Abstract
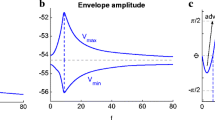
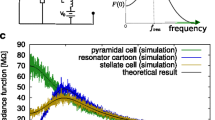
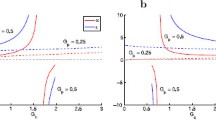
We systematically investigate the response of neurons to oscillatory currents and synaptic-like inputs and we extend our investigation to non-structured synaptic-like spiking inputs with more realistic distributions of presynaptic spike times. We use two types of chirp-like inputs consisting of (i) a sequence of cycles with discretely increasing frequencies over time, and (ii) a sequence having the same cycles arranged in an arbitrary order. We develop and use a number of frequency-dependent voltage response metrics to capture the different aspects of the voltage response, including the standard impedance (Z) and the peak-to-trough amplitude envelope (\(V_{\text {ENV}}\)) profiles. We show that Z-resonant cells (cells that exhibit subthreshold resonance in response to sinusoidal inputs) also show \( V_{\text {ENV}} \)-resonance in response to sinusoidal inputs, but generally do not (or do it very mildly) in response to square-wave and synaptic-like inputs. In the latter cases the resonant response using Z is not predictive of the preferred frequencies at which the neurons spike when the input amplitude is increased above subthreshold levels. We also show that responses to conductance-based synaptic-like inputs are attenuated as compared to the response to current-based synaptic-like inputs, thus providing an explanation to previous experimental results. These response patterns were strongly dependent on the intrinsic properties of the participating neurons, in particular whether the unperturbed Z-resonant cells had a stable node or a focus. In addition, we show that variability emerges in response to chirp-like inputs with arbitrarily ordered patterns where all signals (trials) in a given protocol have the same frequency content and the only source of uncertainty is the subset of all possible permutations of cycles chosen for a given protocol. This variability is the result of the multiple different ways in which the autonomous transient dynamics is activated across cycles in each signal (different cycle orderings) and across trials. We extend our results to include high-rate Poisson distributed current- and conductance-based synaptic inputs and compare them with similar results using additive Gaussian white noise. We show that the responses to both Poisson-distributed synaptic inputs are attenuated with respect to the responses to Gaussian white noise. For cells that exhibit oscillatory responses to Gaussian white noise (band-pass filters), the response to conductance-based synaptic inputs are low-pass filters, while the response to current-based synaptic inputs may remain band-pass filters, consistent with experimental findings. Our results shed light on the mechanisms of communication of oscillatory activity among neurons in a network via subthreshold oscillations and resonance and the generation of network resonance.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Allen EJ, Novosel SJ, Zhang Z (1998) Finite element and difference approximation of some linear stochastic partial differential equations. Stoch Stoch Rep 64:117–142
Alonso AA, Llinás RR (1989) Subthreshold Na\(^{+} \)-dependent theta like rhythmicity in stellate cells of entorhinal cortex layer II. Nature 342:175–177
Amir R, Michaelis M, Devor M (1999) Membrane potential oscillations in dorsal root ganglion neurons: role in normal electrogenesis and neuropathic pain. J Neurosci 19:8589–8596
Amir R, Liu C-N, Kocsis J, Devor M (2002) Oscillatory mechanism in primary sensory neurons. Brain 125:421–435
Amit DJ, Brunel N (1997) Dynamics of a recurrent network of spiking neurons before and following learning. Cereb Cortex 7:237–252
Amit DJ, Tsodyks MV (1991) Quantitative study of attractor neural network retrieving at low spike rates I: substrate spikes, rates and neuronal gain. Network 2:259–274
Art JJ, Crawford AC, Fettiplace R (1986) Electrical resonance and membrane currents in turtle cochlear hair cells. Hear Res 22:31–36
