Abstract
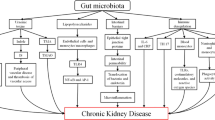
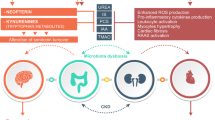
Chronic kidney disease (CKD) represents a growing public health problem associated with loss of kidney function and cardiovascular disease (CVD), the main leading cause of morbidity and mortality in CKD. It is well established that CKD is associated with gut dysbiosis. Over the past few years, there has been a growing interest in studying the composition of the gut microbiota in patients with CKD as well as the mechanisms by which gut dysbiosis contributes to CKD progression, in order to identify possible therapeutic targets to improve the morbidity and survival in CKD. The purpose of this review is to explore the clinical evidence and the mechanisms involved in the gut-kidney crosstalk as well as the possible interventions to restore a normal balance of the gut microbiota in CKD. It is well known that the influence of the gut microbiota on the gut–kidney axis acts in a reciprocal way: on the one hand, CKD significantly modifies the composition and functions of the gut microbiota. On the other hand, gut microbiota is able to manipulate the processes leading to CKD onset and progression through inflammatory, endocrine, and neurologic pathways. Understanding the complex interaction between these two organs (gut microbiota and kidney) may provide novel nephroprotective interventions to prevent the progression of CKD by targeting the gut microbiota. The review is divided into three main sections: evidences from clinical studies about the existence of a gut microbiota dysbiosis in CKD; the complex mechanisms that explain the bidirectional relationship between CKD and gut dysbiosis; and reports regarding the effects of prebiotic, probiotic, and synbiotic supplementation to restore gut microbiota balance in CKD.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Abbreviations
- Ach:
-
Acetylcholine
- AhR:
-
Aryl hydrocarbon receptor
- ANG II:
-
Angiotensin II
- BUN:
-
Blood urea nitrogen
- CFU:
-
Colony-forming unit
- CKD:
-
Chronic kidney disease
- CRP:
-
C-reactive protein
- CVD:
-
Cardiovascular disease
- eGFR:
-
Estimated glomerular filtration rate
- ESRD:
-
End-stage renal disease
- GABA:
-
γ-aminobutyric acid
- GI:
-
Gastrointestinal
- GLP-1:
-
Glucagon-like peptide 1
- GLP-2:
-
Glucagon-like peptide 2
- GFOB:
-
Glutamine, dietary fiber, oligosaccharide and Bifidobacterium longum strain
- GFR:
-
Glomerular filtration rate
- HAM-RS2:
-
High amylose maize resistant starch
- HD:
-
Hemodialysis
- HPA:
-
Hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal
- IPA:
-
Indolepropionic acid
- IS:
-
Indoxyl sulfate
- IL-6:
-
Interleukin-6
- IL-10:
-
Interleukin-10
- IAA:
-
Indole-3-acetic acid
- LPS:
-
Lipopolysaccharide
- NF-κB:
-
Nuclear factor-κB
- OTUs:
-
Operational taxonomic units
- p-CS:
-
p-cresyl sulfate
- PD:
-
Peritoneal dialysis
- PUFAs:
-
Poly-unsaturated fatty acids
- PYY:
-
Peptide YY
- ROS:
-
Reactive oxygen species
- SCFAs:
-
Short-chain fatty acids
- TMAO:
-
Trimethylamine n-oxidase
- TNF-α:
-
Tumor necrosis factor α
References
Ahrén IL, Xu J, Önning G, Olsson C, Ahrné S, Molin G (2015) Antihypertensive activity of blueberries fermented by Lactobacillus plantarum DSM 15313 and effects on the gut microbiota in healthy rats. Clin Nutr 34(4):719–726
Al Khodor S, Shatat IF (2017) Gut microbiome and kidney disease: a bidirectional relationship. Pediatr Nephrol 32(6):921–931
Aronov PA, Luo FJ-G, Plummer NS, Quan Z, Holmes S et al (2011) Colonic contribution to uremic solutes. J Am Soc Nephrol 22(9):1769–1776
