Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study is to estimate the incidence and clinical impact of lymph node micrometastases in hypopharyngeal squamous cell cancer (HSCC).
Materials and methods
In this retrospective study, we enrolled 58 patients who have undergone surgery for HSCC (between January 2004 and January 2011). Pharyngolaryngectomy and oesophagectomy with selective bilateral neck dissection was performed in all patients. Based on standard histological examination, 17 patients met N0 and 8 patients met N1 criteria and were further evaluated for the presence of micrometastases and isolated tumour cells (ITC). Following immunohistochemical analysis, the patients were grouped according to the presence of micrometastases and ITCs.
Results
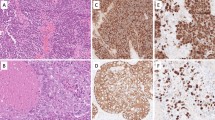
In the pN0 group, cytokeratin-positive cells were detected in five patients, and they were marked as N0/CK+. Among these five patients, two were found to harbour micrometastases and ITCs, whilst in three, only ITCs were found. Two patients (11.75 %) were upstaged to pN1. The patients marked as N0/CK+ had a statistically significant worse overall survival rates than pN0 patients with tissue samples read as negative for cytokeratin immunostaining (p = 0.019, p < 0.05). In the pN1 group, cytokeratin-positive cells were detected in two patients, with one patient showing micrometastases and ITC, and the other showing ITC only. One patient was upstaged to pN2.
Conclusion
Patients with lymph node micrometastases and ITC had worse overall survival rates, which may indicate that more aggressive post-operative treatment regimens should be considered for these HSCC patients.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ferlito A, Partridge M, Brennan J, Hamakawa H (2001) Lymph node micrometastases in head and neck cancer: a review. Acta Otolaryngol 121:660–665
Triboulet JP, Mariette C, Chevalier D, Amrouni H (2001) Surgical management of carcinoma of the hypopharynx and cervical esophagus: analysis of 209 cases. Arch Surg 136:1164–1170. doi:10.1001/archsurg.136.10.1164
Shah JP (1990) Patterns of cervical lymph node metastasis from squamous carcinomas of the upper aerodigestive tract. Am J Surg 160:405–409
Don DM, Anzai Y, Lufkin RB, Fu YS, Calcaterra TC (1995) Evaluation of cervical lymph node metastases in squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Laryngoscope 105:669–674
Tu GY (1999) Upper neck (level II) dissection for N0 neck supraglottic carcinoma. Laryngoscope 109:467–470
Sharma AK, Mishra P, Gupta S (2013) Immunohistochemistry, a valuable tool in detection of cervical lymph node micrometastases in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: a prospective study. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 65:89–94. doi:10.1007/s12070-012-0551-4
Devaney KO, Rinaldo A, Ferlito A (2007) Micrometastases in cervical lymph nodes from patients with squamous carcinoma of the head and neck: should they be actively sought? Maybe. Am J Otolaryngol 28:271–274. doi:10.1016/j.amjoto.2006.09.017
International (Ludwig) Breast Cancer Study Group (1990) Prognostic importance of occult axillary lymph node micrometastases from breast cancers. Lancet 335(8705):1565–1568
Ahmed SS, Thike AA, Iqbal J, Yong WS, Tan B, Madhukumar P, Ong KW, Ho GH, Wong CY, Tan PH (2014) Sentinel lymph nodes with isolated tumour cells and micrometastases in breast cancer: clinical relevance and prognostic significance. J Clin Pathol 67:243–250
Giuliano AE, McCall L, Beitsch P, Whitworth PW, Blumencranz P, Leitch AM, Saha S, Hunt KK, Morrow M, Ballman K (2010) Locoregional recurrence after sentinel lymph node dissection with or without axillary dissection in patients with sentinel lymph node metastases: the American College of Surgeons Oncology Group Z0011 randomized trial. Ann Surg 252:426–432, discussion 423–3
Hermanek P, Hutter RV, Sobin LH, Wittekind C (1999) International union against cancer. Classification of isolated tumor cells and micrometastasis. Cancer 86:2668–2673
Enepekides DJ, Sultanem K, Nguyen C, Shenouda G, Black MJ, Rochon L (1999) Occult cervical metastases: immunoperoxidase analysis of the pathologically negative neck. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 120:713–717. doi:10.1053/hn.1999.v120.a91761