Axmacher N, Mormann F, Fernandez G, Elger CE, Fell J (2006) Memory formation by neuronal synchronization. Brain Res Rev, 170–1802
Balu R, Larimer P, Strowbridge BW (2004) Phasic stimuli evoke precisely timed spikes in intermittently discharging mitral cells. J Neurophysiol 92:743–753
Baroni F, Burkitt AN, Grayden DB (2014) Interplay of intrinsic and synaptic conductances in the generation of high-frequency oscillations in interneuronal networks with irregular spiking. PLoS Comp Biol 10:e1003574
Baspinar E, Schulen L, Olmi S, Zakharova A (2021) Coherence resonance in neuronal populations: mean-field versus network model. Phys Rev E 103:032308
Beatty J, Song SC, Wilson CJ (2015) Cell-type-specific resonances shape the response of striatal neurons to synaptic inputs. J Neurophysiol 113:688–700
Benzi R, Parisi G, Sutera A, Vulpiani A (1982) Stochastic resonance in climatic change. Tellus 34:10–16
Bel A, Rotstein HG (2019) Membrane potential resonance in non-oscillatory neurons interacts with synaptic connectivity to produce network oscillations. J Comp Neurosci 46:169–195
Belluscio MA, Mizuseki K, Schmidt R, Kemper R, Buzsáki G (2012) Cross-frequency phase-phase coupling between theta and gamma oscillations in the hippocampus. J Neurosci 32:423–435
Benda J, Longtin A, Maler L (2005) Spike-frequency adaptation separates transient communication signals from background oscillations. J Neurosci 25:2312–2321
Bernstein JG, Boyden ES (2012) Optogenetic tools for analyzing the neural circuits of behavior. Curr Opin Neurobiol 22:61–71
Bilkey DK, Heinemann U (1999) Intrinsic theta-frequency membrane potential oscillations in layer III/V perirhinal cortex neurons of the rat. Hippocampus 9:510–518
Boehlen A, Heinemann U, Erchova I (2010) The range of intrinsic frequencies represented by medial entorhinal cortex stellate cells extends with age. J Neurosci 30:4585–4589
Boehlen A, Henneberger C, Heinemann U, Erchova I (2013) Contribution of near-threshold currents to intrinsic oscillatory activity in rat medial entorhinal cortex layer II stellate cells. J Neurophysiol 109:445–463
Boehmer G, Greffrath W, Martin E, Hermann S (2000) Subthreshold oscillation of the membrane potential in magnocellular neurones of the rat supraoptic nucleus. J Physiol 526:115–128
Bol K, Marsat G, Harvey-Girard E, Longtin A, Maler L (2011) Frequency-tuned cerebellar channels and burst-induced LTD lead to the cancellation of redundant sensory inputs. J Neurosci 31:11028–11038
Bol K, Marsat G, Mejías JF, Maler L, Longtin A (2013) Modeling cancelation of periodic inputs with burst-stdp and feedback. Neural Netw 47:120–133
Bourdeau M, Morin F, Laurent C, Azzi M, Lacaille J (2007) Kv4.3-mediated A-type K\(^+\) currentes underlie rhythmic activity in hippocampal interneurons. J Neurosci 27:1942–1953
Bracci E, Centonze D, Bernardi G, Calabresi P (2003) Voltage-dependent membrane potential oscillations in rat striatal fast-spiking interneurons. J Physiol 15:121–130
Bragin A, Jando G, Nadasdy Z, Hetke J, Wise K, Buzsáki G (1995) Gamma (40–100 hz) oscillation in the hippocampus of the behaving rat. J Neurosci 15:47–60
Brea JN, Kay LM, Kopell NJ (2009) Biophysical model for gamma rhythms in the olfactory bulb via subthreshold oscillations. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:21954–21959
Brunel N (2000) Dynamics of sparsely connected networks of excitatory and inhibitory spiking neurons. J Comp Neurosci 8:183–208
Brunel N, Chance FS, Fourcaud N, Abbott LF (2001) Effects of synaptic noise and filtering on the frequency response of spiking neurons. Phys Rev Lett 86:2186–2189
Burden RL, Faires JD (1980) Numerical analysis. PWS Publishing Company, Boston
Burgess C, Schuck NW, Burgess N (2011) Temporal neuronal oscillations can produce spatial phase codes. In: Space, Time and Number in the Brain (S. Dehaene & E. M. Brannon, eds.), pp. 59–69
Chapman CA, Lacaille JC (1999) Intrinsic theta-frequency membrane potential oscillations in hippocampal CA1 interneurons of stratum lacunosum-moleculare. J Neurophysiol 81:1296–1307
