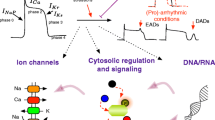
Abstract
Healthy cardiac conduction relies on the coordinated electrical activity of distinct populations of cardiomyocytes. Disruption of cell–cell conduction results in cardiac arrhythmias, a leading cause of morbidity and mortality worldwide. Recent genetic studies have highlighted a major heritable component and identified numerous loci associated with risk of atrial fibrillation, including transcription factor genes, particularly those important in cardiac development, microRNAs, and long noncoding RNAs. Identification of such genetic factors has prompted the search to understand the mechanisms that underlie the genetic component of AF. Recent studies have found several mechanisms by which genetic alterations can result in AF formation via disruption of calcium handling. Loss of developmental transcription factors in adult cardiomyocytes can result in disruption of SR calcium ATPase, sodium calcium exchanger, calcium channels, among other ion channels, which underlie action potential abnormalities and triggered activity that can contribute to AF. This review aims to summarize the complex network of transcription factors and their roles in calcium handling.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andrade J, Khairy P, Dobrev D, Nattel S (2014) The clinical profile and pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation: relationships among clinical features, epidemiology, and mechanisms. Circ Res 114:1453–1468. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.114.303211
Ang YS, Rivas RN, Ribeiro AJS, Srivas R, Rivera J, Stone NR, Pratt K, Mohamed TMA, Fu JD, Spencer CI, Tippens ND, Li M, Narasimha A, Radzinsky E, Moon-Grady AJ, Yu H, Pruitt BL, Snyder MP, Srivastava D (2016) Disease model of GATA4 mutation reveals transcription factor cooperativity in human cardiogenesis. Cell 167:1734-1749.e1722. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.033
Antzelevitch C, Burashnikov A (2011) Overview of basic mechanisms of cardiac arrhythmia. Card Electrophysiol Clin 3:23–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ccep.2010.10.012
Aries A, Paradis P, Lefebvre C, Schwartz RJ, Nemer M (2004) Essential role of GATA-4 in cell survival and drug-induced cardiotoxicity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101:6975–6980. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0401833101
Arnar DO, Thorvaldsson S, Manolio TA, Thorgeirsson G, Kristjansson K, Hakonarson H, Stefansson K (2006) Familial aggregation of atrial fibrillation in Iceland. Eur Heart J 27:708–712. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehi727
Bai J, Gladding PA, Stiles MK, Fedorov VV, Zhao J (2018) Ionic and cellular mechanisms underlying TBX5/PITX2 insufficiency-induced atrial fibrillation: insights from mathematical models of human atrial cells. Sci Rep 8:15642. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-33958-y
Bai J, Lo A, Gladding PA, Stiles MK, Fedorov VV, Zhao J (2020) In silico investigation of the mechanisms underlying atrial fibrillation due to impaired Pitx2. PLoS Comput Biol 16:e1007678. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1007678
Benjamin EJ, Rice KM, Arking DE, Pfeufer A, van Noord C, Smith AV, Schnabel RB, Bis JC, Boerwinkle E, Sinner MF, Dehghan A, Lubitz SA, D’Agostino RB Sr, Lumley T, Ehret GB, Heeringa J, Aspelund T, Newton-Cheh C, Larson MG, Marciante KD, Soliman EZ, Rivadeneira F, Wang TJ, Eiríksdottir G, Levy D, Psaty BM, Li M, Chamberlain AM, Hofman A, Vasan RS, Harris TB, Rotter JI, Kao WH, Agarwal SK, Stricker BH, Wang K, Launer LJ, Smith NL, Chakravarti A, Uitterlinden AG, Wolf PA, Sotoodehnia N, Köttgen A, van Duijn CM, Meitinger T, Mueller M, Perz S, Steinbeck G, Wichmann HE, Lunetta KL, Heckbert SR, Gudnason V, Alonso A, Kääb S, Ellinor PT, Witteman JC (2009) Variants in ZFHX3 are associated with atrial fibrillation in individuals of European ancestry. Nat Genet 41:879–881. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.416
Benson DW, Martin LJ (2010) Complex story of the genetic origins of pediatric heart disease. In: Circulation, vol 121. vol 11. United States, pp 1277–1279. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0b013e3181d98516
Bers DM (2001) Excitation-contraction coupling and cardiac contractile force. Developments in cardiovascular medicine, 2nd edn. Kluwer Academic Publishers, Dordrecht
Bers DM (2002) Cardiac excitation-contraction coupling. Nature 415:198–205. https://doi.org/10.1038/415198a
Biben C, Weber R, Kesteven S, Stanley E, McDonald L, Elliott DA, Barnett L, Köentgen F, Robb L, Feneley M, Harvey RP (2000) Cardiac septal and valvular dysmorphogenesis in mice heterozygous for mutations in the homeobox gene Nkx2-5. Circ Res 87:888–895. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.res.87.10.888
Bisping E, Ikeda S, Kong SW, Tarnavski O, Bodyak N, McMullen JR, Rajagopal S, Son JK, Ma Q, Springer Z, Kang PM, Izumo S, Pu WT (2006) Gata4 is required for maintenance of postnatal cardiac function and protection from pressure overload-induced heart failure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:14471–14476. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0602543103
Blaschke RJ, Hahurij ND, Kuijper S, Just S, Wisse LJ, Deissler K, Maxelon T, Anastassiadis K, Spitzer J, Hardt SE, Schöler H, Feitsma H, Rottbauer W, Blum M, Meijlink F, Rappold G, Gittenberger-de Groot AC (2007) Targeted mutation reveals essential functions of the homeodomain transcription factor Shox2 in sinoatrial and pacemaking development. Circulation 115:1830–1838. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.106.637819
Bootman MD, Higazi DR, Coombes S, Roderick HL (2006) Calcium signalling during excitation-contraction coupling in mammalian atrial myocytes. J Cell Sci 119:3915–3925. https://doi.org/10.1242/jcs.03223
Brandenburg S, Arakel EC, Schwappach B, Lehnart SE (2016) The molecular and functional identities of atrial cardiomyocytes in health and disease. Biochim Biophys Acta 1863:1882–1893. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbamcr.2015.11.025
