Abstract
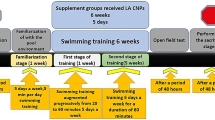
Aging is associated with muscle atrophy, and erosion and destruction of neuronal pathways in the spinal cord. The study aim was to assess the effect of swimming training (Sw) and L-arginine loaded chitosan nanoparticles (LA-CNPs) on the sensory and motor neuron population, autophagy marker LC3, total oxidant status/total antioxidant capacity, behavioural test, GABA and BDNF-TrkB pathway in the spinal cord of aging rats. The rats were randomized to five groups: young (8-weeks) control (n = 7), old control (n = 7), old Sw (n = 7), old LA-CNPs (n = 7) and old Sw + LA-CNPs (n = 7). Groups under LA-CNPs supplementation received 500 mg/kg/day. Sw groups performed a swimming exercise programme 5 days per week for 6 weeks. Upon the completion of the interventions the rats were euthanized and the spinal cord was fixed and frozen for histological assessment, IHC, and gene expression analysis. The old group had more atrophy in the spinal cord with higher changes in LC3 as an indicator of autophagy in the spinal cord compared to the young group (p < 0.0001). The old Sw + LA-CNPs group increased (improved) spinal cord GABA (p = 0.0187), BDNF (p = 0.0003), TrkB (p < 0.0001) gene expression, decreased autophagy marker LC3 protein (p < 0.0001), nerve atrophy and jumping/licking latency (p < 0.0001), improved sciatic functional index score and total oxidant status/total antioxidant capacity compared to the old group (p < 0.0001). In conclusion, swimming and LA-CNPs seems to ameliorate aging‐induced neuron atrophy, autophagy marker LC3, oxidant-antioxidant status, functional restoration, GABA and BDNF-TrkB pathway in the spinal cord of aging rats. Our study provides experimental evidence for a possible positive role of swimming and L-arginine loaded chitosan nanoparticles to decrease complications of aging.







Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Abbadie C, Besson J-M (1993) Effects of morphine and naloxone on basal and evoked Fos-like immunoreactivity in lumbar spinal cord neurons of arthritic rats. Pain 52:29–39
Ashrafi G, Schlehe JS, LaVoie MJ, Schwarz TL (2014) Mitophagy of damaged mitochondria occurs locally in distal neuronal axons and requires PINK1 and Parkin. J Cell Biol 206:655–670
Belviranlı M, Okudan N (2018) Exercise training protects against aging-induced cognitive dysfunction via activation of the hippocampal PGC-1α/FNDC5/BDNF pathway. NeuroMol Med 20:386–400
Brewer S, Desneves K, Pearce L, Mills K, Dunn L, Brown D, Crowe T (2010) Effect of an arginine-containing nutritional supplement on pressure ulcer healing in community spinal patients. J Wound Care 19:311–316
Buchman AS, Leurgans SE, VanderHorst VG, Nag S, Schneider JA, Bennett DA (2019) Spinal motor neurons and motor function in older adults. J Neurol 266:174–182
Castelli V, Benedetti E, Antonosante A, Catanesi M, Pitari G, Ippoliti R, Cimini A, d’Angelo M (2019) Neuronal cells rearrangement during aging and neurodegenerative disease: metabolism, oxidative stress and organelles dynamic. Front Mol Neurosci 12:132
Chen A, Xiong L-J, Tong Y, Mao M (2013) Neuroprotective effect of brain-derived neurotrophic factor mediated by autophagy through the PI3K/Akt/mTOR pathway. Mol Med Rep 8:1011–1016
Chen B, Bohnert D, Borgens RB, Cho Y (2013) Pushing the science forward: chitosan nanoparticles and functional repair of CNS tissue after spinal cord injury. J Biol Eng 7:1–9
Cho Y, Shi R, Borgens RB (2010) Chitosan produces potent neuroprotection and physiological recovery following traumatic spinal cord injury. J Exp Biol 213:1513–1520
Cruz-Sanchez F, Moral A, Tolosa E, De Belleroche J, Rossi M (1998) Evaluation of neuronal loss, astrocytosis and abnormalities of cytoskeletal components of large motor neurons in the human anterior horn in aging. J Neural Transm 105:689–701