Chen Y, Li X, Rotstein HG, Nadim F (2016) Membrane potential resonance frequency directly influences network frequency through gap junctions. J Neurophysiol 116:1554–1563
Chorev E, Yarom Y, Lampl I (2007) Rhythmic episodes of subthreshold membrane potential oscillations in the rat inferior olive nuclei in vivo. J Neurosci 27:5043–5052
Chow CC, White JA (1996) Spontaneous action potentials due to channel fluctuation. Biophys J 71:3013–3021
Chrobak JJ, Buzsáki G (1998) Gamma oscillations in the entorhinal cortex of the freely behaving rat. J Neurosci 18:388–398
Cobb SR, Buhl EH, Halasy K, Paulsen O, Somogyi P (1995) Synchronization of neuronal activity in the hippocampus by individual GABAergic interneurons. Nature 378:75–78
Colgin LL (2013) Mechanisms and functions of theta rhythms. Annu Rev Neurosci 36:295–312
Colgin LL, Denninger T, Fyhn M, Hafting T, Bonnevie T, Jensen O, Moser M-B, Moser EI (2009) Frequency of gamma oscillations routes flow of information in the hippocampus. Nature 462:353–358
Collins JJ, Imhoff TT, Grigg P (1996) Noise-enhanced information transmission in rat SA1 cutaneous mechanoreceptors via aperiodic stochastic resonance. J Neurophysiol 76:642–645
D’angelo E, Nieus T, Maffei A, Armano S, Rossi P, Taglietti V, Fontana A, Naldi G (2001) Theta-frequency bursting and resonance in cerebellar granule cells: experimental evidence and modeling of a slow K\(^{+} \) - dependent mechanism. J Neurosci 21:759–770
D’Angelo E, Koekkoek SKE, Lombardo P, Solinas S, Ros E, Garrido J, Schonewille M, De Zeeuw CI (2009) Timing in the cerebellum: oscillations and resonance in the granular layer. Neuroscience 162:805–815
Deisseroth K (2011) Optogenetics. Nat Methods 8:26–29
Desmaisons D, Vincent J-D, Lledo P-M (1999) Control of action potential timing by intrinsic subthreshold oscillations in olfactory bulb output neurons. J Neurosci 19:10727–10737
DeVille E, Vanden-Eijnden REL, Muratov CB (2005) Two distinct mechanisms of coherence in randomly perturbed dynamical systems. Phys Rev E 72:031105
Dickson CT, Magistretti J, Shalinsky MH, Fransén E, Hasselmo M, Alonso AA (2000) Properties and role of I\(_{h} \) in the pacing of subthreshold oscillation in entorhinal cortex layer II neurons. J Neurophysiol 83:2562–2579
Dickson CT, Magistretti J, Shalinsky M, Hamam B, Alonso AA (2000) Oscillatory activity in entorhinal neurons and circuits. Ann Y Acad Sci 911:127–150
Dorval AD Jr, White JA (2005) Channel noise is essential for perithreshold oscillations in entorhinal stellate neurons. J Neurosci 25:10025–10028
Douglass JK, Wilkens L, Pantazelou E, Moss F (1993) Noise enhancement of information transfer in crayfish mechanoreceptors by stochastic resonance. Nature 365:337–340
Drover JD, Tohidi V, Bose A, Nadim F (2007) Combining synaptic and cellular resonance in a feedforward neuronal network. Neurocomputing 70:2041–2045
Dwyer J, Lee H, Martell A, van Drongelen W (2012) Resonance in neocortical neurons and networks. Eur J Neurosci 36:3698–3708
Einstein MC, Pollack P-O, Tran DT, Golshani P (2017) Visually evoked 35 Hz membrane potential oscillations reduce the responsiveness of visual cortex neurons in awake behaving mice. J Neurosci 37:5084–5098
Engel TA, Schimansky-Geier L, Herz AV, Schreiber S, Erchova I (2008) Subthreshold membrane-potential resonances shape spike-train patterns in the entorhinal cortex. J Neurophysiol 100:1576–1588
Erchova I, Kreck G, Heinemann U, Herz AVM (2004) Dynamics of rat entorhinal cortex layer II and III cells: Characteristics of membrane potential resonance at rest predict oscillation properties near threshold. J Physiol 560:89–110
Farries MA, Wilson CJ (2012) Phase response curves of subthalamic neurons measured with synaptic input and current injection. J Neurophysiol 108:1822–1837
Farries MA, Wilson CJ (2012) Biophysical basis of the phase response curve of subthalamic neurons with generalization to other cell types. J Neurophysiol 108:1838–1855