Brandenburg S, Kohl T, Williams GS, Gusev K, Wagner E, Rog-Zielinska EA, Hebisch E, Dura M, Didié M, Gotthardt M, Nikolaev VO, Hasenfuss G, Kohl P, Ward CW, Lederer WJ, Lehnart SE (2016) Axial tubule junctions control rapid calcium signaling in atria. J Clin Invest 126:3999–4015. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci88241
Briggs LE, Takeda M, Cuadra AE, Wakimoto H, Marks MH, Walker AJ, Seki T, Oh SP, Lu JT, Sumners C, Raizada MK, Horikoshi N, Weinberg EO, Yasui K, Ikeda Y, Chien KR, Kasahara H (2008) Perinatal loss of Nkx2-5 results in rapid conduction and contraction defects. Circ Res 103:580–590. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.108.171835
Bruneau BG, Logan M, Davis N, Levi T, Tabin CJ, Seidman JG, Seidman CE (1999) Chamber-specific cardiac expression of Tbx5 and heart defects in Holt-Oram syndrome. Dev Biol 211:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1006/dbio.1999.9298
Bruneau BG, Nemer G, Schmitt JP, Charron F, Robitaille L, Caron S, Conner DA, Gessler M, Nemer M, Seidman CE, Seidman JG (2001) A murine model of Holt-Oram syndrome defines roles of the T-box transcription factor Tbx5 in cardiogenesis and disease. Cell 106:709–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00493-7
Burashnikov A, Antzelevitch C (2003) Reinduction of atrial fibrillation immediately after termination of the arrhythmia is mediated by late phase 3 early afterdepolarization-induced triggered activity. Circulation 107:2355–2360. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.CIR.0000065578.00869.7C
Chen J, Xu S, Li W, Wu L, Wang L, Li Y, Zhou W (2019) Nkx2.5 insufficiency leads to atrial electrical remodeling through Wnt signaling in HL-1 cells. Exp Ther Med 18:4631–4636. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.8134
Chiang DY, Kongchan N, Beavers DL, Alsina KM, Voigt N, Neilson JR, Jakob H, Martin JF, Dobrev D, Wehrens XH, Li N (2014) Loss of microRNA-106b-25 cluster promotes atrial fibrillation by enhancing ryanodine receptor type-2 expression and calcium release. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 7:1214–1222. https://doi.org/10.1161/circep.114.001973
Chinchilla A, Daimi H, Lozano-Velasco E, Dominguez JN, Caballero R, Delpón E, Tamargo J, Cinca J, Hove-Madsen L, Aranega AE, Franco D (2011) PITX2 insufficiency leads to atrial electrical and structural remodeling linked to arrhythmogenesis. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 4:269–279. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.110.958116
Choi EK, Chang PC, Lee YS, Lin SF, Zhu W, Maruyama M, Fishbein MC, Chen Z, Rubart-von der Lohe M, Field LJ, Chen PS (2012) Triggered firing and atrial fibrillation in transgenic mice with selective atrial fibrosis induced by overexpression of TGF-β1. Circ J 76:1354–1362. https://doi.org/10.1253/circj.cj-11-1301
Christoffels VM, Mommersteeg MT, Trowe MO, Prall OW, de Gier-de VC, Soufan AT, Bussen M, Schuster-Gossler K, Harvey RP, Moorman AF, Kispert A (2006) Formation of the venous pole of the heart from an Nkx2-5-negative precursor population requires Tbx18. Circ Res 98:1555–1563. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000227571.84189.65
Chu L, Yin H, Gao L, Xia Y, Zhang C, Chen Y, Liu T, Huang J, Boheler KR, Zhou Y, Yang HT (2020) Cardiac Na(+)-Ca(2+) exchanger 1 (ncx1h) is critical for the ventricular cardiomyocyte formation via regulating the expression levels of gata4 and hand2 in zebrafish. Sci China Life Sci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11427-019-1706-1
Dai W, Laforest B, Tyan L, Shen KM, Nadadur RD, Alvarado FJ, Mazurek SR, Lazarevic S, Gadek M, Wang Y, Li Y, Valdivia HH, Shen L, Broman MT, Moskowitz IP, Weber CR (2019) A calcium transport mechanism for atrial fibrillation in Tbx5-mutant mice. Elife 8.https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.41814
Darbar D, Roden DM (2013) Genetic mechanisms of atrial fibrillation: impact on response to treatment. Nat Rev Cardiol 10:317–329. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2013.53
Delaney JA, Yin X, Fontes JD, Wallace ER, Skinner A, Wang N, Hammill BG, Benjamin EJ, Curtis LH, Heckbert SR (2018) Hospital and clinical care costs associated with atrial fibrillation for Medicare beneficiaries in the Cardiovascular Health Study and the Framingham Heart Study. SAGE Open Med 6:2050312118759444. https://doi.org/10.1177/2050312118759444
Denham NC, Pearman CM, Caldwell JL, Madders GWP, Eisner DA, Trafford AW, Dibb KM (2018) Calcium in the pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation and heart failure. Front Physiol 9:1380. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphys.2018.01380
Dobrev D, Teos LY, Lederer WJ (2009) Unique atrial myocyte Ca2+ signaling. In: J Mol Cell Cardiol, vol 46. vol 4. pp 448–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2008.12.004
Dobrev D, Wehrens XHT (2017) Calcium-mediated cellular triggered activity in atrial fibrillation. J Physiol 595:4001–4008. https://doi.org/10.1113/jp273048
Ellinor PT, Lunetta KL, Albert CM, Glazer NL, Ritchie MD, Smith AV, Arking DE, Müller-Nurasyid M, Krijthe BP, Lubitz SA, Bis JC, Chung MK, Dörr M, Ozaki K, Roberts JD, Smith JG, Pfeufer A, Sinner MF, Lohman K, Ding J, Smith NL, Smith JD, Rienstra M, Rice KM, Van Wagoner DR, Magnani JW, Wakili R, Clauss S, Rotter JI, Steinbeck G, Launer LJ, Davies RW, Borkovich M, Harris TB, Lin H, Völker U, Völzke H, Milan DJ, Hofman A, Boerwinkle E, Chen LY, Soliman EZ, Voight BF, Li G, Chakravarti A, Kubo M, Tedrow UB, Rose LM, Ridker PM, Conen D, Tsunoda T, Furukawa T, Sotoodehnia N, Xu S, Kamatani N, Levy D, Nakamura Y, Parvez B, Mahida S, Furie KL, Rosand J, Muhammad R, Psaty BM, Meitinger T, Perz S, Wichmann HE, Witteman JC, Kao WH, Kathiresan S, Roden DM, Uitterlinden AG, Rivadeneira F, McKnight B, Sjögren M, Newman AB, Liu Y, Gollob MH, Melander O, Tanaka T, Stricker BH, Felix SB, Alonso A, Darbar D, Barnard J, Chasman DI, Heckbert SR, Benjamin EJ, Gudnason V, Kääb S (2012) Meta-analysis identifies six new susceptibility loci for atrial fibrillation. Nat Genet 44:670–675. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2261