Darband SG, Sadighparvar S, Yousefi B, Kaviani M, Mobaraki K, Majidinia M (2020) Combination of exercise training and L-arginine reverses aging process through suppression of oxidative stress, inflammation, and apoptosis in the rat heart. Pflügers Archiv-Eur J Physiol 472:169–178
de Medinaceli L, Freed WJ, Wyatt RJ (1982) An index of the functional condition of rat sciatic nerve based on measurements made from walking tracks. Exp Neurol 77:634–643
Dong D, Lei T, Song M, Ma L, Zhao H (2020) The antidepressant effects of l-arginine on chronic mild stress-induced depression by augmenting the expression of brain-derived neurotrophic factor in rats. Brain Res Bull 158:128–134
Ducaji EC, Pareja-Cajiao M, Gransee HM, Sieck GC, Mantilla CB (2020) BDNF/TrkB Signaling Increases Autophagy Flux in Cervical Spinal Cord. FASEB J 34:1–1
Eddy NB, Leimbach D (1953) Synthetic analgesics. II. Dithienylbutenyl-and dithienylbutylamines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 107:385–393
Erens C, Van Broeckhoven J, Bronckaers A, Lemmens S, Hendrix S (2022) The dark side of an essential amino acid-L-arginine in spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma
Fantozzi S, Cortesi M, Giovanardi A, Borra D, Di Michele R, Gatta G (2020) Effect of walking speed during gait in water of healthy elderly. Gait Posture 82:6–13
Farzad B, Rajabi H, Gharakhanlou R, Allison DJ, Hayat P, Jameie SB (2018) Swimming training attenuates allodynia and hyperalgesia induced by peripheral nerve injury in an adult male rat neuropathic model: effects on irisin and GAD65. Pain Med 19:2236–2245
Frake RA, Ricketts T, Menzies FM, Rubinsztein DC (2015) Autophagy and neurodegeneration. J Clin Investig 125:65–74
Freiberger E, Sieber CC, Kob R (2020) Mobility in older community-dwelling persons: a narrative review. Front Physiol 11:881
Fukuie M, Yamabe T, Nomura Y, Hashitomi T, Maeda S, Sugawara J (2019) The effect of head-out aquatic exercise on arterial stiffness in middle-aged and elderly people. Pulse 7:51–59
Gad MZ (2010) Anti-aging effects of L-arginine. J Adv Res 1:169–177
Geertsen SS, Willerslev-Olsen M, Lorentzen J, Nielsen JB (2017) Development and aging of human spinal cord circuitries. J Neurophysiol 118:1133–1140
Gómez-Pinilla F, Ying Z, Opazo P, Roy R, Edgerton V (2001) Differential regulation by exercise of BDNF and NT-3 in rat spinal cord and skeletal muscle. Eur J Neurosci 13:1078–1084
Gonzalez Porras MA, Sieck GC, Mantilla CB (2018) Impaired autophagy in motor neurons: a final common mechanism of injury and death. Physiology 33:211–224
Gwak YS, Tan HY, Nam TS, Paik KS, Hulsebosch CE, Leem JW (2006) Activation of spinal GABA receptors attenuates chronic central neuropathic pain after spinal cord injury. J Neurotrauma 23:1111–1124
Inoue H, Tsukita K, Iwasato T, Suzuki Y, Tomioka M, Tateno M, Nagao M, Kawata A, Saido TC, Miura M (2003) The crucial role of caspase-9 in the disease progression of a transgenic ALS mouse model. EMBO J 22:6665–6674
Iwabe S, Moreno-Mendoza NA, Trigo-Tavera F, Crowder C, García-Sánchez GA (2007) Retrograde axonal transport obstruction of brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) and its TrkB receptor in the retina and optic nerve of American Cocker Spaniel dogs with spontaneous glaucoma. Vet Ophthalmol 10:12–19
Jia S, Lu Z, Gao Z, An J, Wu X, Li X, Dai X, Zheng Q, Sun Y (2016) Chitosan oligosaccharides alleviate cognitive deficits in an amyloid-β1–42-induced rat model of Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Biol Macromol 83:416–425
Koo J-H, Jang Y-C, Hwang D-J, Um H-S, Lee N-H, Jung J-H, Cho J-Y (2017) Treadmill exercise produces neuroprotective effects in a murine model of Parkinson’s disease by regulating the TLR2/MyD88/NF-κB signaling pathway. Neuroscience 356:102–113