Fernandez R, White JA (2008) Artificial synaptic conductances reduce subthreshold oscillations and periodic firing in stellate cells of the entorhinal cortex. J Neurosci 28:3790–3803
Flores A, Manilla S, Huidobro N, De la Torre-Valdovinos B, Kristeva R, Mendez-Balbuena I, Galindo F, Treviño M, Manjarrez E (2016) Stochastic resonance in the synaptic transmission between hair cells and vestibular primary afferents in development. Neuroscience 322:416–429
Fortune E, Rose G (2001) Short-term plasticity as a temporal filter. Trends Neurosci 24:381–385
Fox DM, Tseng H, Smolinsky T, Rotstein HG, Nadim F (2017) Mechanisms of generation of membrane potential resonance in a neuron with multiple resonant ionic currents. PLoS Comp Biol 13:e1005565
Gammaitoni L, Hanggi P, Jung P, Marchesoni F (1998) Stochastic resonance. Rev Mod Phys 70:223–287
Gastrein P, Campanac E, Gasselin C, Cudmore RH, Bialowas A, Carlier E, Fronzaroli-Molinieres L, Ankri N, Debanne D (2011) The role of hyperpolarization-activated cationic current in spike-time precision and intrinsic resonance in cortical neurons in vitro. J Physiol 589:3753–3773
Giocomo LM, Zilli EA, Fransén E, Hasselmo ME (2007) Temporal frequency of subthreshold oscillations scales with entorhinal grid cell field spacing. Science 315:1719–1722
Gireesh E, Plenz D (2008) Neuronal avalanches organize as nested theta- and beta/gamma-oscillations during development of cortical layer 2/3. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:7576–7581
Gloveli T, Dugladze T, Rotstein HG, Traub R, Monyer H, Heinemann U, Whittington MA, Kopell N (2005) Orthogonal arrangement of rhythm-generating microcircuits in the hippocampus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:13295–13300
Golomb D, Donner K, Shacham L, Shlosberg D, Amitai Y, Hansel D (2007) Mechanisms of firing patterns in fast-spiking cortical interneurons. PLoS Comp Biol 3:e156
Gutfreund Y, Yarom Y, Segev I (1995) Subthreshold oscillations and resonant frequency in guinea pig cortical neurons: physiology and modeling. J Physiol 483:621–640
Heys JG, Giacomo LM, Hasselmo ME (2010) Cholinergic modulation of the resonance properties of stellate cells in layer II of the medial entorhinal. J Neurophysiol 104:258–270
Heys JG, Schultheiss NW, Shay CF, Tsuno Y, Hasselmo ME (2012) Effects of acetylcholine on neuronal properties in entorhinal cortex. Front Behav Neurosci 6:32
Higgs MH, Spain WJ (2009) Conditional bursting enhances resonant firing in neocortical layer 2–3 pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci 29:1285–1299
Hinzer K, Longtin A (1996) Encoding with bursting, subthreshold oscillations, and noise in mammalian cold receptors. Neural Comput 8:215–255
Hu H, Vervaeke K, Storm JF (2002) Two forms of electrical resonance at theta frequencies generated by M-current, h-current and persistent Na\(^{+}\) current in rat hippocampal pyramidal cells. J Physiol 545(3):783–805
Hu H, Vervaeke K, Graham LJ, Storm JF (2009) Complementary theta resonance filtering by two spatially segregated mechanisms in CA1 hippocampal pyramidal neurons. J Neurosci 29:14472–14483
Hutcheon B, Yarom Y (2000) Resonance, oscillations and the intrinsic frequency preferences in neurons. Trends Neurosci 23:216–222
Hutcheon B, Miura RM, Puil E (1996) Models of subthreshold membrane resonance in neocortical neurons. J Neurophysiol 76:698–714
Hutcheon B, Miura RM, Puil E (1996) Subthreshold membrane resonance in neocortical neurons. J Neurophysiol 76:683–697
Izhikevich EM (2002) Resonance and selective communication via bursts in neurons having subthreshold oscillations. Biosystems 67:95–102
Jensen O, Colgin LL (2007) Cross-frequency coupling between neuronal oscillations. Trends Cogn Sci 11:267–269
Kay LM, Beshel J, Brea J, Martin C, Rojas-Líbano D, Kopell N (2008) Olfactory oscillations: the what, how and what for. Trends Neurosci 32:207–214
Khosrovani S, Van Der Giessen RS, De Zeeuw CI, De Jeu MTG (2007) In vivo mouse inferior olive neurons exhibit heterogeneous subthreshold oscillations and spiking patterns. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 104:15911–15916