Van den Brekel MW, van der Waal I, Meijer CJ, Freeman JL, Castelijns JA, Snow GB (1996) The incidence of micrometastases in neck dissection specimens obtained from elective neck dissections. Laryngoscope 106:987–991
Ferlito A, Rinaldo A, Devaney KO, Nakashiro K, Hamakawa H (2008) Detection of lymph node micrometastases in patients with squamous carcinoma of the head and neck. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 265:1147–1153. doi:10.1007/s00405-008-0715-8
Buckley JG, MacLennan K (2000) Cervical node metastases in laryngeal and hypopharyngeal cancer: a prospective analysis of prevalence and distribution. Head Neck 22:380–385. doi:10.1002/1097-0347(200007)22:4
Woolgar JA (1999) Micrometastasis in oral/oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma: incidence, histopathological features and clinical implications. Br J Oral Maxillofac Surg 37:181–186
Fielding LP, Fenoglio-Preiser CM, Freedman LS (1992) The future of prognostic factors in outcome prediction for patients with cancer. Cancer 70:2367–2377
Becker MT, Shores CG, Yu KK, Yarbrough WG (2004) Molecular assay to detect metastatic head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 130:21–27. doi:10.1001/archotol.130.1.21
Brennan JA, Mao L, Hruban RH, Boyle JO, Eby YJ, Koch WM, Goodman SN, Sidransky D (1995) Molecular assessment of histopathological staging in squamous-cell carcinoma of the head and neck. N Engl J Med 332:429–435. doi:10.1056/NEJM199502163320704
Guo CB, Li YA, Gao Y (2007) Immunohistochemical staining with cytokeratin combining semi-serial sections for detection of cervical lymph node metastases of oral squamous cell carcinoma. Auris Nasus Larynx 34:347–351. doi:10.1016/j.anl.200612.001
Hamakawa H, Takemura K, Sumida T, Kayahara H, Tanioka H, Sogawa K (2000) Histological study on pN upgrading of oral cancer. Virchows Arch 437:116–121
Gould VE, Bloom KJ, Franke WW, Warren WH, Moll R (1995) Increased numbers of cytokeratin-positive interstitial reticulum cells (CIRC) in reactive, inflammatory and neoplastic lymphadenopathies: hyperplasia or induced expression? Virchows Arch 425:617–629
Kwon SY, Kim HJ, Woo JS, Jung KY, Kim I (2004) The usefulness of cytokeratin immunohistochemistry in detection of lymph node micrometastasis in neck dissection specimens. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 131:300–306. doi:10.1016/j.otohns.2004.02.020
de Boer M, van Dijck JA, Bult P, Borm GF, Tjan-Heijnen VC (2010) Breast cancer prognosis and occult lymph node metastases, isolated tumor cells, and micrometastases. J Natl Cancer Inst 102(6):410–425
Li SH, Wang Z, Liu XY, Liu FY, Sun ZY, Xue H (2007) Lymph node micrometastasis: a predictor of early tumor relapse after complete resection of histologically node-negative esophageal cancer. Surg Today 37(12):1047–1052
Prenzel KL, Hölscher AH, Drebber U, Agavonova M, Gutschow CA, Bollschweiler E (2012) Prognostic impact of nodal micrometastasis in early esophageal cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 38:314–318
Rhee D, Wenig BM, Smith RV (2002) The significance of immunohistochemically demonstrated nodal micrometastases in patients with squamous cell carcinoma of the head and neck. Laryngoscope 112:1970–1974. doi:10.1097/00005537-200211000-00011
Nieuwenhuis EJ, Leemans CR, Kummer JA, Denkers F, Snow GB, Brakenhoff RH (2003) Assessment and clinical significance of micrometastases in lymph nodes of head and neck cancer patients detected by E48 (Ly-6D) quantitative reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction. Lab Investig 83:1233–1240
Colnot DR, Nieuwenhuis EJ, Kuik DJ, Leemans CR, Dijkstra J, Snow GB, van Dongen GA, Brakenhoff RH (2004) Clinical significance of micrometastatic cells detected by E48 (Ly-6D) reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction in bone marrow of head and neck cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 10:7827–7833. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1090
Xu Y, Fei M, Wang J, Zheng L, Chen Y, Liu Q (2012) Clinical significance of micrometastases in lymph nodes from laryngeal squamous cell carcinoma. Am J Otolaryngol 33:402–407. doi:10.1016/j.amjoto.2011.10.012
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sabljak, P., Pesko, P., Stojakov, D. et al. Micrometastasis of hypopharyngeal cancer. Langenbecks Arch Surg 399, 765–771 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-014-1204-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00423-014-1204-8