Barreto FC, Barreto DV, Liabeuf S, Meert N, Glorieux G, Temmar M, Choukroun G, Vanholder R, Massy ZA, European Uremic Toxin Work Group (EUTox) (2009) Serum indoxyl sulfate is associated with vascular disease and mortality in chronic kidney disease patients. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 4:1551–1558
Bendheim PE, Poeggeler B, Neria E, Ziv V, Pappolla MA (2002) Development of indole-3-propionic acid (OXIGON™) for alzheimer's disease. J Mol Neurosci 19:213–217
Biruete A, Allen JM, Kistler BM, Jeong JH, Fitschen PJ, Swanson KS, Wilund KR (2019) Gut microbiota and Cardiometabolic risk factors in hemodialysis patients: a pilot study. Top Clin Nutr 34(2):153–160
Borges NA, Stenvinkel P, Bergman P, Qureshi AR, Lindholm B, Moraes C, Stockler-Pinto MB, Mafra D (2019) Effects of probiotic supplementation on Trimethylamine-N-oxide plasma levels in hemodialysis patients: a pilot study. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins 11(2):648–654
Brito JS, Borges NA, Anjos JSD, Nakao LS, Stockler-Pinto MB, Paiva BR, Cardoso-Weide LC, Cardozo LFMF, Mafra D (2019) Aryl hydrocarbon receptor and uremic toxins from the gut microbiota in chronic kidney disease patients: is there a relationship between them? Biochemistry 58(15):2054–2060
Cani PD, Neyrinck AM, Maton N, Delzenne NM (2005) Oligofructose promotes satiety in rats fed a high-fat diet: involvement of glucagon-like Peptide-1. Obes Res 13(6):1000–1007
Carpenter S, O'Neill LA (2009) Recent insights into the structure of toll-like receptors and post-translational modifications of their associated signalling. Biochem J 422(1):1–10
Castillo-Rodriguez E, Fernandez-Prado R, Esteras R, Perez-Gomez MV, Gracia-Iguacel C et al (2018) Impact of Altered Intestinal Microbiota on Chronic Kidney Disease Progression. Toxins (Basel) 10(7):300
Cheema MU, Pluznick JL (2019) Gut microbiota plays a central role to modulate the plasma and fecal Metabolomes in response to angiotensin II. Hypertension 74(1):184–193
Chen TK, Knicely DH, Grams ME (2019) Chronic kidney disease diagnosis and management: a review. JAMA 322(13):1294–1304
Chen Y, Chen D, Chen L, Liu J, Vaziri ND et al (2019) Microbiome–metabolome reveals the contribution of gut–kidney axis on kidney disease. J Transl Med 17:5
Chung S, Barnes JL, Astroth KS (2019) Gastrointestinal microbiota in patients with chronic kidney disease: a systematic review. Adv Nutr 10(5):888–901
Cigarran Guldris E, González Parra E, Cases Amenós A (2017) Gut microbiota in chronic kidney disease. Nefrología 37(1):9–19
Cremon C, Barbaro MR, Ventura M, Barbara G (2018) Pre- and probiotic overview. Curr Opin Pharmacol 43:87–92
Cruz-Mora J, Martínez-Hernández NE, Martín del Campo-López F, Viramontes-Hörner D, Vizmanos-Lamotte B, Muñoz-Valle JF, García-García G, Parra-Rojas I, Castro-Alarcón N (2014) Effects of a symbiotic on gut microbiota in Mexican patients with end-stage renal disease. J Ren Nutr 24(5):330–335
Darisipudi MN, Knauf F (2016) An update on the role of the inflammasomes in the pathogenesis of kidney diseases. Pediatr Nephrol 31:535–544
Dehghani H, Heidari F, Mozaffari-Khosravi H, Nouri-Majelan N, Dehghani A (2016) Synbiotic supplementations for azotemia in patients with chronic kidney disease: a randomized controlled trial. Iran J Kidney Dis 10(6):351–357
Deltombe O, Van Biesen W, Glorieux G, Massy Z, Dhondt A et al (2015) Exploring protein binding of uremic toxins in patients with different stages of chronic kidney disease and during hemodialysis. Toxins 7:3933–3946
Devine E, Krieter DH, Rüth M, Jankovski J, LHD (2014) Binding affinity and capacity for the uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate. Toxins 6:416–429
Di Iorio BR, Marzocco S, Bellasi A, De Simone E, Dal Piaz F et al (2018) Nutritional therapy reduces protein carbamylation through urea lowering in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 33(5):804–813