Kispersky TJ, Fernandez FR, Economo MN, White JA (2012) Spike resonance properties in hippocampal O-LM cells are dependent on refractory dynamics. J Neurosci 32:3637–3651
Klink RM, Alonso A (1993) Ionic mechanisms for the subthreshold oscillations and differential electroresponsiveness of medial entorhinal cortex layer II neurons. J Neurophysiol 70:128–143
Lampl I, Yarom Y (1993) Subthreshold oscillations of the membrane potential: a functional synchronizing and timing device. J Neurophysiol 70:2181–2186
Lampl I, Yarom Y (1997) Subthreshold oscillations and resonant behaviour: two manifestations of the same mechanism. Neuroscience 78:325–341
Lau T, Zochowski M (2011) The resonance frequency shift, pattern formation, and dynamical network reorganization via sub-threshold input. PLoS ONE 6:e18983
Lee S-G, Neiman A, Kim S (1998) Coherence resonance in a hodgkin-huxley neuron. Phys Rev E 57:3292–3297
Li G, Cleland T (2017) A coupled-oscillator model of olfactory bulb gamma oscillations. PLoS Comp Biol 13:e1005760
Lindner B, García-Ojalvo J, Neiman A, Schimansky-Geier L (2004) Effects of noise in excitable systems. Phys Rep 392:321–424
Llinás RR, Yarom Y (1986) Oscillatory properties of guinea pig olivary neurons and their pharmachological modulation: an in vitro study. J Physiol 376:163–182
Llinás RR, Grace AA, Yarom Y (1991) In vitro neurons in mammalian cortical layer 4 exhibit intrinsic oscillatory activity in the 10- to 50-hz frequency range. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:897–901
Loewenstein Y, Yarom Y, Sompolinsky H (2001) The generation of oscillations in networks of electrically coupled cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:8095–8100
Manis PB, Molitor SC, Wu H (1999) Subthreshold oscillations generated by TTX-sensitive sodium currents in dorsal cochlear nucleus pyramidal cells. Exp Brain Res 153:443–451
Manor Y, Rinzel J, Segev I, Yarom Y (1997) Low-amplitude oscillations in the inferior olive: a model based on electrical coupling of neurons with heterogeneous channel densities. J Neurophysiol 77:2736–2752
Marcelin B, Becker A, Migliore M, Esclapez M, Bernard C (2009) h channel-dependent deficit of theta oscillation resonance and phase shift in temporal lobe epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 33:436–447
Mato G (1989) Stochastic resonance using noise generated by a neural network. Phys Rev E 59:3339–3343
McDonnell MD, Abboott D (2009) What is stochastic resonance? Definitions, misconceptions, debates, and its relevance to biology. PLoS Comp Biol 5:e1000348
McNamara B, Wiesenfeld K (1989) Theory of stochastic resonance. Phys Rev A 39:4854–4869
Mejias JF, Marsat G, Bol K, Maler L, Longtin A (2013) Learning contrast-invariant cancellation of redundant signals in neural systems. PLoS Comp Biol 9:e1003180
Mikiel-Hunter J, Kotak V, Rinzel J (2016) High-frequency resonance in the gerbil medial superior olive. PLoS Comp Biol 12:1005166
Mondal Y (2021) Effects of heterogeneity in oscillatory network dynamics. PhD Thesis, Stony Brook University, Stony Brook, NY
Mondal Y, Pena RFO, Rotsten HG (2021) Temporal filters in response to presynaptic spike trains: Interplay of cellular, synaptic and short-term plasticity time scales. bioRxiv, p. 460719
Morin F, Haufler D, Skinner FK, Lacaille J-C (2010) Characterization of voltage-gated K\(^+\) currents contributing to subthreshold membrane potential oscillations in hippocampal CA1 interneurons. J Neurophysiol 103:3472–3489
Muratov CB, Vanden-Eijnden E, WE (2005) Self-induced stochastic resonance in excitable systems. Physica D, 210: 227–240
Muresan R, Savin C (2007) Resonance or integration? Self-sustained dynamics and excitability of neural microcircuits. J Neurophysiol 97:1911–1930
Narayanan R, Johnston D (2007) Long-term potentiation in rat hippocampal neurons is accompanied by spatially widespread changes in intrinsic oscillatory dynamics and excitability. Neuron 56:1061–1075
