel of the thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop. Pflügers Arch 415: 449–460
Burckhardt BC, Gögelein H (1992) Small and maxi K+ channels in the basolateral membrane of isolated crypts from rat distal colon. Pflügers Arch 420: 54–60
Ecke D, Bleich M, Lohrmann E, Hropot M, Englert HC, Lang HJ, Warth R, Rohm W, Schwartz B, Fraser G, Greger R (1995) A chromanol type of K+ channel blocker inhibits forskolin —but not carbachol mediated Cl− secretion in rat and rabbit colon. Cell Physiol Biochem 5: 204–210
Ecke D, Bleich M, Greger R (1996) Crypt base cells show cAMP-dependent Cl− secretion but no cation inward current. Pflügers Arch 431: 427–434
Ecke D, Bleich M, Schwartz B, Fraser G, Greger R (1996) Theion conductances of dexamethasone-treated rat colonic crypts. Pflügers Arch 431: 419–426
Fischer KG, Leipziger J, Rubini-Illes P, Nitschke R, Greger R (1996) Attenuation of stimulated Ca2+ influx in colonic epithelial (HT29) cells by cAMP. Pflügers Arch 432: 735–740
Gögelein H, Greger R (1986) A voltage dependent ionic channel in the basolateral membrane of late proximal tubules of the rabbit kidney. Pflügers Arch 407: S142-S148
Gögelein H, Pfannmüller B (1989) The non-selective cation channel in the basolateral membrane of rat exocrine pancreas. Inhibition by 3′,5-dichlorodiphenylamine-2-carboxylic acid (DCDPC) and activation by stilbene disulfonates. Pflügers Arch 413: 287–298
Gögelein H, Greger R, Schlatter E (1987) Potassium channels in the basolateral membrane of the rectal gland of Squalus acanthias. Regulation and inhibitors. Pflügers Arch 409: 107–113
Greger R, Gögelein H, Schlatter E (1987) Potassium channels in the basolateral membrane of the rectal gland of the dogfish (Squalus acanthias). Pflügers Arch 409: 100–106
Greger R, Schlatter E, Gögelein H (1986) Sodium chloride secretion in rectal gland of dogfish Squalus acanthias. News Physiol Sci 1: 134–136
Grynkiewicz G, Poenie M, Tsien RY (1985) A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem 260: 3440–3450
Hamill OP, Marty A, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391: 85–100
Hayslett JP, Gögelein H, Kunzelmann K, Greger R (1987) Characteristics of apical chloride channels in human colon cells (HT29). Pflügers Arch 410: 487–494
Hirsch J, Leipziger J, Fröbe U, Schlatter E (1993) Regulation and possible physiological role of the Ca2+-dependent K+-channel of cortical collecting ducts of the rat. Pflügers Arch 422: 492–498
Ho K, Nichols CG, Lederer WJ, Lytton J, Vassilev PM, Kanazirska MV, Hebert SC (1993) Cloning and expression of aninwardly rectifying ATP-regulated potassium channel. Nature 362: 31–38
Kerst G, Fischer KG, Normann C, Kramer A, Leipziger J, Greger R (1995) Ca2+ influx induced by store release and cytosolic Ca2+ chelation in HT29 colon carcinoma cells. Pflügers Arch 430: 653–665
Klaerke DA, Wiener H, Zeuthen T, Jorgensen PL (1993) Ca2+ activation and pH dependence of a maxi K+ channel from rabbit distal colon epithelium. J Membr Biol 136: 9–21
Klär B, Leipziger I, Nitschke R, Greger R (1993) Ca2+ as a second messenger in CFPAC-1 cells. Cell Physiol Biochem 3: 17–27
Kunzelmann K, Tilmann M, Hansen CP, Greger R (1991) Inhibition of epithelial chloride channels by cytosol. Pflügers Arch 418: 479–490
Leipziger J, Fischer KG, Greger R (1994) Voltage dependent Ca2+ influx in the epithelial cell line HT29: simultaneous use of intracellular Ca2+ measurements and nystatin perforated patch-clamp. Pflügers Arch 426: 427–432
Lohrmann E, Burhoff I, Nitschke RB, Lang HJ, Mania D, Englert HC, Hropot M, Warth R, Rohm W, Bleich M, Greger R (1995) A new class of inhibitors of cAMP-mediated Cl− secretion in rabbit colon, acting by the reduction of cAMP-activated K+ conductance. Pflügers Arch 429: 517–530
Maruyama Y, Petersen OH (1984) Single calcium-dependent cation channels in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. J Membr Biol 81: 83–87
Nitschke R, Fröbe U, Greger R (1991) ADH increases cytosolic Ca2+-activity in isolated perfused rabbit thick ascending limb via a V1 receptor. Pflügers Arch 417: 622–632
Petersen OH (1992) Stimulus-secretion coupling: cytoplasmic calcium signals and the control of ion channels in exocrine acinar cells. J Physiol (Lond) 448: 1–51
Sandle GI, McNicholas CM, Lomax RB (1994) Potassium channels in colonie crypts. Lancet 343: 23–25
Schmid A, Schulz I (1995) Characterization of single potassium channels in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. J Physiol (Lond) 484: 661–676
Siemer C, Gögelein H (1992) Activation of non-selective cation channels in the basolateral membrane of rat distal colon crypt cells by prostaglandin E2. Pflügers Arch 420: 319–328
Siemer C, Gögelein H (1993) Effects of forskolin on crypt cells of rat distal colon. Activation of non-selective cation channels in the crypt base and of chloride conductance in other parts of the crypt. Pflügers Arch 424: 321–328
Strabel D, Diener M (1995) Evidence against direct activation of chloride secretion by carbachol in the rat distal colon. Eur J Pharmacol 274: 181–191
Thorn P, Petersen OH (1992) Activation of non-selective cation channels by physiological cholecystokinin concentrations in mouse pancreatic acinar cells. J Gen Physiol 100: 11–25
Tilmann M, Kunzelmann K, Fröbe U, Cabantchik ZI, Lang HJ, Englert HC, Greger R (1991) Different types of blockers of the intermediate conductance outwardly rectifying chloride channel (ICOR) of epithelia. Pflügers Arch 418: 556–563
Van Driessche W (1994) Noise and impedance analysis. In: Schafer JA, Giebisch G, Kristensen P, Ussing HH (eds) Methods in membrane and transporter research. Landes, Copenhagen, pp 19–80
Wang W, White S, Geibel J, Giebisch G (1990) A potassium channel in the apical membrane of rabbit thick ascending limb of Henle’s loop. Am J Physiol 258: F244-F253
Wangemann P, Wittner M, Di Stefano A, Englert HC, Lang HJ, Schlatter E, Greger R (1986) Cl—channel blockers in the thick ascending limb of the loop of Henle. Structure activity relationship. Pflügers Arch 407: S128-S141
Warth R, Riedemann N, Bleich M, Van Driessche W, Busch AE, Greger R (1996) The cAMP regulated K+ conductance of rat colonic crypt base cells. Pflügers Arch 432: 81–88
Welsh MJ, Smith PL, Fromm M, Frizzell RA (1982) Crypts are the site of intestinal fluid and electrolyte secretion. Science 218: 1219–1221
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bleich, M., Riedemann, N., Warth, R. et al. Ca2+ regulated K+ and non-selective cation channels in the basolateral membrane of rat colonic crypt base cells. Pflügers Arch — Eur J Physiol 432, 1011–1022 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050229
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004240050229