Ellinor PT, Yoerger DM, Ruskin JN, MacRae CA (2005) Familial aggregation in lone atrial fibrillation. Hum Genet 118:179–184. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-005-0034-8
Faggioni M, Savio-Galimberti E, Venkataraman R, Hwang HS, Kannankeril PJ, Darbar D, Knollmann BC (2014) Suppression of spontaneous ca elevations prevents atrial fibrillation in calsequestrin 2-null hearts. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 7:313–320. https://doi.org/10.1161/circep.113.000994
Fatkin D, Santiago CF, Huttner IG, Lubitz SA, Ellinor PT (2017) Genetics of atrial fibrillation: state of the art in 2017. Heart Lung Circ 26:894–901. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hlc.2017.04.008
Firouzi M, Bierhuizen MF, Kok B, Teunissen BE, Jansen AT, Jongsma HJ, Groenewegen WA (2006) The human Cx40 promoter polymorphism -44G–>A differentially affects transcriptional regulation by Sp1 and GATA4. Biochim Biophys Acta 1759:491–496. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbaexp.2006.09.002
Fox CS, Parise H, D’Agostino RB, Lloyd-Jones DM, Vasan RS, Wang TJ, Levy D, Wolf PA, Benjamin EJ (2004) Parental atrial fibrillation as a risk factor for atrial fibrillation in offspring. JAMA 291:2851–2855. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.291.23.2851
Fozzard HA, Schoenberg M (1972) Strength-duration curves in cardiac Purkinje fibres: effects of liminal length and charge distribution. J Physiol 226:593–618. https://doi.org/10.1113/jphysiol.1972.sp009999
Friedman RC, Farh KK, Burge CB, Bartel DP (2009) Most mammalian mRNAs are conserved targets of microRNAs. Genome Res 19:92–105. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.082701.108
Furtado MB, Wilmanns JC, Chandran A, Tonta M, Biben C, Eichenlaub M, Coleman HA, Berger S, Bouveret R, Singh R, Harvey RP, Ramialison M, Pearson JT, Parkington HC, Rosenthal NA, Costa MW (2016) A novel conditional mouse model for Nkx2-5 reveals transcriptional regulation of cardiac ion channels. Differentiation 91:29–41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diff.2015.12.003
Garg V, Kathiriya IS, Barnes R, Schluterman MK, King IN, Butler CA, Rothrock CR, Eapen RS, Hirayama-Yamada K, Joo K, Matsuoka R, Cohen JC, Srivastava D (2003) GATA4 mutations cause human congenital heart defects and reveal an interaction with TBX5. Nature 424:443–447. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01827
Gilmour RF, Moïse NS (1996) Triggered activity as a mechanism for inherited ventricular arrhythmias in German shepherd Dogs. J Am Coll Cardiol 27:1526–1533. https://doi.org/10.1016/0735-1097(95)00618-4
Gore-Panter SR, Hsu J, Barnard J, Moravec CS, Van Wagoner DR, Chung MK, Smith JD (2016) PANCR, the PITX2 Adjacent Noncoding RNA, Is expressed in human left atria and regulates PITX2c expression. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 9:e003197. https://doi.org/10.1161/circep.115.003197
Gudbjartsson DF, Holm H, Gretarsdottir S, Thorleifsson G, Walters GB, Thorgeirsson G, Gulcher J, Mathiesen EB, Njølstad I, Nyrnes A, Wilsgaard T, Hald EM, Hveem K, Stoltenberg C, Kucera G, Stubblefield T, Carter S, Roden D, Ng MC, Baum L, So WY, Wong KS, Chan JC, Gieger C, Wichmann HE, Gschwendtner A, Dichgans M, Kuhlenbäumer G, Berger K, Ringelstein EB, Bevan S, Markus HS, Kostulas K, Hillert J, Sveinbjörnsdóttir S, Valdimarsson EM, Løchen ML, Ma RC, Darbar D, Kong A, Arnar DO, Thorsteinsdottir U, Stefansson K (2009) A sequence variant in ZFHX3 on 16q22 associates with atrial fibrillation and ischemic stroke. Nat Genet 41:876–878. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.417
Guzzolino E, Pellegrino M, Ahuja N, Garrity D, D’Aurizio R, Groth M, Baumgart M, Hatcher CJ, Mercatanti A, Evangelista M, Ippolito C, Tognoni E, Fukuda R, Lionetti V, Pellegrini M, Cremisi F, Pitto L (2020) miR-182-5p is an evolutionarily conserved Tbx5 effector that impacts cardiac development and electrical activity in zebrafish. Cell Mol Life Sci 77:3215–3229. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-019-03343-7
Heijman J, Voigt N, Nattel S, Dobrev D (2014) Cellular and molecular electrophysiology of atrial fibrillation initiation, maintenance, and progression. Circ Res 114:1483–1499. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.114.302226
Hoffmann S, Clauss S, Berger IM, Weiß B, Montalbano A, Röth R, Bucher M, Klier I, Wakili R, Seitz H, Schulze-Bahr E, Katus HA, Flachsbart F, Nebel A, Guenther SP, Bagaev E, Rottbauer W, Kääb S, Just S, Rappold GA (2016) Coding and non-coding variants in the SHOX2 gene in patients with early-onset atrial fibrillation. Basic Res Cardiol 111:36. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-016-0557-2
Hoffmann S, Paone C, Sumer SA, Diebold S, Weiss B, Roeth R, Clauss S, Klier I, Kääb S, Schulz A, Wild PS, Ghrib A, Zeller T, Schnabel RB, Just S, Rappold GA (2019) Functional characterization of rare variants in the SHOX2 gene identified in sinus node dysfunction and atrial fibrillation. Front Genet 10:648. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00648
Hsu J, Gore-Panter S, Tchou G, Castel L, Lovano B, Moravec CS, Pettersson GB, Roselli EE, Gillinov AM, McCurry KR, Smedira NG, Barnard J, Van Wagoner DR, Chung MK, Smith JD (2018) Genetic control of left atrial gene expression yields insights into the genetic susceptibility for atrial fibrillation. Circ Genom Precis Med 11:e002107. https://doi.org/10.1161/circgen.118.002107
Huang RT, Xue S, Xu YJ, Zhou M, Yang YQ (2013) A novel NKX2.5 loss-of-function mutation responsible for familial atrial fibrillation. Int J Mol Med 31:1119–1126. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2013.1316
Huang Y, Wang C, Yao Y, Zuo X, Chen S, Xu C, Zhang H, Lu Q, Chang L, Wang F, Wang P, Zhang R, Hu Z, Song Q, Yang X, Li C, Li S, Zhao Y, Yang Q, Yin D, Wang X, Si W, Li X, Xiong X, Wang D, Luo C, Li J, Wang J, Chen J, Wang L, Han M, Ye J, Chen F, Liu J, Liu Y, Wu G, Yang B, Cheng X, Liao Y, Wu Y, Ke T, Chen Q, Tu X, Elston R, Rao S, Yang Y, Xia Y, Wang QK (2015) Molecular basis of gene-gene interaction: cyclic cross-regulation of gene expression and post-GWAS gene-gene interaction involved in atrial fibrillation. PLoS Genet 11:e1005393. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1005393