Narayanan R, Johnston D (2008) The h channel mediates location dependence and plasticity of intrinsic phase response in rat hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 28:5846–5850
Neiman A, Saparin PI, Stone L (1997) Coherence resonance at noisy precursors of bifurcations in nonlinear dynamical systems. Phys Rev E 56:270–273
Nolan MF, Dudman JT, Dodson PD, Santoro B (2007) HCN1 channels control resting and active integrative properties of stellate cells from layer II of the entorhinal cortex. J Neurosci 27:12440–12551
Pedroarena CM, Pose IE, Yamuy J, Chase MH, Morales FR (1999) Oscillatory membrane potential activity in the soma of a primary afferent neuron. J Neurophysiol 82:1465–1476
Pena RFO, Rotstein HG (2021) Oscillations and variability in neuronal systems: the role of autonomous transient dynamics in the presence of fast deterministic fluctuations. bioRxiv, p. 448371
Pena RFO, Ceballos CC, Lima V, Roque AC (2018) Interplay of activation kinetics and the derivative conductance determines resonance properties of neurons. Phys Rev E 97:042408
Pena RFO, Lima V, Shimoura RO, Ceballos CC, Rotstein HG, Roque AC (2019) Asymmetrical voltage response in resonant neurons shaped by nonlinearities. Chaos 29:103135
Pike FG, Goddard RS, Suckling JM, Ganter P, Kasthuri N, Paulsen O (2000) Distinct frequency preferences of different types of rat hippocampal neurons in response to oscillatory input currents. J Physiol 529:205–213
Pikovsky AS, Kurths J (1997) Coherence resonance in a noise-driven excitable system. Phys Rev Lett 78:775–778
Pradines JR, Osipov GV, Collins JJ (1999) Coherence resonance in excitable and oscillatory systems: the essential role of slow and fast dynamics. Phys Rev E 60:6407–6410
Prinz AA, Thirumalai V, Marder E (2003) The functional consequences of changes in the strength and duration of synaptic inputs to oscillatory neurons. J Neurosci 23:943–954
Rathour RK, Narayanan R (2012) Inactivating ion channels augment robustness of subthreshold intrinsic response dynamics to parametric variability in hippocampal model neurons. J Physiol 590:5629–5652
Rathour RK, Narayanan R (2014) Homeostasis of functional maps in inactive dendrites emerges in the absence of individual channelostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:E1787–E1796
Rau F, Clemens J, Naumov V, Hennig RM, Schreiber S (2015) Firing-rate resonances in the peripheral auditory system of the cricket, gryllus bimaculatus. J Comp Physiol 201:1075–1090
Reboreda A, Sanchez E, Romero M, Lamas JA (2003) Intrinsic spontaneous activity and subthreshold oscillations in neurones of the rat dorsal column nuclei in culture. J Physiol 551:191–205
Remme MWH, Lengyel M, Gutkin BS (2012) A theoretical framework for the dynamics of multiple intrinsic oscillators in single neurons. In: Phase Response Curves in Neuroscience: Theory, Experiments and Analysis. N. W. Schultheiss, A. A. Prinz and R. A. Butera, Eds. (Springer), pp. 53–72
Remme MWH, Lengyel M, Gutkin BS (2014) A trade-off between dendritic democracy and independence in neurons with intrinsic subthreshold membrane potential oscillations. In: Cuntz H, Remme MWH, Torben-Nielsen B (eds) The Computing Dendrite. Springer, New York
Remme WH, Donato R, Mikiel-Hunter J, Ballestero JA, Foster S, Rinzel J, McAlpine D (2014) Subthreshold resonance properties contribute to the efficient coding of auditory spatial cues. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 111:E2339–E2348
Richardson MJE, Brunel N, Hakim V (2003) From subthreshold to firing-rate resonance. J Neurophysiol 89:2538–2554
Rotstein HG (2014) Frequency preference response to oscillatory inputs in two-dimensional neural models: a geometric approach to subthreshold amplitude and phase resonance. J Math Neurosci 4:11
Rotstein HG (2015) Subthreshold amplitude and phase resonance in models of quadratic type: nonlinear effects generated by the interplay of resonant and amplifying currents. J Comp Neurosci 38:325–354
