Abstract
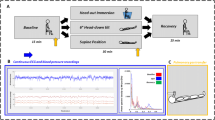
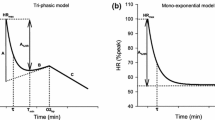
To define the dynamics of cardiovascular adjustments to apnoea during immersion, beat-to-beat heart rate (HR) and systolic (SBP) and diastolic (DBP) blood pressures were recorded in six divers during and after prolonged apnoeas while resting fully immersed in 27°C water. Apnoeas lasted 215 ± 35 s. Compared to control values, HR decreased by 20 beats min−1 and SBP and DBP increased by 23 and 17 mmHg, respectively, in the initial 20 ± 3 s (phase I). Both HR and BP remained stable during the following 92 ± 15 s (phase II). Subsequently, during the final 103 ± 29 s, SBP and DBP increased linearly to values about 60% higher than control, whereas HR remained unchanged (phase III). Cardiac output (Q′) decreased by 35% in phase I and did not further change in phases II and III. Compared to control, total peripheral resistances were twice and three times higher than control, respectively, at the end of phases I and III. After resumption of breathing, HR and BP returned to control values in 5 and 30 s, respectively. The time courses of cardiovascular adjustments to immersed breath-holding indicated that cardiac response took place only at the beginning of apnoea. In contrast, vascular responses showed two distinct adjustments. This pattern suggests that the chronotropic control via the baroreflex is modified during apnoea. These cardiovascular changes during immersed static apnoea are in agreement with those already reported for static dry apnoeas.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andersson J, Schagatay E (1998) Effects of lung volume and involuntary breathing movements on the human diving response. Eur J Appl Physiol 77:19–24
Andersson J, Schagatay E, Gislen A, Holm B (2000) Cardiovascular responses to cold-water immersions of the forearm and face, and their relationship to apnoea. Eur J Appl Physiol 83:566–572
Azabji Kenfack M, Lador F, Licker M, Moia C, Tam E, Capelli C, Ferretti G (2004) Cardiac output by Modelflow method from intra-arterial and fingertip pulse pressure profiles. Clin Sci (Lond) 106:365–369
Campbell LB, Gooden BA, Horowitz JD (1969) Cardiovascular responses to partial and total immersion in man. J Physiol 202:239–250
Cooper VL, Pearson SB, Bowker CM, Elliott MW, Hainsworth R (2005) Interaction of chemoreceptor and baroreceptor reflexes by hypoxia and hypercapnia—a mechanism for promoting hypertension in obstructive sleep apnoea. J Physiol 568:677–687
Ferretti G (2001) Extreme human breath-hold diving. Eur J Appl Physiol 84:254–271
Ferretti G, Costa M, Ferrigno M, Grassi B, Marconi C, Lundgren CEG, Cerretelli P (1991) Alveolar gas composition and exchange during deep breath-hold diving and dry breath-holds in elite divers. J Appl Physiol 70:794–802
Ferrigno M, Hickey DD, Liner MH, Lundgren CR (1986) Cardiac performance in humans during breath holding. J Appl Physiol 60:1871–1877
Ferrigno M, Hickey DD, Liner MH, Lundgren CEG (1987) Simulated breath-hold diving to 20 meters: cardiac performance in humans. J Appl Physiol 62:2160–2167
Ferrigno M, Grassi B, Ferretti G, Costa M, Marconi C, Cerretelli P, Lundgren C (1991) Electrocardiogram during deep breath-hold dives by elite divers. Undersea Biomed Res 18:81–91
Ferrigno M, Ferretti G, Ellis A, Warkander D, Costa M, Cerretelli P, Lundgren CEG (1997) Cardiovascular changes during deep breath-hold dives in a pressure chamber. J Appl Physiol 83:1282–1290
Foster GE, Sheel AW (2005) The human diving response, its function, and its control. Scand J Med Sci Sports 15:3–12
Hansel J, Solleder I, Gfroere W, Muth CM, Paulat K, Simon P, Heitkamp HC, Niess A, Tetzlaff K (2009) Hypoxia and cardiac arrhythmias in breath-hold divers during voluntary immersed breath-holds. Eur J Appl Physiol 105:673–678
Hong SK, Lin YC, Lally DA, Yim BJ, Kominami N, Hong PW, Moore TO (1971) Alveolar gas exchanges and cardiovascular functions during breath holding with air. J Appl Physiol 30:540–547
Jay O, Christensen JPH, White MD (2007) Human face-only immersion in cold water reduces maximal apnoeic times and stimulates ventilation. Exp Physiol 92:197–206
Journeay WS, Reardon FD, Kenny GP (2003) Cardiovascular responses to apneic facial immersion during altered cardiac filling. J Appl Physiol 94:2249–2254