Di Iorio BR, Rocchetti MT, De Angelis M, Cosola C, Marzocco S et al (2019) Nutritional therapy modulates intestinal microbiota and reduces serum levels of total and free Indoxyl sulfate and P-cresyl sulfate in chronic kidney disease (Medika study). J Clin Med 8(9):E1424
Ding C, Han F, Xiang H, Wang Y, Li Y, Zheng J, Xue W, Ding X, Tian P (2019) Probiotics ameliorate renal ischemia-reperfusion injury by modulating the phenotype of macrophages through the IL-10/GSK-3β/PTEN signaling pathway. Pflugers Arch 471(4):573–581
Dou L, Sallée M, Cerini C, Poitevin S, Gondouin B, Jourde-Chiche N, Fallague K, Brunet P, Calaf R, Dussol B, Mallet B, Dignat-George F, Burtey S (2015) The cardiovascular effect of the uremic solute indole-3 acetic acid. J Am Soc Nephrol 26:876–887
Eidi F, Poor-Reza Gholi F, Ostadrahimi A, Dalili N, Samadian F, Barzegari A (2018) Effect of Lactobacillus Rhamnosus on serum uremic toxins (phenol and P-cresol) in hemodialysis patients: a double blind randomized clinical trial. Clin Nutr ESPEN 28:158–164
Esgalhado M, Kemp JA, Azevedo R, Paiva BR, Stockler-Pinto MB, Dolenga CJ, Borges NA, Nakao LS, Mafra D (2018) Could resistant starch supplementation improve inflammatory and oxidative stress biomarkers and uremic toxins levels in hemodialysis patients? A pilot randomized controlled trial. Food Funct 9(12):6508–6516
Evenepoel P, Poesen R, Meijers B (2017) The gut-kidney axis. Pediatr Nephrol 32(11):2005–2014
Fujimura S, Shimakage H, Tanioka H, Yoshida M, Suzuki-Kusaba M, Hisa H, Satoh S (1999) Effects of GABA on noradrenaline release and vasoconstriction induced by renal nerve stimulation in isolated perfused rat kidney. Br J Pharmacol 127:109–114
Furuse SU, Ohse T, Jo-Watanabe A, Shigehisa A, Kawakami K et al (2014) Galacto-oligosaccharides attenuate renal injury with microbiota modification. Phys Rep 2(7):e12029
García-Arroyo FE, Gonzaga G, Muñoz-Jiménez I, Blas-Marron MG, Silverio O, Tapia E, Soto V, Ranganathan N, Ranganathan P, Vyas U, Irvin A, Ir D, Robertson CE, Frank DN, Johnson RJ, Sánchez-Lozada LG (2018) Probiotic supplements prevented oxonic acid-induced hyperuricemia and renal damage. PLoS One 13(8):e0202901
Gibson GR, Hutkins R, Sanders ME, Prescott SL, Reimer RA, Salminen SJ, Scott K, Stanton C, Swanson KS, Cani PD, Verbeke K, Reid G (2017) Expert consensus document: the international scientific Association for Probiotics and Prebiotics (ISAPP) consensus statement on the definition and scope of prebiotics. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 14(8):491–502
Gryp T, Vanholder R, Vaneechoutte M, Glorieux G (2017) P-Cresyl sulfate. Toxins 9:E52
Guida B, Cataldi M, Memoli A, Trio R, di Maro M, Grumetto L, Capuano I, Federico S, Pisani A, Sabbatini M (2017) Effect of a short-course treatment with Synbiotics on plasma p-cresol concentration in kidney transplant recipients. J Am Coll Nutr 36(7):586–591
Hand TW, Vujkovic-Cvijin I, Ridaura VK, Belkaid Y (2016) Linking the microbiota, chronic disease, and the immune system. Trends Endocrinol Metab 27:831–843
Heaney LM, Davies OG, Selby NM (2019) Gut microbial metabolites as mediators of renal disease: do short-chain fatty acids offer some hope? Future Sci OA 5(4):FSO384
Hida M, Aiba Y, Sawamura S, Suzuki N, Satoh T, Koga Y (1996) Inhibition of the accumulation of uremic toxins in the blood and their precursors in the feces after oral administration of Lebenin, a lactic acid bacteria preparation, to uremic patients undergoing hemodialysis. Nephron 74(2):349–355
Hobby GP, Karaduta O, Dusio GF, Singh M, Zybailov BL (2019) Chronic kidney disease and the gut microbiome. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 316(6):F1211–F1217