Rotstein HG (2017) Resonance modulation, annihilation and generation of antiresonance and antiphasonance in 3d neuronal systems: interplay of resonant and amplifying currents with slow dynamics. J Comp Neurosci 43:35–63
Rotstein HG (2017) Spiking resonances in models with the same slow resonant and fast amplifying currents but different subthreshold dynamic properties. J Comp Neurosci 43:243–271
Rotstein HG (2017) The shaping of intrinsic membrane potential oscillations: positive/negative feedback, ionic resonance/amplification, nonlinearities and time scales. J Comp Neurosci 42:133–166
Rotstein HG, Nadim F (2014) Frequency preference in two-dimensional neural models: a linear analysis of the interaction between resonant and amplifying currents. J Comp Neurosci 37:9–28
Rotstein HG, Nadim F (2019) Frequency dependent responses of neuronal models to oscillatory inputs in current versus voltage clamp. Biol Cybern 113:373–395
Rotstein HG, Oppermann T, White JA, Kopell N (2006) The dynamic structure underlying subthreshold oscillatory activity and the onset of spikes in a model of medial entorhinal cortex stellate cells. J Comp Neurosci 21:271–292
Schmitz D, Gloveli T, Behr J, Dugladze T, Heinemann U (1998) Subthreshold membrane potential oscillations in neurons of deep layers of the entorhinal cortex. Neuron 85:999–1004
Schreiber S, Erchova I, Heinemann U, Herz AV (2004) Subthreshold resonance explains the frequency-dependent integration of periodic as well as random stimuli in the entorhinal cortex. J Neurophysiol 92:408–415
Sciamanna G, Wilson CJ (2011) The ionic mechanism of gamma resonance in rat striatal fast-spiking neurons. J Neurophysiol 106:2936–2949
Sharp AA, O’Neil MB, Abbott LF, Marder E (1993) The dynamic clamp: artificial conductances in biological neurons. Trends Neurosci 16:389–394
Solinas S, Forti L, Cesana E, Mapelli J, De Schutter E, D’Angelo E (2007) Fast-reset of pacemaking and theta-frequency resonance in cerebellar Golgi cells: simulations of their impact in vivo. Front Cell Neurosci 1:4
Song SC, Beatty JA, Wilson CJ (2016) The ionic mechanism of membrane potential oscillations and membrane resonance in striatal lts interneurons. J Neurophysiol 116:1752–1764
Stark E, Eichler R, Roux L, Fujisawa S, Rotstein HG, Buzsáki G (2013) Inhibition-induced theta resonance in cortical circuits. Neuron 80:1263–1276
Stiefel KM, Fellous J-M, Thomas PJ, Sejnowski TJ (2010) Intrinsic subthreshold oscillations extend the influence of inhibitory synaptic inputs on cortical pyramidal neurons. Eur J Neurosci 31:1019–1026
Surmeier DJ, Mercer JN, Chan CS (2005) Autonomous pacemakers in the basal ganglia: Who needs excitatory synapses anyway? Curr Opin Neurobiol 15:312–318
Szucs A, Ráktak A, Schlett K, Huerta R (2017) Frequency-dependent regulation of intrinsic excitability by voltage-activated membrane conductances, computational modeling and dynamic clamp. Eur J Neurosci 46:2429–2444
Tateno T, Pakdaman K (2004) Random dynamics of the morris-lecar neural model. Chaos 14:511–530
Tohidi V, Nadim F (2009) Membrane resonance in bursting pacemaker neurons of an oscillatory network is correlated with network frequency. J Neurosci 29:6427–6435
Torres JJ, Marro J, Mejias JF (2011) Can intrinsic noise induce various resonant peaks? New J Phys 13:053014
Tseng H, Nadim F (2010) The membrane potential waveform on bursting pacemaker neurons is a predictor of their preferred frequency and the network cycle frequency. J Neurosci 30:10809–10819
Tuckwell HC (1989) Stochastic processes in the neurosciences. The Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics
Tuckwell HC (1988) Introduction to Theoretical Neurobiology, vol 2. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Uhlenbeck GE, Ornstein LS (1930) On the theory of brownian motion. Phys Rev 36:823–841
Uzuntarla M, Barreto E, Torres J (2017) Inverse stochastic resonance in networks of spiking neurons. PLoS Comp Biol 13:e1005646
van Brederode JFM, Berger AJ (2008) Spike-firing resonance in hypoglossal motoneurons. J Neurophysiol 99:2916–2928