Husser D, Büttner P, Ueberham L, Dinov B, Sommer P, Arya A, Hindricks G, Bollmann A (2017) Association of atrial fibrillation susceptibility genes, atrial fibrillation phenotypes and response to catheter ablation: a gene-based analysis of GWAS data. J Transl Med 15:71. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-017-1170-3
Iwasaki YK, Nishida K, Kato T, Nattel S (2011) Atrial fibrillation pathophysiology: implications for management. Circulation 124:2264–2274. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.111.019893
January CT, Riddle JM (1989) Early afterdepolarizations: mechanism of induction and block. A role for L-type Ca2+ current. Circ Res 64:977–990. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.res.64.5.977
Jay PY, Harris BS, Maguire CT, Buerger A, Wakimoto H, Tanaka M, Kupershmidt S, Roden DM, Schultheiss TM, O’Brien TX, Gourdie RG, Berul CI, Izumo S (2004) Nkx2-5 mutation causes anatomic hypoplasia of the cardiac conduction system. J Clin Invest 113:1130–1137. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci19846
Jiang JQ, Shen FF, Fang WY, Liu X, Yang YQ (2011) Novel GATA4 mutations in lone atrial fibrillation. Int J Mol Med 28:1025–1032. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2011.783
Jiang L, Li L, Ruan Y, Zuo S, Wu X, Zhao Q, Xing Y, Zhao X, Xia S, Bai R, Du X, Liu N, Ma CS (2019) Ibrutinib promotes atrial fibrillation by inducing structural remodeling and calcium dysregulation in the atrium. Heart Rhythm 16:1374–1382. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2019.04.008
Jiang Q, Ni B, Shi J, Han Z, Qi R, Xu W, Wang D, Wang DW, Chen M (2014) Down-regulation of ATBF1 activates STAT3 signaling via PIAS3 in pacing-induced HL-1 atrial myocytes. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 449:278–283. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2014.05.041
Joyner RW, Wang YG, Wilders R, Golod DA, Wagner MB, Kumar R, Goolsby WN (2000) A spontaneously active focus drives a model atrial sheet more easily than a model ventricular sheet. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 279:H752-763. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.2000.279.2.H752
Kao YH, Chung CC, Cheng WL, Lkhagva B, Chen YJ (2019) Pitx2c inhibition increases atrial fibroblast activity: Implications in atrial arrhythmogenesis. Eur J Clin Invest 49:e13160. https://doi.org/10.1111/eci.13160
Kao YH, Hsu JC, Chen YC, Lin YK, Lkhagva B, Chen SA, Chen YJ (2016) ZFHX3 knockdown increases arrhythmogenesis and dysregulates calcium homeostasis in HL-1 atrial myocytes. Int J Cardiol 210:85–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2016.02.091
Kim GE, Ross JL, Xie C, Su KN, Zaha VG, Wu X, Palmeri M, Ashraf M, Akar JG, Russell KS, Akar FG, Young LH (2015) LKB1 deletion causes early changes in atrial channel expression and electrophysiology prior to atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res 108:197–208. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvv212
Kirchhof P, Kahr PC, Kaese S, Piccini I, Vokshi I, Scheld HH, Rotering H, Fortmueller L, Laakmann S, Verheule S, Schotten U, Fabritz L, Brown NA (2011) PITX2c is expressed in the adult left atrium, and reducing Pitx2c expression promotes atrial fibrillation inducibility and complex changes in gene expression. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 4:123–133. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.110.958058
Kirchhof P, Marijon E, Fabritz L, Li N, Wang W, Wang T, Schulte K, Hanstein J, Schulte JS, Vogel M, Mougenot N, Laakmann S, Fortmueller L, Eckstein J, Verheule S, Kaese S, Staab A, Grote-Wessels S, Schotten U, Moubarak G, Wehrens XH, Schmitz W, Hatem S, Muller FU (2013) Overexpression of cAMP-response element modulator causes abnormal growth and development of the atrial myocardium resulting in a substrate for sustained atrial fibrillation in mice. Int J Cardiol 166:366–374. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcard.2011.10.057
Kistamás K, Veress R, Horváth B, Bányász T, Nánási PP, Eisner DA (2020) Calcium handling defects and cardiac arrhythmia syndromes. Front Pharmacol 11:72. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2020.00072
Laforest B, Dai W, Tyan L, Lazarevic S, Shen KM, Gadek M, Broman MT, Weber CR, Moskowitz IP (2019) Atrial fibrillation risk loci interact to modulate Ca2+-dependent atrial rhythm homeostasis. J Clin Invest 129:4937–4950. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI124231
Landstrom AP, Dobrev D, Wehrens XHT (2017) Calcium signaling and cardiac arrhythmias. Circ Res 120:1969–1993. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.310083
Li D, Fareh S, Leung TK, Nattel S (1999) Promotion of atrial fibrillation by heart failure in dogs: atrial remodeling of a different sort. Circulation 100:87–95. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.100.1.87
Li N, Chiang DY, Wang S, Wang Q, Sun L, Voigt N, Respress JL, Ather S, Skapura DG, Jordan VK, Horrigan FT, Schmitz W, Muller FU, Valderrabano M, Nattel S, Dobrev D, Wehrens XHT (2014) Ryanodine receptor-mediated calcium leak drives progressive development of an atrial fibrillation substrate in a transgenic mouse model. Circulation 129:1276–1285. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.113.006611
Li N, Wang ZS, Wang XH, Xu YJ, Qiao Q, Li XM, Di RM, Guo XJ, Li RG, Zhang M, Qiu XB, Yang YQ (2018) A SHOX2 loss-of-function mutation underlying familial atrial fibrillation. Int J Med Sci 15:1564–1572. https://doi.org/10.7150/ijms.27424
Li Z, Wang X, Wang W, Du J, Wei J, Zhang Y, Wang J, Hou Y (2017) Altered long non-coding RNA expression profile in rabbit atria with atrial fibrillation: TCONS_00075467 modulates atrial electrical remodeling by sponging miR-328 to regulate CACNA1C. J Mol Cell Cardiol 108:73–85. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2017.05.009
