Abstract
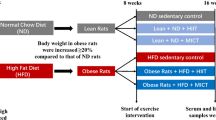
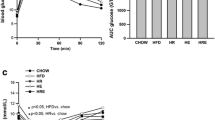
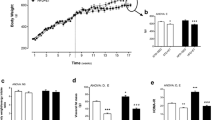
Obesity-induced endoplasmatic reticulum (ER) stress has been demonstrated to underlie the induction of obesity-induced JNK and NF-κB activation inflammatory responses, and generation of peripheral insulin resistance. On the other hand, exercise has been used as a crucial tool in obese and diabetic patients, and may reduce inflammatory pathway stimulation. However, the ability of exercise training to reverse endoplasmatic reticulum stress in adipose and hepatic tissue in obesity has not been investigated in the literature. Here, we demonstrate that exercise training ameliorates ER stress and insulin resistance in DIO-induced rats. Rats were fed with standard rodent chow (3,948 kcal kg−1) or high-fat diet (5,358 kcal kg−1) for 2 months. After that rats were submitted to swimming training (1 h per day, 5 days for week with 5% overload of the body weight for 8 weeks). Samples from epididymal fat and liver were obtained and western blot analysis was performed. Our results showed that swimming protocol reduces pro-inflammatory molecules (JNK, IκB and NF-κB) in adipose and hepatic tissues. In addition, exercise leads to reduction in ER stress, by reducing PERK and eIF2α phosphorylation in these tissues. In parallel, an increase in insulin pathway signaling was observed, as confirmed by increases in IR, IRSs and Akt phosphorylation following exercise training in DIO rats. Thus, results suggest that exercise can reduce ER stress, improving insulin resistance in adipose and hepatic tissue.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aguirre V, Uchida T, Yenush L, Davis R, White MF (2000) The c-Jun NH(2)-terminal kinase promotes insulin resistance during association with insulin receptor substrate-1 and phosphorylation of Ser(307). J Biol Chem 275(12):9047–9054
Barbuio R, Milanski M, Bertolo MB, Saad MJ, Velloso LA (2007) Infliximab reverses steatosis and improves insulin signal transduction in liver of rats fed a high-fat diet. J Endocrinol 194:539–550
Bonora E, Moghetti P, Zancanaro C, Cigolini M, Querena M, Cacciatori V, Corgnati A, Muggeo M (1989) Estimates of in vivo insulin action in man: comparison of insulin tolerance tests with euglycemic and hyperglycemic glucose clamp studies. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 68:374–378
Boppart MD, Asp S, Wojtaszewski JF, Fielding RA, Mohr T, Goodyear LJ (2000) Marathon running transiently increases c-Jun NH2-terminal kinase and p38 activities in human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 526(Pt 3):663–669
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bray GA (2004) Medical consequences of obesity. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 89:2583–2589
Cai D, Frantz JD, Tawa NE Jr, Melendez PA, Oh BC, Lidov HG, Hasselgren PO, Frontera WR, Lee J, Glass DJ, Shoelson SE (2004) IKKbeta/NF-kappaB activation causes severe muscle wasting in mice. Cell 119:285–298
Cintra DE, Pauli JR, Araujo EP, Moraes JC, De Souza CT, Milanski M, Morari J, Gambero A, Saad MJ, Velloso LA (2008) Interleukin-10 is a protective factor against diet-induced insulin resistance in liver. J Hepatol 48:628–637
De Souza CT, Araújo EP, Prada PO, Saad MJ, Boschero AC, Velloso LA (2005) Short-term inhibition of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor gamma coactivator-1alpha expression reverses diet-induced diabetes mellitus and hepatic steatosis in mice. Diabetologia 48:1860–1871
Frosig C, Rose AJ, Treebak JT, Kiens B, Richter EA, Wojtaszewski JF (2007) Effects of endurance exercise training on insulin signaling in human skeletal muscle: interactions at the level of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, Akt, and AS160. Diabetes 56:2093–2102
Gao Z, Hwang D, Bataille F, Lefevre M, York D, Quon MJ, Ye J (2002) Serine phosphorylation of insulin receptor substrate 1 by inhibitor kappa B kinase complex. J Biol Chem 277(50):48115–48121
Hirosumi J, Tuncman G, Chang L, Gorgun CZ, Uysal KT, Maeda K, Karin M, Hotamisligil GS (2002) A central role for JNK in obesity and insulin resistance. Nature 420:333–336
Hotamisligil GS (2008) Inflammation and endoplasmic reticulum stress in obesity and diabetes. Int J Obes (Lond) 32:S52–S54
Hu P, Han Z, Couvillon AD, Kaufman RJ, Exton JH (2006) Autocrine tumor necrosis factor alpha links endoplasmic reticulum stress to the membrane death receptor pathway through IRE1alpha-mediated NF-kappaB activation and down-regulation of TRAF2 expression. Mol Cell Biol 8:3071–3084
Ji LL, Gomez-Cabrera MC, Steinhafel N, Vina J (2004) Acute exercise activates nuclear factor (NF)-kappaB signaling pathway in rat skeletal muscle. FASEB J 18(13):1499–1506