Hsu CN, Yl T (2019) The good, the bad, and the ugly of pregnancy nutrients and developmental programming of adult disease. Nutrients 11(4):894
Hsu CN, Lu PC, Lo MH, Lin IC, Chang-Chien GP et al (2018) Gut microbiota-dependent trimethylamine N-oxide pathway associated with cardiovascular risk in children with early-stage chronic kidney disease. Int J Mol Sci 19(12):E3699
Huang W, Zhou L, Guo H, Xu Y, Xu Y (2017) The role of short-chain fatty acids in kidney injury induced by gut-derived inflammatory response. Metabolism 68:20–30
Hung TV, Suzuki T (2018) Dietary fermentable fibers attenuate chronic kidney disease in mice by protecting the intestinal barrier. J Nutr 148:552–561
Hyun HS, Paik KH, Cho HY (2013) P-Cresyl sulfate and indoxyl sulfate in pediatric patients on chronic dialysis. Korean J Pediatr 56(4):159–164
Iwashita Y, Ohya M, Yashiro M, Sonou T, Kawakami K, Nakashima Y, Yano T, Iwashita Y, Mima T, Negi S, Kubo K, Tomoda K, Odamaki T, Shigematsu T (2018) Dietary changes involving Bifidobacterium longum and other nutrients delays chronic kidney disease progression. Am J Nephrol 47(5):325–332
Jandhyala SM, Talukdar R, Subramanyam C, Vuyyuru H, Sasikala M, Nageshwar Reddy D (2015) Role of the normal gut microbiota. World J Gastroenterol 21(29):8787–8803
Jazani NH, Savoj J, Lustgarten M, Lau WL, Vaziri ND (2019) Impact of gut dysbiosis on neurohormonal pathways in chronic kidney disease. Diseases 7(1):E21
Jiang S, Xie S, Lv D, Zhang Y, Deng J et al (2016) A reduction in the butyrate producing species Roseburia spp. and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii is associated with chronic kidney disease progression. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek 109(10):1389–1396
Joossens M, Faust K, Gryp T, Nguyen ATL, Wang J, Eloot S, Schepers E, Dhondt A, Pletinck A, Vieira-Silva S, Falony G, Vaneechoutte M, Vanholder R, van Biesen W, Huys GRB, Raes J, Glorieux G (2019) Gut microbiota dynamics and uraemic toxins: one size does not fit all. Gut 68(12):2257–2260
Kanbay M, Onal EM, Afsar B, Dagel T, Yerlikaya A, Covic A, Vaziri ND (2018) The crosstalk of gut microbiota and chronic kidney disease: role of inflammation, proteinuria, hypertension, and diabetes mellitus. Int Urol Nephrol 50(8):1453–1466
Kemp JA, Esgalhado M, Macedo RA, Regis B, Damasceno NRT et al (2019) A possible link between polyunsaturated fatty acids and uremic toxins from the gut microbiota in hemodialysis patients: a hypothesis. Hemodial Int 23(2):189–197
Kieffer DA, Piccolo BD, Vaziri ND, Liu S, Lau WL, Khazaeli M, Nazertehrani S, Moore ME, Marco ML, Martin RJ, Adams SH (2016) Resistant starch alters gut microbiome and metabolomic profiles concurrent with amelioration of chronic kidney disease in rats. Am J Physiol Ren Physiol 310(9):F857–F871
Koeth RA, Wang Z, Levison BS, Buffa JA, Org E, Sheehy BT, Britt EB, Fu X, Wu Y, Li L, Smith JD, DiDonato J, Chen J, Li H, Wu GD, Lewis JD, Warrier M, Brown JM, Krauss RM, Tang WH, Bushman FD, Lusis AJ, Hazen SL (2013) Intestinal microbiota metabolism of L-carnitine, a nutrient in red meat, promotes atherosclerosis. Nat Med 19(5):576–585
Koppe L, Fouque D, Soulage CO (2018) The role of gut microbiota and diet on uremic retention solutes production in the context of chronic kidney disease. Toxins (Basel) 10(4):E155
Korkmaz OA, Sumlu E, Koca HB, Pektas MB, Kocabas A et al (2019) Effects of Lactobacillus plantarum and Lactobacillus helveticus on renal insulin signaling, inflammatory markers, and glucose transporters in high-fructose-fed rats. Medicina (Kaunas) 55(5):E207