Liu L, Ebana Y, Nitta JI, Takahashi Y, Miyazaki S, Tanaka T, Komura M, Isobe M, Furukawa T (2017) Genetic variants associated with susceptibility to atrial fibrillation in a Japanese population. Can J Cardiol 33:443–449. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjca.2016.10.029
Liu L, Zhao W, Liu J, Gan Y, Tian J (2018) Epigallocatechin-3 gallate prevents pressure overload-induced heart failure by up-regulating SERCA2a via histone acetylation modification in mice. PLoS One 13:e0205123. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0205123
Lu Y, Zhang Y, Wang N, Pan Z, Gao X, Zhang F, Shan H, Luo X, Bai Y, Sun L, Song W, Xu C, Wang Z, Yang B (2010) MicroRNA-328 contributes to adverse electrical remodeling in atrial fibrillation. Circulation 122:2378–2387. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.110.958967
Lubitz SA, Lunetta KL, Lin H, Arking DE, Trompet S, Li G, Krijthe BP, Chasman DI, Barnard J, Kleber ME, Dörr M, Ozaki K, Smith AV, Müller-Nurasyid M, Walter S, Agarwal SK, Bis JC, Brody JA, Chen LY, Everett BM, Ford I, Franco OH, Harris TB, Hofman A, Kääb S, Mahida S, Kathiresan S, Kubo M, Launer LJ, MacFarlane PW, Magnani JW, McKnight B, McManus DD, Peters A, Psaty BM, Rose LM, Rotter JI, Silbernagel G, Smith JD, Sotoodehnia N, Stott DJ, Taylor KD, Tomaschitz A, Tsunoda T, Uitterlinden AG, Van Wagoner DR, Völker U, Völzke H, Murabito JM, Sinner MF, Gudnason V, Felix SB, März W, Chung M, Albert CM, Stricker BH, Tanaka T, Heckbert SR, Jukema JW, Alonso A, Benjamin EJ, Ellinor PT (2014) Novel genetic markers associate with atrial fibrillation risk in Europeans and Japanese. J Am Coll Cardiol 63:1200–1210. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2013.12.015
Lubitz SA, Yi BA, Ellinor PT (2010) Genetics of atrial fibrillation. Heart Fail Clin 6:239–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hfc.2009.12.004
Luo X, Pan Z, Shan H, Xiao J, Sun X, Wang N, Lin H, Xiao L, Maguy A, Qi XY, Li Y, Gao X, Dong D, Zhang Y, Bai Y, Ai J, Sun L, Lu H, Luo XY, Wang Z, Lu Y, Yang B, Nattel S (2013) MicroRNA-26 governs profibrillatory inward-rectifier potassium current changes in atrial fibrillation. J Clin Invest 123:1939–1951. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI62185
Luo X, Yang B, Nattel S (2015) MicroRNAs and atrial fibrillation: mechanisms and translational potential. Nat Rev Cardiol 12:80–90. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrcardio.2014.178
Mahida S (2014) Transcription factors and atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res 101:194–202. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvt261
Mahida S, Ellinor PT (2012) New advances in the genetic basis of atrial fibrillation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 23:1400–1406. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-8167.2012.02445.x
Maitra M, Schluterman MK, Nichols HA, Richardson JA, Lo CW, Srivastava D, Garg V (2009) Interaction of Gata4 and Gata6 with Tbx5 is critical for normal cardiac development. Dev Biol 326:368–377. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2008.11.004
Maxwell JT, Blatter LA (2017) A novel mechanism of tandem activation of ryanodine receptors by cytosolic and SR luminal Ca(2+) during excitation-contraction coupling in atrial myocytes. J Physiol 595:3835–3845. https://doi.org/10.1113/jp273611
McDermott DA, Hatcher CJ, Basson CT (2008) Atrial fibrillation and other clinical manifestations of altered TBX5 dosage in typical Holt-Oram syndrome. In: Circ Res, vol 103. vol 7. p e96. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.108.181834
Molina CE, Voigt N (2017) Finding Ms or Mr right: which miRNA to target in AF? J Mol Cell Cardiol 102:22–25. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2016.11.007
Mommersteeg MT, Brown NA, Prall OW, de Gier-de VC, Harvey RP, Moorman AF, Christoffels VM (2007) Pitx2c and Nkx2-5 are required for the formation and identity of the pulmonary myocardium. Circ Res 101:902–909. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.107.161182
Mommersteeg MT, Hoogaars WM, Prall OW, de Gier-de VC, Wiese C, Clout DE, Papaioannou VE, Brown NA, Harvey RP, Moorman AF, Christoffels VM (2007) Molecular pathway for the localized formation of the sinoatrial node. Circ Res 100:354–362. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.RES.0000258019.74591.b3
Muller FU, Lewin G, Baba HA, Boknik P, Fabritz L, Kirchhefer U, Kirchhof P, Loser K, Matus M, Neumann J, Riemann B, Schmitz W (2005) Heart-directed expression of a human cardiac isoform of cAMP-response element modulator in transgenic mice. J Biol Chem 280:6906–6914. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M407864200
Nadadur RD, Broman MT, Boukens B, Mazurek SR, Yang X, van den Boogaard M, Bekeny J, Gadek M, Ward T, Zhang M, Qiao Y, Martin JF, Seidman CE, Seidman J, Christoffels V, Efimov IR, McNally EM, Weber CR, Moskowitz IP (2016) Pitx2 modulates a Tbx5-dependent gene regulatory network to maintain atrial rhythm. Sci Transl Med 8:354ra115. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf4891
Nadeau M, Georges RO, Laforest B, Yamak A, Lefebvre C, Beauregard J, Paradis P, Bruneau BG, Andelfinger G, Nemer M (2010) An endocardial pathway involving Tbx5, Gata4, and Nos3 required for atrial septum formation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:19356–19361. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0914888107
Nattel S, Burstein B, Dobrev D (2008) Atrial remodeling and atrial fibrillation: mechanisms and implications. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 1:62–73. https://doi.org/10.1161/circep.107.754564
Nattel S, Dobrev D (2012) The multidimensional role of calcium in atrial fibrillation pathophysiology: mechanistic insights and therapeutic opportunities. Eur Heart J 33:1870–1877. https://doi.org/10.1093/eurheartj/ehs079
Nicholas SB, Philipson KD (1999) Cardiac expression of the Na(+)/Ca(2+) exchanger NCX1 is GATA factor dependent. Am J Physiol 277:H324-330. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.1999.277.1.H324