Wang XJ (2010) Neurophysiological and computational principles of cortical rhythms in cognition. Physiol Rev 90:1195–1268
White JA, Budde T, Kay AR (1995) A bifurcation analysis of neuronal subthreshold oscillations. Biophys J 69:1203–1217
White JA, Klink R, Alonso A, Kay AR (1998) Noise from voltage-gated ion channels may influence neuronal dynamics in the entorhinal cortex. J Neurophysiol 80:262–269
Wiesenfeld K, Moss F (1995) Stochastic resonance and the benefits of noise: from ice ages to crayfish and SQUIDs. Nature 373:33–36
Wilson CJ, Callaway JC (2000) A coupled oscillator model of the dopaminergic neurons of the substantia Nigra. J Neurophysiol 83:3084–3100
Wu N, Hsiao C-F, Chandler SH (2001) Membrane resonance and subthreshold membrane oscillations in mesencephalic V neurons: Participants in burst generation. J Neurosci 21:3729–3739
Yang S, Lin W, Feng AA (2009) Wide-ranging frequency preferences of auditory midbrain neurons: roles of membrane time constant and synaptic properties. Eur J Neurosci 30:76–90
Yoshida M, Alonso A (2007) Cell-type-specific modulation of intrinsic firing properties and subthreshold membrane oscillations by the M(Kv7)-currents in neurons of the entorhinal cortex. J Neurophysiol 98:2779–2994
Yoshida M, Giocomo LM, Boardman I, Hasselmo ME (2011) Frequency of subthreshold oscillations at different membrane potential voltages in neurons at different anatomical positions on the dorsoventral axis in the rat medial entorhinal cortex. J Neurosci 31:12683–12694
Zemankovics R, Káli S, Paulsen O, Freund TF, Hájos N (2010) Differences in subthreshold resonance of hippocampal pyramidal cells and interneurons: The role of h-current and passive membrane characteristics. J Physiol 588:2109–2132
Zhang F, Wang L-P, Brauner M, Lewwald JF, Kay K, Watzke N, Wookd PG, Bamberg E, Nagel G, Gottschalk A, Deisseroth K (2007) Multimodal fast optical interrogation of neural circuitry. Nature 446:633–641
Zhuchkova E, Remme MWH, Schreiber S (2014) Subthreshold resonance and membrane potential oscillations in a neuron with nonuniform active dendrite properties. In: Cuntz H, Remme MWH, Torben-Nielsen B (eds) The Computing Dendrite. Springer, New York
Acknowledgements
This work was partially supported by the National Science Foundation grant DMS-1608077 (HGR).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Antonio C. Roque.
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article belongs to Special Issue: Stochastic Oscillators.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Appendix: Intrinsic and resonant oscillatory properties of 2D linear systems
Appendix: Intrinsic and resonant oscillatory properties of 2D linear systems
Consider
where a, b, c and d are constants, \( \omega = 2 \pi f / 1000 > 0 \) is the input frequency and \( A_{in} \ge 0 \) is the input amplitude. The prime sign represents the derivative with respect to t. The units of t are ms and the units of f are Hz.
1.1 Intrinsic oscillations
The characteristic polynomial for the corresponding homogeneous system (\(A_{in} = 0 \)) is given by
The eigenvalues are given by
and the natural (intrinsic) frequency of the (damped) oscillations (in Hz if t has units of ms) is given by
assuming \( (a-d)^2+4 b c < 0 \).
1.2 Resonance and the impedance amplitude profile
The impedance amplitude profile \( Z(\omega ) \) for system (15)–(16) is the magnitude
of the complex valued coefficient of the particular solution to the system
For 1D system, these quantities are given, respectively, by
and
The resonance frequency \( f_{\text {res}} \) (in Hz if t has units of ms) is the frequency at which Z reaches its maximum
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pena, R.F.O., Rotstein, H.G. The voltage and spiking responses of subthreshold resonant neurons to structured and fluctuating inputs: persistence and loss of resonance and variability. Biol Cybern 116, 163–190 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-021-00919-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00422-021-00919-0