Kurella Tamura M, Yaffe K, Hsu CY, Yang J, Sozio S, Fischer M, Chen J, Ojo A, DeLuca J, Xie D, Vittinghoff E, Go AS, Chronic Renal Insufficiency Cohort (CRIC) Study Investigators (2016) Cognitive impairment and progression of CKD. Am J Kidney Dis 68:77–83
Kuzmich NN, Sivak KV, Chubarev VN, Porozov YB, Savateeva-Lyubimova TN et al (2017) TLR4 signaling pathway modulators as potential therapeutics in inflammation and sepsis. Vaccines (Basel) 5:E34
Laffin MR, Tayebi Khosroshahi H, Park H, Laffin LJ, Madsen K, Kafil HS, Abedi B, Shiralizadeh S, Vaziri ND (2019) Amylose resistant starch (HAM-RS2) supplementation increases the proportion of Faecalibacterium bacteria in end-stage renal disease patients: microbial analysis from a randomized placebo-controlled trial. Hemodial Int 23(3):343–347
Lau WL, Vaziri ND (2017) The leaky gut and altered microbiome in chronic kidney disease. J Ren Nutr 27(6):458–461
Lee JR, Huang J, Magruder M, Zhang LT, Gong C, Sholi AN, Albakry S, Edusei E, Muthukumar T, Lubetzky M, Dadhania DM, Taur Y, Pamer EG, Suthanthiran M (2019) Butyrate-producing gut bacteria and viral infections in kidney transplant recipients: a pilot study. Transpl Infect Dis 21(6):e13180
Lehto M, Groop P-H (2018) The gut-kidney axis: putative interconnections between gastrointestinal and renal disorders. Front Endocrinol 9(553):1–11
Li F, Wang M, Wang J, Li R, Zhang Y (2019) Alterations to the gut microbiota and their correlation with inflammatory factors in chronic kidney disease. Front Cell Infect Microbiol 9:206
Li LZ, Tao SB, Ma L, Fu P (2019) Roles of short-chain fatty acids in kidney diseases. Chin Med J 132(10):1228–1232
Lin J, Hu FB, Curhan C (2010) Associations of diet with albuminuria and kidney function decline. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 5:836–843
Lippi I, Perondi F, Ceccherini G, Marchetti V, Guidi G (2017) Effects of probiotic VSL#3 on glomerular filtration rate in dogs affected by chronic kidney disease: a pilot study. Can Vet J 58(12):1301–1305
Liu H, Wang J, He T, Becker S, Zhang G, Li D, Ma X (2018) Butyrate: a double-edged sword for health? Adv Nutr 9(1):21–29
Lopes RCSO, de Lima SLS, da Silva BP, Toledo RCL, Moreira MEC, Anunciação PC, Walter EHM, Carvalho CWP, Queiroz VAV, Ribeiro AQ, Martino HSD (2018) Evaluation of the health benefits of consumption of extruded tannin sorghum with unfermented probiotic milk in individuals with chronic kidney disease. Food Res Int 107:629–638
Lopes RCSO, Theodoro JMV, da Silva BP, Queiroz VAV, de Castro Moreira ME et al (2018) Synbiotic meal decreases uremic toxins in hemodialysis individuals: a placebo-controlled trial. Food Res Int 116:241–248
Lu CY, Chen YC, Lu YW, Muo CH, Chang RE (2019) Association of Constipation with risk of end-stage renal disease in patients with chronic kidney disease. BMC Nephrol 20(1):304
Macfarlane GT, Macfarlane S (2011) Fermentation in the human large intestine: its physiologic consequences and the potential contribution of prebiotics. J Clin Gastroenterol 45(suppl):S120–S127
Mafi A, Namazi G, Soleimani A, Bahmani F, Aghadavod E, Asemi Z (2018) Metabolic and genetic response to probiotics supplementation in patients with diabetic nephropathy: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Food Funct 9(9):4763–4770
Mafra D, Fouque D (2015) Gut microbiota and inflammation in chronic kidney disease patients. Clin Kidney J 8:332–334
Mafra D, Borges N, Alvarenga L, Esgalhado M, Cardozo L et al (2019) Dietary components that may influence the disturbed gut microbiota in chronic kidney disease. Nutrients 11(3):496
Mahmoodpoor F, Rahbar Saadat Y, Barzegari A, Ardalan M, Zununi Vahed S (2017) The impact of gut microbiota on kidney function and pathogenesis. Biomed Pharmacother 93:412–419