Nishida K, Datino T, Macle L, Nattel S (2014) Atrial fibrillation ablation: translating basic mechanistic insights to the patient. J Am Coll Cardiol 64:823–831. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2014.06.1172
Patterson E, Po SS, Scherlag BJ, Lazzara R (2005) Triggered firing in pulmonary veins initiated by in vitro autonomic nerve stimulation. Heart Rhythm 2:624–631. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2005.02.012
Pezhouman A, Cao H, Fishbein MC, Belardinelli L, Weiss JN, Karagueuzian HS (2018) Atrial fibrillation initiated by early afterdepolarization-mediated triggered activity during acute oxidative stress: efficacy of late sodium current blockade. J Heart Health 4.https://doi.org/10.16966/2379-769x.146
Plotnikov AN, Shlapakova I, Szabolcs MJ, Danilo P, Lorell BH, Potapova IA, Lu Z, Rosen AB, Mathias RT, Brink PR, Robinson RB, Cohen IS, Rosen MR (2007) Xenografted adult human mesenchymal stem cells provide a platform for sustained biological pacemaker function in canine heart. Circulation 116:706–713. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.107.703231
Pluteanu F, Seidl MD, Hamer S, Scholz B, Muller FU (2020) Inward Rectifier K(+) Currents contribute to the proarrhythmic electrical phenotype of atria overexpressing cyclic adenosine monophosphate response element modulator isoform CREM-IbDeltaC-X. J Am Heart Assoc 9:e016144. https://doi.org/10.1161/JAHA.119.016144
Pogwizd SM, Schlotthauer K, Li L, Yuan W, Bers DM (2001) Arrhythmogenesis and contractile dysfunction in heart failure: roles of sodium-calcium exchange, inward rectifier potassium current, and residual beta-adrenergic responsiveness. Circ Res 88:1159–1167. https://doi.org/10.1161/hh1101.091193
Poon EN, Hao B, Guan D, Jun Li M, Lu J, Yang Y, Wu B, Wu SC, Webb SE, Liang Y, Miller AL, Yao X, Wang J, Yan B, Boheler KR (2018) Integrated transcriptomic and regulatory network analyses identify microRNA-200c as a novel repressor of human pluripotent stem cell-derived cardiomyocyte differentiation and maturation. Cardiovasc Res 114:894–906. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvy019
Posch MG, Boldt LH, Polotzki M, Richter S, Rolf S, Perrot A, Dietz R, Ozcelik C, Haverkamp W (2010) Mutations in the cardiac transcription factor GATA4 in patients with lone atrial fibrillation. Eur J Med Genet 53:201–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejmg.2010.03.008
Postma AV, van de Meerakker JB, Mathijssen IB, Barnett P, Christoffels VM, Ilgun A, Lam J, Wilde AA, Lekanne Deprez RH, Moorman AF (2008) A gain-of-function TBX5 mutation is associated with atypical Holt-Oram syndrome and paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circ Res 102:1433–1442. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.107.168294
Puskaric S, Schmitteckert S, Mori AD, Glaser A, Schneider KU, Bruneau BG, Blaschke RJ, Steinbeisser H, Rappold G (2010) Shox2 mediates Tbx5 activity by regulating Bmp4 in the pacemaker region of the developing heart. Hum Mol Genet 19:4625–4633. https://doi.org/10.1093/hmg/ddq393
Pérez-Hernández M, Matamoros M, Barana A, Amorós I, Gómez R, Núñez M, Sacristán S, Pinto Á, Fernández-Avilés F, Tamargo J, Delpón E, Caballero R (2016) Pitx2c increases in atrial myocytes from chronic atrial fibrillation patients enhancing IKs and decreasing ICa, L. Cardiovasc Res 109:431–441. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvv280
Qi XY, Yeh YH, Xiao L, Burstein B, Maguy A, Chartier D, Villeneuve LR, Brundel BJ, Dobrev D, Nattel S (2008) Cellular signaling underlying atrial tachycardia remodeling of L-type calcium current. Circ Res 103:845–854. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.108.175463
Reyat JS, Chua W, Cardoso VR, Witten A, Kastner PM, Kabir SN, Sinner MF, Wesselink R, Holmes AP, Pavlovic D, Stoll M, Kääb S, Gkoutos GV, de Groot JR, Kirchhof P, Fabritz L (2020) Reduced left atrial cardiomyocyte PITX2 and elevated circulating BMP10 predict atrial fibrillation after ablation. JCI Insight 5.https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.139179
Rommel C, Hein L (2020) Four dimensions of the cardiac myocyte epigenome: from fetal to adult heart. Curr Cardiol Rep 22:26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11886-020-01280-7
Rommel C, Rösner S, Lother A, Barg M, Schwaderer M, Gilsbach R, Bömicke T, Schnick T, Mayer S, Doll S, Hesse M, Kretz O, Stiller B, Neumann FJ, Mann M, Krane M, Fleischmann BK, Ravens U, Hein L (2018) The transcription factor ETV1 induces atrial remodeling and arrhythmia. Circ Res 123:550–563. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.118.313036
Rothschild SC, Easley CAt, Francescatto L, Lister JA, Garrity DM, Tombes RM, (2009) Tbx5-mediated expression of Ca(2+)/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II is necessary for zebrafish cardiac and pectoral fin morphogenesis. Dev Biol 330:175–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ydbio.2009.03.024
Schmidt C, Wiedmann F, Kallenberger SM, Ratte A, Schulte JS, Scholz B, Muller FU, Voigt N, Zafeiriou MP, Ehrlich JR, Tochtermann U, Veres G, Ruhparwar A, Karck M, Katus HA, Thomas D (2017) Stretch-activated two-pore-domain (K2P) potassium channels in the heart: focus on atrial fibrillation and heart failure. Prog Biophys Mol Biol 130:233–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbiomolbio.2017.05.004
Schotten U, Verheule S, Kirchhof P, Goette A (2011) Pathophysiological mechanisms of atrial fibrillation: a translational appraisal. Physiol Rev 91:265–325. https://doi.org/10.1152/physrev.00031.2009
Seidl MD, Stein J, Hamer S, Pluteanu F, Scholz B, Wardelmann E, Huge A, Witten A, Stoll M, Hammer E, Volker U, Muller FU (2017) Characterization of the genetic program linked to the development of atrial fibrillation in CREM-IbDeltaC-X mice. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol 10. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCEP.117.005075