Kruman I, Bruce-Keller AJ, Bredesen D, Waeg G, Mattson MP (1997) Evidence that 4-hydroxynonenal mediates oxidative stress-induced neuronal apoptosis. J Neurosci 17:5089–5100
Kullberg S, Ramirez-Leon V, Johnson H, Ulfhake B (1998) Decreased axosomatic input to motoneurons and astrogliosis in the spinal cord of aged rats. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 53:B369–B379
Lee J, Ryu H, Kowall NW (2009) Motor neuronal protection by L-arginine prolongs survival of mutant SOD1 (G93A) ALS mice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 384:524–529
Lee JW, Furmanski O, Castellanos DA, Daniels LA, Hama AT, Sagen J (2008) Prolonged nociceptive responses to hind paw formalin injection in rats with a spinal cord injury. Neurosci Lett 439:212–215
Li D-J, Li Y-H, Yuan H-B, Qu L-F, Wang P (2017) The novel exercise-induced hormone irisin protects against neuronal injury via activation of the Akt and ERK1/2 signaling pathways and contributes to the neuroprotection of physical exercise in cerebral ischemia. Metabolism 68:31–42
Li X, Wu Q, Xie C, Wang C, Wang Q, Dong C, Fang L, Ding J, Wang T (2019) Blocking of BDNF-TrkB signaling inhibits the promotion effect of neurological function recovery after treadmill training in rats with spinal cord injury. Spinal Cord 57:65–74
Liang M, Wang Z, Li H, Cai L, Pan J, He H, Wu Q, Tang Y, Ma J, Yang L (2018) l-Arginine induces antioxidant response to prevent oxidative stress via stimulation of glutathione synthesis and activation of Nrf2 pathway. Food Chem Toxicol 115:315–328
López-Otín C, Blasco MA, Partridge L, Serrano M, Kroemer G (2013) The hallmarks of aging. Cell 153:1194–1217
Löw P (2011) The role of ubiquitin–proteasome system in ageing. Gen Comp Endocrinol 172:39–43
Luo L, Salunga RC, Guo H, Bittner A, Joy K, Galindo JE, Xiao H, Rogers KE, Wan JS, Jackson MR (1999) Gene expression profiles of laser-captured adjacent neuronal subtypes. Nat Med 5:117–122
Malysz T, Ilha J, Nascimento PSd, Angelis KD, Schaan BDA, Achaval M (2010) Beneficial effects of treadmill training in experimental diabetic nerve regeneration. Clinics 65:1329–1337
Mantilla CB, Gransee HM, Zhan W-Z, Sieck GC (2013) Motoneuron BDNF/TrkB signaling enhances functional recovery after cervical spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 247:101–109
Mirdar S, Kazemzadeh Y, Arabzadeh E, Shirvani H, Hamidian G (2019) The effects of tapering with and without ethanolic extract of Nigella sativa on Hypoxia Inducible Factor-1α and exercise-induced bronchial changes. J Mil Med 21:131–141
Morimoto N, Nagai M, Ohta Y, Miyazaki K, Kurata T, Morimoto M, Murakami T, Takehisa Y, Ikeda Y, Kamiya T (2007) Increased autophagy in transgenic mice with a G93A mutant SOD1 gene. Brain Res 1167:112–117
Nagaratnam N, Nagaratnam K, Cheuk G (2016) Neurological disorders and related problems in the elderly. In: Diseases in the Elderly. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-25787-7_7
Nikoletopoulou V, Sidiropoulou K, Kallergi E, Dalezios Y, Tavernarakis N (2017) Modulation of autophagy by BDNF underlies synaptic plasticity. Cell Metab 26(230–242):e235
Oppenheim RW (1997) Related mechanisms of action of growth factors and antioxidants in apoptosis: an overview. Adv Neurol 72:69–78
Pareja-Cajiao M, Gransee HM, Stowe JM, Rana S, Sieck GC, Mantilla CB (2021) Age-related impairment of autophagy in cervical motor neurons. Exp Gerontol 144:111193
Perluigi M, Di Domenico F, Butterfield DA (2015) mTOR signaling in aging and neurodegeneration: At the crossroad between metabolism dysfunction and impairment of autophagy. Neurobiol Dis 84:39–49
Philippidou P, Valdez G, Akmentin W, Bowers WJ, Federoff HJ, Halegoua S (2011) Trk retrograde signaling requires persistent, Pincher-directed endosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 108:852–857