Manaer T, Yu L, Zhang Y, Xiao XJ, Nabi XH (2015) Anti-diabetic effects of shubat in type 2 diabetic rats induced by combination of high-glucose-fat diet and low-dose streptozotocin. J Ethnopharmacol 169:269–274
McFarlane C, Ramos CI, Johnson DW, Campbell KL (2019) Prebiotic, probiotic, and synbiotic supplementation in chronic kidney disease: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Ren Nutr 29(3):209–220
Meijers BK, Evenepoel P (2011) The gut kidney axis: indoxyl sulfate, p-cresyl sulfate and CKD progression. Nephrol Dial Transplant 26(3):759–761
Natarajan R, Pechenyak B, Vyas U, Ranganathan P, Weinberg A et al (2014) Randomized controlled trial of strain-specific probiotic formulation (Renadyl) in dialysis patients. Biomed Res Int 2014:568571
Neirynck N, Vanholder R, Schepers E, Eloot S, Pletinck A, Glorieux G (2013) An update on uremic toxins. Int Urol Nephrol 45:139–150
Noureen S, Riaz A, Arshad M, Arshad N (2019) In vitro selection and in vivo confirmation of the antioxidant ability of Lactobacillus brevis MG000874. J Appl Microbiol 126(4):1221–1232
Onal EM, Afsar B, Covic A, Vaziri ND, Kanbay M (2019) Gut microbiota and inflammation in chronic kidney disease and their roles in the development of cardiovascular disease. Hypertens Res 42(2):123–140
Païssé S, Valle C, Servant F, Courtney M, Burcelin R, Amar J, Lelouvier B (2016) Comprehensive description of blood microbiome from healthy donors assessed by 16S targeted metagenomic sequencing. Transfusion 56:1138–1147
Pan W, Kang Y (2018) Gut microbiota and chronic kidney disease: implications for novel mechanistic insights and therapeutic strategies. Int Urol Nephrol 50(2):289–299
Pavan M (2016) Influence of prebiotic and probiotic supplementation on the progression of chronic kidney disease. Minerva Urol Nefrol 68(2):222–226
Pelletier CC, Croyal M, Ene L, Aguesse A, Billon-Crossouard S et al (2019) Elevation of Trimethylamine-N-oxide in chronic kidney disease: contribution of decreased glomerular filtration rate. Toxins (Basel) 11(11):E635
Plata C, Cruz C, Cervantes LG, Ramírez V (2019) The gut microbiota and its relationship with chronic kidney disease. Int Urol Nephrol 51(12):2209–2226
Poesen R, Evenepoel P, de Loor H, Delcour JA, Courtin CM et al (2016) The influence of prebiotic arabinoxylan oligosaccharides on microbiota derived uremic retention solutes in patients with chronic kidney disease: a randomized controlled trial. PLoS One 11(4):e0153893
Pryde SE, Duncan SH, Hold GL, Stewart CS, Flint HJ (2002) The microbiology of butyrate formation in the human colon. FEMS Microbiol Lett 217:133–139
Qian Q (2017) Inflammation: a key contributor to the genesis and progression of chronic kidney disease. Contrib Nephrol 191:72–83
Ramezani A, Massy ZA, Meijers B, Evenepoel P, Vanholder R et al (2016) Role of the gut micro-biome in uremia: a potential therapeutic target. Am J Kidney Dis 67(3):483–498
Ramos CI, Armani RG, Canziani MEF, Dalboni MA, Dolenga CJR et al (2019) Effect of prebiotic (fructooligosaccharide) on uremic toxins of chronic kidney disease patients: a randomized controlled trial. Nephrol Dial Transplant 34(11):1876–1884
Ranganathan N, Patel BP, Marczely J, Dheer R, Chordia T, Dunn SR, Friedman EA (2005) Probiotic amelioration of azotemia in 5/6th nephrectomized Sprague-Dawley rats. Sci World J 5:652–660
Ranganathan N, Patel BG, Ranganathan P, Marczely J, Dheer R, Pechenyak B, Dunn SR, Verstraete W, Decroos K, Mehta R, Friedman EA (2006) In vitro and in vivo assessment of intraintestinal bacteriotherapy in chronic kidney disease. ASAIO J 52(1):70–79
Rossi M, Campbell KL, Johnson DW, Stanton T, Vesey DA, Coombes JS, Weston KS, Hawley CM, McWhinney B, Ungerer JP, Isbel N (2014) Protein-bound uremic toxins, inflammation and oxidative stress: a cross-sectional study in stage 3–4 chronic kidney disease. Arch Med Res 45:309–317