Shang LL, Sanyal S, Pfahnl AE, Jiao Z, Allen J, Liu H, Dudley SC Jr (2008) NF-kappaB-dependent transcriptional regulation of the cardiac scn5a sodium channel by angiotensin II. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 294:C372-379. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpcell.00186.2007
Shekhar A, Lin X, Lin B, Liu FY, Zhang J, Khodadadi-Jamayran A, Tsirigos A, Bu L, Fishman GI, Park DS (2018) ETV1 activates a rapid conduction transcriptional program in rodent and human cardiomyocytes. Sci Rep 8:9944. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-28239-7
Shekhar A, Lin X, Liu FY, Zhang J, Mo H, Bastarache L, Denny JC, Cox NJ, Delmar M, Roden DM, Fishman GI, Park DS (2016) Transcription factor ETV1 is essential for rapid conduction in the heart. J Clin Invest 126:4444–4459. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci87968
Shen C, Kong B, Liu Y, Xiong L, Shuai W, Wang G, Quan D, Huang H (2018) YY1-induced upregulation of lncRNA KCNQ1OT1 regulates angiotensin II-induced atrial fibrillation by modulating miR-384b/CACNA1C axis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 505:134–140. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2018.09.064
Shimizu A, Centurion OA (2002) Electrophysiological properties of the human atrium in atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res 54:302–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0008-6363(02)00262-6
Sinner MF, Tucker NR, Lunetta KL, Ozaki K, Smith JG, Trompet S, Bis JC, Lin H, Chung MK, Nielsen JB, Lubitz SA, Krijthe BP, Magnani JW, Ye J, Gollob MH, Tsunoda T, Müller-Nurasyid M, Lichtner P, Peters A, Dolmatova E, Kubo M, Smith JD, Psaty BM, Smith NL, Jukema JW, Chasman DI, Albert CM, Ebana Y, Furukawa T, Macfarlane PW, Harris TB, Darbar D, Dörr M, Holst AG, Svendsen JH, Hofman A, Uitterlinden AG, Gudnason V, Isobe M, Malik R, Dichgans M, Rosand J, Van Wagoner DR, Benjamin EJ, Milan DJ, Melander O, Heckbert SR, Ford I, Liu Y, Barnard J, Olesen MS, Stricker BH, Tanaka T, Kääb S, Ellinor PT (2014) Integrating genetic, transcriptional, and functional analyses to identify 5 novel genes for atrial fibrillation. Circulation 130:1225–1235. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.114.009892
Stefanovic S, Barnett P, van Duijvenboden K, Weber D, Gessler M, Christoffels VM (2014) GATA-dependent regulatory switches establish atrioventricular canal specificity during heart development. Nat Commun 5:3680. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms4680
Steimle JD, Moskowitz IP (2017) TBX5: A key regulator of heart development. Curr Top Dev Biol 122:195–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/bs.ctdb.2016.08.008
Stümpel FT, Stein J, Himmler K, Scholz B, Seidl MD, Skryabin BV, Müller FU (2018) Homozygous CREM-IbΔC-X overexpressing mice are a reliable and effective disease model for atrial fibrillation. Front Pharmacol 9:706. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00706
Suzuki YJ (2011) Cell signaling pathways for the regulation of GATA4 transcription factor: Implications for cell growth and apoptosis. Cell Signal 23:1094–1099. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellsig.2011.02.007
Syeda F, Holmes AP, Yu TY, Tull S, Kuhlmann SM, Pavlovic D, Betney D, Riley G, Kucera JP, Jousset F, de Groot JR, Rohr S, Brown NA, Fabritz L, Kirchhof P (2016) PITX2 modulates atrial membrane potential and the antiarrhythmic effects of sodium-channel blockers. J Am Coll Cardiol 68:1881–1894. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2016.07.766
Syeda F, Kirchhof P, Fabritz L (2017) PITX2-dependent gene regulation in atrial fibrillation and rhythm control. J Physiol 595:4019–4026. https://doi.org/10.1113/JP273123
Szabo B, Sweidan R, Rajagopalan CV, Lazzara R (1994) Role of Na+:Ca2+ exchange current in Cs(+)-induced early afterdepolarizations in Purkinje fibers. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 5:933–944. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1540-8167.1994.tb01133.x
Tao Y, Zhang M, Li L, Bai Y, Zhou Y, Moon AM, Kaminski HJ, Martin JF (2014) Pitx2, an atrial fibrillation predisposition gene, directly regulates ion transport and intercalated disc genes. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 7:23–32. https://doi.org/10.1161/circgenetics.113.000259
Torrado M, Franco D, Lozano-Velasco E, Hernández-Torres F, Calviño R, Aldama G, Centeno A, Castro-Beiras A, Mikhailov A (2015) A microRNA-transcription factor blueprint for early atrial arrhythmogenic remodeling. Biomed Res Int 2015:263151. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/263151
Tse G (2016) Mechanisms of cardiac arrhythmias. J Arrhythm 32:75–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joa.2015.11.003
Tucker NR, Dolmatova EV, Lin H, Cooper RR, Ye J, Hucker WJ, Jameson HS, Parsons VA, Weng LC, Mills RW, Sinner MF, Imakaev M, Leyton-Mange J, Vlahakes G, Benjamin EJ, Lunetta KL, Lubitz SA, Mirny L, Milan DJ, Ellinor PT (2017) Diminished PRRX1 expression is associated with increased risk of atrial fibrillation and shortening of the cardiac action potential. Circ Cardiovasc Genet 10.https://doi.org/10.1161/circgenetics.117.001902
Tucker NR, Ellinor PT (2014) Emerging directions in the genetics of atrial fibrillation. Circ Res 114:1469–1482. https://doi.org/10.1161/circresaha.114.302225
van den Berg NWE, Kawasaki M, Berger WR, Neefs J, Meulendijks E, Tijsen AJ, de Groot JR (2017) MicroRNAs in atrial fibrillation: from expression signatures to functional implications. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther 31:345–365. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10557-017-6736-z
van Ouwerkerk AF, Hall AW, Kadow ZA, Lazarevic S, Reyat JS, Tucker NR, Nadadur RD, Bosada FM, Bianchi V, Ellinor PT, Fabritz L, Martin JF, de Laat W, Kirchhof P, Moskowitz IP, Christoffels VM (2020) Epigenetic and transcriptional networks underlying atrial fibrillation. Circ Res 127:34–50. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.120.316574
Vermij SH, Abriel H, van Veen TA (2017) Refining the molecular organization of the cardiac intercalated disc. Cardiovasc Res 113:259–275. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvw259