Jung K, Stolle W (1981) Behavior of heart rate and incidence of arrhythmia in swimming and diving. Biotelem Patient Monit 8:228–239
Lemaitre F, Bernier F, Petit I, Renard N, Gardette B, Joulia F (2005) Heart rate responses during a breath hold competition in well-trained divers. Int J Sports Med 26:409–413
Leuenberger UA, Hardy JC, Herr MD, Gray KS, Sinoway LI (2001) Hypoxia augments apnea-induced peripheral vasoconstriction in humans. J Appl Physiol 90:1516–1522
Lin YC, Lally DA, Moore TO, Hong SK (1974) Physiological and conventional breath-hold breaking points. J Appl Physiol 37:291–296
Lin YC, Shida KK, Hong SK (1983) Effects of hypercapnia, hypoxia, and rebreathing on circulatory response to apnea. J Appl Physiol 54:172–177
Lindholm P, Lundgren CEG (2009) The physiology and pathophysiology of human breath-hold diving. J Appl Physiol 106:284–292
Lindholm P, Nordh J, Linnarsson D (2002) Role of hypoxemia for the cardiovascular response to apnea during exercise. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 283:R1227–R1235
Marabotti C, Belardinelli A, L’Abbate A, Scalzini A, Chiesa F, Cialoni D, Passera M, Bedini R (2008) Cardiac function during breath-hold diving in humans: an echocardiographic study. Undersea Hyperb Med 35:83–90
Marabotti C, Scalzini A, Cialoni D, Passera M, L’Abbate A, Bedini R (2009) Cardiac changes induced by immersion and breath-hold diving in humans. J Appl Physiol 106:293–297
Moore TO, Lin YC, Lally DA, Hong SK (1972) Effects of temperature, immersion, and ambient pressure on human apneic bradycardia. J Appl Physiol 33:36–41
Moore TO, Elsner R, Lin YC, Lally DA, Hong SK (1973) Effects of alveolar pO2 and pCO2 on apneic bradycardia in man. J Appl Physiol 34:795–798
Palada I, Eterovic D, Obad A, Bakovic D, Valic Z, Ivancev V, Lojour M, Shoemaker JK, Dujic Z (2007) Spleen and cardiovascular function during short apneas in divers. J Appl Physiol 103:1958–1963
Palada I, Bakovic D, Valic Z, Obad A, Ivancev V, Eterovic D, Shoemaker JK, Dujic Z (2008) Restoration of hemodynamics in apnea struggle phase in association with involuntary breathing movements. Resp Physiol Neurobiol 161:174–181
Pendergast DR, Lundgren CEG (2009) The underwater environment: cardiopulmonary, thermal, and energetic demand. J Appl Physiol 106:276–283
Perini R, Tironi A, Gheza A, Butti F, Moia C, Ferretti G (2008) Heart rate and blood pressure time courses during prolonged dry apnoea in breath-hold divers. Eur J Appl Physiol 104:1–7
Pingitore A, Gemignani A, Menicucci D, Di Bella G, De Marchi D, Passera M, Bedini R, Ghelarducci B, L’Abbate A (2008) Cardiovascular response to acute hypoxemia induced by prolonged breath holding in air. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 294:H449–H455
Sterba JA, Lundgren CE (1985) Diving bradycardia and breath-holding time in man. Undersea Biomed Res 12:139–150
Task Force of the European Society of Cardiology, the North American Society of Pacing, Electrophysiology (1996) Heart rate variability: Standards of measurements, physiological interpretation, and clinical use. Circulation 93:1043–1065
Zbrozyna AW, Westwood DM (1992) Cardiovascular responses elicited by simulated diving and their habituation in man. Clin Auton Res 2:225–233
Acknowledgments
The Authors are grateful to the divers who participated in this study for their essential contribution. The experiments were carried out at Cala Montjoi, Roses, Catalunya, Spain. We thank David Arroniz and Oliver Herrera for logistic support. The collaboration of the Spanish Federation of Underwater Activities is acknowledged. The study was partly supported by Centro di Studio e Ricerca di Fisiologia dell’Esercizio Muscolare e dello Sport, Università di Brescia, by a grant from the University of Brescia to Renza Perini and Guido Ferretti, by Swiss National Science Foundation Grants 3200-061780 and 3200B0-102181 and by a grant from Swiss Federal Office of Sport of Magglingen to Guido Ferretti.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Communicated by Dag Linnarsson.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Perini, R., Gheza, A., Moia, C. et al. Cardiovascular time courses during prolonged immersed static apnoea. Eur J Appl Physiol 110, 277–283 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1489-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-010-1489-4