Jiang HY, Wek SA, McGrath BC, Scheuner D, Kaufman RJ, Cavener DR, Wek RC (2003) Phosphorylation of the alpha subunit of eukaryotic initiation factor 2 is required for activation of NF-KappaB in response to diverse cellular stresses. Mol Cell Biol 16:5651–5663
Lee YH, Giraud J, Davis RJ, White MF (2003) c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK) mediates feedback inhibition of the insulin signaling cascade. J Biol Chem 278(5):2896–2902
Ozcan U, Cao Q, Yilmaz E, Lee AH, Iwakoshi NN, Ozdelen E, Tuncman G, Gorgun C, Glimcher LH, Hotamisligil GS (2004) Endoplasmic reticulum stress links obesity, insulin action, and type 2 diabetes. Science 306:457–461
Pauli JR, Ropelle ER, Cintra DE, Carvalho-Filho MA, Moraes JC, De Souza CT, Velloso LA, Carvalheira JB, Saad MJ (2008) Acute physical exercise reverses S-nitrosation of the insulin receptor, insulin receptor substrate 1 and protein kinase B/Akt in diet-induced obese Wistar rats. J Physiol 586(2):659–671
Prada PO, Ropelle ER, Mourão RH, De Souza CT, Pauli JR, Cintra DE, Schenka A, Rocco SA, Rittner R, Franchini KG, Vassalo J, Velloso LA, Carvalheira JB, Saad MJ (2009) EGFR tyrosine kinase inhibitor (PD153035) improves glucose tolerance and insulin action in high-fat diet fed mice. Diabetes 58:2910–2919
Ragheb R, Medhat AM, Shanab GM, Seoudi DM, Fantus IG (2008) Links between enhanced fatty acid flux, protein kinase C and NFkappaB activation, and apoB-lipoprotein production in the fructose-fed hamster model of insulin resistance. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 370:134–139
Romanatto T, Roman EA, Arruda AP, Denis RG, Solon C, Milanski M, Moraes JC, Bonfleur ML, Degaspari GR, Picardi PK, Hirabara S, Boschero AC, Curi R, Velloso LA (2009) Deletion of tumor necrosis factor-alpha receptor 1 (TNFR1) protects against diet-induced obesity by means of increased thermogenesis. J Biol Chem 284:36213–36222
Ropelle ER, Pauli JR, Prada PO, de Souza CT, Picardi PK, Faria MC, Cintra DE, Fernandes MF, Flores MB, Velloso LA, Saad MJ, Carvalheira JB (2006) Reversal of diet-induced insulin resistance with a single bout of exercise in the rat: the role of PTP1B and IRS-1 serine phosphorylation. J Physiol 577:997–1007
Schenk S, Horowitz JF (2007) Acute exercise increases triglyceride synthesis in skeletal muscle and prevents fatty acid-induced insulin resistance. J Clin Invest 117:1690–1698
Scott MD, Atwater I, Rojas E (1981) A method for the simultaneous measurement of insulin release and B cell membrane potential in single mouse islets of Langerhans. Diabetologia 21:470–475
Shoelson SE, Lee J, Yuan M (2003) Inflammation and the IKK beta/I kappa B/NF-kappa B axis in obesity- and diet-induced insulin resistance. Int J Obes Relat Metab Disord 27:S49–S52
Sriwijitkamol A, Christ-Roberts C, Berria R, Eagan P, Pratipanawatr T, DeFronzo RA, Mandarino LJ, Musi N (2006) Reduced skeletal muscle inhibitor of kappaB beta content is associated with insulin resistance in subjects with type 2 diabetes: reversal by exercise training. Diabetes 55:760–767
Sutherland C, O’Brien RM, Granner DK (1996) New connections in the regulation of PEPCK gene expression by insulin. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 351(1336):191–199
Thompson HS, Maynard EB, Morales ER, Scordilis SP (2003) Exercise-induced HSP27, HSP70 and MAPK responses in human skeletal muscle. Acta Physiol Scand 178(1):61–72
Wellen KE, Hotamisligil GS (2005) Inflammation, stress, and diabetes. J Clin Invest 5:1111–1119
Williamson D, Gallagher P, Harber M, Hollon C, Trappe S (2003) Mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway activation: effects of age and acute exercise on human skeletal muscle. J Physiol 547:977–987
Zhang X, Zhang G, Zhang H, Karin M, Bai H, Cai D (2008) Hypothalamic IKKbeta/NF-kappaB and ER stress link overnutrition to energy imbalance and obesity. Cell 135:61–73
Zierath JR (2002) Invited review: exercise training-induced changes in insulin signaling in skeletal muscle. J Appl Physiol 93:773–781
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by grants from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq). We thank Dr Nicola Conran for English language editing.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Klaas R Westerterp.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
da Luz, G., Frederico, M.J.S., da Silva, S. et al. Endurance exercise training ameliorates insulin resistance and reticulum stress in adipose and hepatic tissue in obese rats. Eur J Appl Physiol 111, 2015–2023 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1802-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1802-2