Vlasblom R, Muller A, Beckers CM, van Nieuw Amerongen GP, Zuidwijk MJ, van Hardeveld C, Paulus WJ, Simonides WS (2009) RhoA-ROCK signaling is involved in contraction-mediated inhibition of SERCA2a expression in cardiomyocytes. Pflugers Arch 458:785–793. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-009-0659-x
Voigt N, Heijman J, Wang Q, Chiang DY, Li N, Karck M, Wehrens XHT, Nattel S, Dobrev D (2014) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of atrial arrhythmogenesis in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation. Circulation 129:145–156. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.113.006641
Wakili R, Voigt N, Kääb S, Dobrev D, Nattel S (2011) Recent advances in the molecular pathophysiology of atrial fibrillation. J Clin Invest 121:2955–2968. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci46315
Wang J, Bai Y, Li N, Ye W, Zhang M, Greene SB, Tao Y, Chen Y, Wehrens XH, Martin JF (2014) Pitx2-microRNA pathway that delimits sinoatrial node development and inhibits predisposition to atrial fibrillation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:9181–9186. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1405411111
Wang J, Klysik E, Sood S, Johnson RL, Wehrens XH, Martin JF (2010) Pitx2 prevents susceptibility to atrial arrhythmias by inhibiting left-sided pacemaker specification. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 107:9753–9758. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0912585107
Wang J, Sun YM, Yang YQ (2012) Mutation spectrum of the GATA4 gene in patients with idiopathic atrial fibrillation. Mol Biol Rep 39:8127–8135. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-012-1660-6
Wang Y, Morishima M, Zheng M, Uchino T, Mannen K, Takahashi A, Nakaya Y, Komuro I, Ono K (2007) Transcription factors Csx/Nkx2.5 and GATA4 distinctly regulate expression of Ca2+ channels in neonatal rat heart. J Mol Cell Cardiol 42:1045–1053. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yjmcc.2007.03.905
Weiss JN, Garfinkel A, Karagueuzian HS, Chen PS, Qu Z (2010) Early afterdepolarizations and cardiac arrhythmias. Heart Rhythm 7:1891–1899. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2010.09.017
Weng LC, Preis SR, Hulme OL, Larson MG, Choi SH, Wang B, Trinquart L, McManus DD, Staerk L, Lin H, Lunetta KL, Ellinor PT, Benjamin EJ, Lubitz SA (2018) Genetic predisposition, clinical risk factor burden, and lifetime risk of atrial fibrillation. Circulation 137:1027–1038. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.117.031431
Xie WH, Chang C, Xu YJ, Li RG, Qu XK, Fang WY, Liu X, Yang YQ (2013) Prevalence and spectrum of Nkx2.5 mutations associated with idiopathic atrial fibrillation. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 68:777–784. https://doi.org/10.6061/clinics/2013(06)09
Xie Y, Sato D, Garfinkel A, Qu Z, Weiss JN (2010) So little source, so much sink: requirements for afterdepolarizations to propagate in tissue. Biophys J 99:1408–1415. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpj.2010.06.042
Xu L, Renaud L, Müller JG, Baicu CF, Bonnema DD, Zhou H, Kappler CS, Kubalak SW, Zile MR, Conway SJ, Menick DR (2006) Regulation of Ncx1 expression. Identification of regulatory elements mediating cardiac-specific expression and up-regulation. J Biol Chem 281:34430–34440. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M607446200
Yang XH, Nadadur RD, Hilvering CR, Bianchi V, Werner M, Mazurek SR, Gadek M, Shen KM, Goldman JA, Tyan L, Bekeny J, Hall JM, Lee N, Perez-Cervantes C, Burnicka-Turek O, Poss KD, Weber CR, de Laat W, Ruthenburg AJ, Moskowitz IP (2017) Transcription-factor-dependent enhancer transcription defines a gene regulatory network for cardiac rhythm. Elife 6.https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.31683
Yang YQ, Wang MY, Zhang XL, Tan HW, Shi HF, Jiang WF, Wang XH, Fang WY, Liu X (2011) GATA4 loss-of-function mutations in familial atrial fibrillation. Clin Chim Acta 412:1825–1830. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cca.2011.06.017
Yuan F, Qiu XB, Li RG, Qu XK, Wang J, Xu YJ, Liu X, Fang WY, Yang YQ, Liao DN (2015) A novel NKX2-5 loss-of-function mutation predisposes to familial dilated cardiomyopathy and arrhythmias. Int J Mol Med 35:478–486. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2014.2029
Yue L, Melnyk P, Gaspo R, Wang Z, Nattel S (1999) Molecular mechanisms underlying ionic remodeling in a dog model of atrial fibrillation. Circ Res 84:776–784. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.res.84.7.776
Yue L, Xie J, Nattel S (2011) Molecular determinants of cardiac fibroblast electrical function and therapeutic implications for atrial fibrillation. Cardiovasc Res 89:744–753. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvq329
Zhu Y, Gramolini AO, Walsh MA, Zhou YQ, Slorach C, Friedberg MK, Takeuchi JK, Sun H, Henkelman RM, Backx PH, Redington AN, Maclennan DH, Bruneau BG (2008) Tbx5-dependent pathway regulating diastolic function in congenital heart disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:5519–5524. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0801779105
Zipes DP (2004) Mechanisms of clinical arrhythmias. Heart Rhythm 1:4C-18C. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hrthm.2004.10.015
Funding
This study was funded by the Biological Sciences Collegiate Division Research Endowments at the University of Chicago NIH T32HL007381.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the special issue on Calcium Signal Dynamics in Cardiac Myocytes and Fibroblasts: Mechanisms in Pflügers Archiv—European Journal of Physiology
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dai, W., Kesaraju, S. & Weber, C.R. Transcriptional factors in calcium mishandling and atrial fibrillation development. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 473, 1177–1197 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-021-02553-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-021-02553-y