Powers ET, Morimoto RI, Dillin A, Kelly JW, Balch WE (2009) Biological and chemical approaches to diseases of proteostasis deficiency. Annu Rev Biochem 78:959–991
Qiu L-L, Pan W, Luo D, Zhang G-F, Zhou Z-Q, Sun X-Y, Yang J-J, Ji M-H (2020) Dysregulation of BDNF/TrkB signaling mediated by NMDAR/Ca2+/calpain might contribute to postoperative cognitive dysfunction in aging mice. J Neuroinflammation 17:1–15
Reichardt LF (2006) Neurotrophin-regulated signalling pathways. Philos Trans R Soc B Biol Sci 361:1545–1564
Reynolds AJ, Bartlett SE, Hendry IA (2000) Molecular mechanisms regulating the retrograde axonal transport of neurotrophins. Brain Res Rev 33:169–178
Rodemer W, Selzer ME (2019) Role of axon resealing in retrograde neuronal death and regeneration after spinal cord injury. Neural Regen Res 14:399
Romaus-Sanjurjo D, Ledo-García R, Fernández-López B, Hanslik K, Morgan JR, Barreiro-Iglesias A, Rodicio MC (2018) GABA promotes survival and axonal regeneration in identifiable descending neurons after spinal cord injury in larval lampreys. Cell Death Dis 9:1–15
Romaus-Sanjurjo D, Rodicio MC, Barreiro-Iglesias A (2019) Gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA) promotes recovery from spinal cord injury in lampreys: role of GABA receptors and perspective on the translation to mammals. Neural Regen Res 14:1695
Ruegsegger C, Saxena S (2016) Proteostasis impairment in ALS. Brain Res 1648:571–579
Sadri S, Sharifi G, Dehkordi KJ (2020) Effects of high intensity interval training (up & downward running) with BCAA/nano chitosan on Foxo3 and SMAD soleus muscles of aging rat. Life Sci 252:117641
Sharebiani H, Fazeli B, Maniscalco R, Ligi D, Mannello F (2020) The imbalance among oxidative biomarkers and antioxidant defense systems in thromboangiitis obliterans (Winiwarter-Buerger Disease). J Clin Med 9:1036
Shetty AK, Bates A (2016) Potential of GABA-ergic cell therapy for schizophrenia, neuropathic pain, and Alzheimer׳ s and Parkinson׳ s diseases. Brain Res 1638:74–87
Shirvani H, Rahmati-Ahmadabad S, Broom DR, Mirnejad R (2019) Eccentric resistance training and β-hydroxy-β-methylbutyrate free acid affects muscle PGC-1α expression and serum irisin, nesfatin-1 and resistin in rats. J Exp Biol 222:jeb198424
Shobeiri P, Karimi A, Momtazmanesh S, Teixeira AL, Teunissen CE, van Wegen EE, Hirsch MA, Yekaninejad MS, Rezaei N (2022) Exercise-induced increase in blood-based brain-derived neurotrophic factor (BDNF) in people with multiple sclerosis: A systematic review and meta-analysis of exercise intervention trials. PLoS One 17:e0264557
Silveira EMSd, Kroth A, Santos MdCQ, Silva TCBd, Silveira D, Riffel APK, Scheid T, Trapp M, Partata WA (2019) Age-related changes and effects of regular low-intensity exercise on gait, balance, and oxidative biomarkers in the spinal cord of Wistar rats. Braz J Med Biol Res 52(7):1–13
Simmonite M, Carp J, Foerster BR, Ossher L, Petrou M, Weissman DH, Polk TA (2019) Age-related declines in occipital GABA are associated with reduced fluid processing ability. Acad Radiol 26:1053–1061
Smart TG, Stephenson FA (2019) A half century of γ-aminobutyric acid. Brain Neurosci Adv 3:2398212819858249
Smith ED, Prieto GA, Tong L, Sears-Kraxberger I, Rice JD, Steward O, Cotman CW (2014) Rapamycin and interleukin-1β impair brain-derived neurotrophic factor-dependent neuron survival by modulating autophagy. J Biol Chem 289:20615–20629
Song X-Y, Li F, Zhang F-H, Zhong J-H, Zhou X-F (2008) Peripherally-derived BDNF promotes regeneration of ascending sensory neurons after spinal cord injury. PLoS One 3:e1707
Song X, Liu B, Cui L, Zhou B, Liu W, Xu F, Hayashi T, Hattori S, Ushiki-Kaku Y, Tashiro S-i (2017) Silibinin ameliorates anxiety/depression-like behaviors in amyloid β-treated rats by upregulating BDNF/TrkB pathway and attenuating autophagy in hippocampus. Physiol Behav 179:487–493