Rossi M, Johnson DW, Morrison M, Pascoe EM, Coombes JS, Forbes JM, Szeto CC, McWhinney B, Ungerer JP, Campbell KL (2016) Synbiotics Easing renal failure by improving gut microbiology (SYNERGY): a randomized trial. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 11(2):223–231
Sabatino A, Regolisti G, Brusasco I, Cabassi A, Morabito S et al (2015) Alterations of intestinal barrier and microbiota in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 30:924–933
Salguero MV, Al-Obaide MAI, Singh R, Siepmann T, Vasylyeva TL (2019) Dysbiosis of gram-negative gut microbiota and the associated serum lipopolysaccharide exacerbates inflammation in type 2 diabetic patients with chronic kidney disease. Exp Ther Med 18(5):3461–3469
Schiattarella GG, Sannino A, Toscano E, Giugliano G, Gargiulo G et al (2017) Gut microbe-generated metabolite trimethylamine-N-oxide as cardiovascular risk biomarker: a systematic review and dose-response meta-analysis. Eur Heart J 38(39):2948–2956
Shah NB, Allegretti AS, Nigwekar SU, Kalim S, Zhao S, Lelouvier B, Servant F, Serena G, Thadhani RI, Raj DS, Fasano A (2019) Bloodd microbiome profile in CKD: a pilot study. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol 14(5):692–701
Sircana A, De Michieli F, Parente R, Framarin L, Leone N et al (2019) Gut microbiota, hypertension and chronic kidney disease: recent advances. Pharmacol Res 144:390–408
Skov J (2014) Effects of GLP-1 in the kidney. Rev Endocr Metab Disord 15:197–207
Stockler-Pinto MB, Saldanha JF, Yi D, Mafra D, Fouque D, Soulage CO (2016) The uremic toxin indoxyl sulfate exacerbates reactive oxygen species production and inflammation in 3T3-L1 adipose cells. Free Radic Res 50:337–344
Stubbs JR, House JA, Ocque AJ, Zhang S, Johnson C et al Serum trimethylamine-N-Oxide is Elevated in CKD and correlates with coronary atherosclerosis burden. J Am Soc Nephrol 27:305–313
Sueyoshi M, Fukunaga M, Mei M, Nakajima A, Tanaka G, Murase T, Narita Y, Hirata S, Kadowaki D (2019) Effects of lactulose on renal function and gut microbiota in adenine-induced chronic kidney disease rats. Clin Exp Nephrol 23(7):908–919
Sun CY, Lin CJ, Pan HC, Lee CC, Lu SC, Hsieh YT, Huang SY, Huang HY (2019) Clinical association between the metabolite of healthy gut microbiota, 3-indolepropionic acid and chronic kidney disease. Clin Nutr 38(6):2945–2948
Tang WHW, Wang Z, Levison BS, Koeth RA, Britt EB et al (2013) Intestinal microbial metabolism of phosphatidylcholine and cardiovascular risk. N Engl J Med 368:1575–1584
Tang WHW, Wang Z, Kennedy DJ, Wu Y, Buffa JA, Agatisa-Boyle B, Li XS, Levison BS, Hazen SL (2015) Gut microbiota dependent trimethylamine N-oxide (TMAO) pathway contributes to both development of renal insufficiency and mortality risk in chronic kidney disease. Circ Res 116:448–455
Tayebi-Khosroshahi H, Habibzadeh A, Niknafs B, Ghotaslou R, Yeganeh Sefidan F, Ghojazadeh M, Moghaddaszadeh M, Parkhide S (2016) The effect of lactulose supplementation on fecal microflora of patients with chronic kidney disease; a randomized clinical trial. J Renal Inj Prev 5(3):162–167
Tuomainen M, Lindstrom J, Lehtonen M, Auriola S, Pihlajamaki J, Peltonen M et al (2018) Associations of serum indolepropionic acid, a gut microbiota metabolite, with type 2 diabetes and low-grade inflammation in high-risk individuals. Nutr Diabetes 8:35
Vangay P, Ward T, Gerber JS, Knights D (2015) Antibiotics, pediatric dysbiosis, and disease. Cell Host Microbe 17(5):553–564
Vaziri ND, Wong J, Pahl M, Piceno YM, Yuan J, DeSantis T, Ni Z, Nguyen TH, Andersen GL (2013) Chronic kidney disease alters intestinal microbial flora. Kidney Int 83(2):308–315
Vaziri ND, Liu SM, Lau WL, Khazaeli M, Nazertehrani S, Farzaneh SH, Kieffer DA, Adams SH, Martin RJ (2014) High amylose resistant starch diet ameliorates oxidative stress, inflammation, and progression of chronic kidney disease. PLoS One 9(12):e114881
Velasquez MT, Centron P, Barrows I, Dwivedi R, Raj DS (2018) Gut microbiota and cardiovascular uremic toxicities. Toxins (Basel) 10(7):E287
Wanchai K, Yasom S, Tunapong W, Chunchai T, Thiennimitr P, Chaiyasut C, Pongchaidecha A, Chatsudthipong V, Chattipakorn S, Chattipakorn N, Lungkaphin A (2018) Prebiotic prevents impaired kidney and renal Oat3 functions in obese rats. J Endocrinol 237(1):29–42
Wanchai K, Yasom S, Tunapong W, Chunchai T, Eaimworawuthikul S et al (2018) Probiotic Lactobacillus paracasei HII01 protects rats against obese-insulin resistance-induced kidney injury and impaired renal organic anion transporter 3 function. Clin Sci (Lond) 132(14):1545–1563
Wang S, Lv D, Jiang S, Jiang J, Liang M et al (2019) Quantitative reduction in short-chain fatty acids, especially butyrate, contributes to the progression of chronic kidney disease. Clin Sci (Lond) 133(17):1857–1870
Wang YF, Zheng LJ, Liu Y, Ye YB, Luo S et al (2019) The gut microbiota-inflammation-brain axis in end-stage renal disease: perspectives from default mode network. Theranostics 9(26):8171–8181
Webster AC, Nagler EV, Morton RL, Masson P (2017) Chronic kidney disease. Lancet 389:1238–1252
Wierema TK, Houben AJ, de Leeuw PW (1997) Acetylcholine-induced vasodilatation in the human hypertensive kidney: inhibition by muscarinic receptor antagonism. J Hypertens 15:1649–1651
Wilkins LJ, Monga M, Miller AW (2019) Defining dysbiosis for a cluster of chronic diseases. Sci Rep 9(1):12918
Yamasaki K, Hyodo S, Taguchi K, Nishi K, Yamaotsu N et al (2017) Long chain fatty acids alter the interactive binding of ligands to the two principal drug binding sites of human serum albumin. PLoS One 12:e0180404
Yang J, Li Q, Henning SM, Zhong J, Hsu M et al (2018) Effects of prebiotic fiber Xylooligosaccharide in adenine-induced nephropathy in mice. Mol Nutr Food Res 62:1–34
Yang T, Richards EM, Pepine CJ, Raizada MK (2018) The gut microbiota and the brain-gut-kidney axis in hypertension and chronic kidney disease. Nat Rev Nephrol 14(7):442–456
Yang J, Lim SY, Ko YS, Lee HY, Oh SW et al (2019) Intestinal barrier disruption and dysregulated mucosal immunity contribute to kidney fibrosis in chronic kidney disease. Nephrol Dial Transplant 34(3):419–428
Yisireyili M, Takeshita K, Saito S, Murohara T, Niwa T (2017) Indole-3-propionic acid suppresses indoxyl sulfate-induced expression of fibrotic and inflammatory genes in proximal tubular cells. Nagoya J Med Sci 79:477
Younan S, Sakita GZ, Coluna JGY, Rufino MN, Keller R, Bremer-Neto H (2019) Probiotic mitigates the toxic effects of potassium dichromate in a preclinical study: a randomized controlled trial. J Sci Food Agric 99(1):183–190
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the Universidad de Buenos Aires (UBACYT 20020170100621BA (2018–2022) and Sociedad Argentina de Hipertensión Arterial (Stimulus Grant for Research on Hypertension 2019–2020).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure statement
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rukavina Mikusic, N.L., Kouyoumdzian, N.M. & Choi, M.R. Gut microbiota and chronic kidney disease: evidences and mechanisms that mediate a new communication in the gastrointestinal-renal axis. Pflugers Arch - Eur J Physiol 472, 303–320 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-020-02352-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00424-020-02352-x