Taniguchi H (2014) Genetic dissection of GABAergic neural circuits in mouse neocortex. Front Cell Neurosci 8:8
Terao S-i, Sobue G, Hashizume Y, Li M, Inagaki T, Mitsuma T (1996) Age-related changes in human spinal ventral horn cells with special reference to the loss of small neurons in the intermediate zone: a quantitative analysis. Acta Neuropathol 92:109–114
Tu W-Z, Li S-S, Jiang X, Qian X-R, Yang G-H, Gu P-P, Lu B, Jiang S-H (2018) Effect of electro-acupuncture on the BDNF-TrkB pathway in the spinal cord of CCI rats. Int J Mol Med 41:3307–3315
Tuncer MC, Hatipoglu ES, Ozturk H, Kervancioglu P, Buyukbayram H (2005) The effects of L-arginine on neurological function, histopathology, and expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha following spinal cord ischemia in rats. Eur Surg Res 37:323–329
Ulmann L, Hatcher JP, Hughes JP, Chaumont S, Green PJ, Conquet F, Buell GN, Reeve AJ, Chessell IP, Rassendren F (2008) Up-regulation of P2X4 receptors in spinal microglia after peripheral nerve injury mediates BDNF release and neuropathic pain. J Neurosci 28:11263–11268
Vinsova J, Vavrikova E (2011) Chitosan derivatives with antimicrobial, antitumour and antioxidant activities-a review. Curr Pharm Des 17:3596–3607
Weishaupt N, Blesch A, Fouad K (2012) BDNF: the career of a multifaceted neurotrophin in spinal cord injury. Exp Neurol 238:254–264
Xu Y, Du Y, Huang R, Gao L (2003) Preparation and modification of N-(2-hydroxyl) propyl-3-trimethyl ammonium chitosan chloride nanoparticle as a protein carrier. Biomaterials 24:5015–5022
Yardim A, Gur C, Comakli S, Ozdemir S, Kucukler S, Celik H, Kandemir FM (2022) Investigation of the effects of berberine on bortezomib-induced sciatic nerve and spinal cord damage in rats through pathways involved in oxidative stress and neuro-inflammation. Neurotoxicology 89:127–139
Zarei M, Sabetkasaei M, Moini Zanjani T, Sahebi Vaighan N (2022) The effect of microglial inhibition on the expression of BDNF, KCC2, and GABAA receptor before and after the establishment of CCI-induced neuropathic pain model. Fundam Clin Pharmacol 36:277–285
Zargani M, Hatami Nasab Z, Feizolahi F, Arabzadeh E (2022) Swimming exercise with l-arginine coated nanoparticles supplementation upregulated HAND2 and TBX5 expression in the cardiomyocytes of aging male rats. Biogerontology 23:473–484
Zhang E, Yi M-H, Ko Y, Kim H-W, Seo JH, Lee YH, Lee W, Kim DW (2013) Expression of LC3 and Beclin 1 in the spinal dorsal horn following spinal nerve ligation-induced neuropathic pain. Brain Res 1519:31–39
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
M. Z. and E. A. contributed to the study conception and design, material preparation and data collection. Data were analysed and interpreted by all authors. E. A. and R. R. C. were involved in the drafting of the manuscript and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All animal experiments were according to the NIH Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals, country laws and regulations, and in compliance with the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (IACUC) at Azad University (Karaj, Iran). The study was endorsed by the Ethics Committee of the University underneath protocol number IR.IAU.K.REC.1400.37.
Competing interests
The authors declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zargani, M., Ramirez-Campillo, R. & Arabzadeh, E. Swimming and L-arginine loaded chitosan nanoparticles ameliorates aging‐induced neuron atrophy, autophagy marker LC3, GABA and BDNF-TrkB pathway in the spinal cord of rats. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 475, 621–635 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-023-02795-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-023-02795-y