Abstract
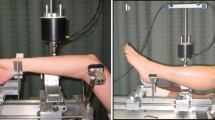
The purpose of this study is to compare a mechanical property of bone in world-class female athletes with different loading histories. Bone bending stiffness or EI (E is the modulus of elasticity and I, the moment of inertia) was measured noninvasively with the mechanical response tissue analyzer, that analyzes the response of bone to a vibratory stimulus. We evaluated the ulna, ulnar width, wrist density and tibia in 13 synchronized swimmers (SYN), eight gymnasts (GYM) and 16 untrained women (UNT) of similar age. Muscle strength in the flexors and extensors at elbows and knees was measured in the athletes. SYN were taller than GYM or UNT (168±0.7 vs. 152±1.1 or 157±1.2 cm, P< 0.01). Ulnar EI, Nm2, was similar in SYN and GYM (41±5.4 vs. 42±4.2, NS) and 50% higher than in UNT (27±2.1, P<0.05). Ulnar EI, Nm2 was related to ulnar width (r=0.497, P<0.002, n=37) but not to wrist density. Tibial EI, Nm2, in SYN and GYM (270±42 vs. 285±49, NS) was similar and more than twice as high as in UNT (119±6; p<0.05). Knee flexor strength measured at 60° s−1 and elbow extensor strength at 200° s−1 correlated with tibial EI (r=0.44 and 0.41, P<0.05). In spite of different loading histories, the tibiae and ulnas of world-class athletes showed similar high values for bending stiffness that exceeded values in untrained women. EI in the ulna could be related to bone width and in the tibia, to muscle strength.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnaud SB, Steele CR, Zhou L-Z, Hutchinson T, Marcus R (1991) A direct non-invasive measure of long bone strength. Proc Ann Int Cong IEEE Eng Int Med Biol Soc 13:1984–1985
Blank RD (2001) Breaking down bone strength: a perspective on future skeletal genetics. J Bone Miner Res 16:1207–1211
Burr DB, Martin RB (1983) The effects of composition, structure and age on the torsional properties of the human radius. J Biomech 16:603–608
Courteix DE, Lespessailes E, Peres SL, Obert P, Germain P, Benhamou CL (1998) Effect of physical training on bone mineral density in prepubertal girls: a comparative study between impact loading and non-impact loading sports. Osteoporosis Int 8:152–158
Duncan CS, Blimkie CJR, Kemp A, Cowell CT, Burke ST, Brody JN, Howman-Giles R (2002a) Bone mineral density in adolescent female athletes: relationship to exercise type and muscle strength. Med Sci Sports Exerc 34:286–294
Duncan CS, Blimkie CJR, Kemp A, Higgs W, Cowell CT, Woodhead H, Brody JN, Howman-Giles R (2002b) Mid-femur geometry and biomechanical properties in 15- to 18-yr-old female athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 34:673–681
Elmslander HC, Sinaki M, Muhs JM, Chao EY, Wahner HW, Bryant SC, Riggs BL, Eastell R (1998) Bone mass and muscle strength in female college athletes (runners and swimmers). Mayo Clin Proc 73:1151–1160
Fehling PC, Alekel L, Clasey J, Rector A, Stillman RJ (1995) A comparison of bone mineral densities among female athletes in impact loading sports. Bone 17:206–210
Helge EW, Kanstrup JL (2002) Bone density in female elite gymnasts: impact of muscle strength and sex hormones. Med Sci Sports Exerc 34:174–180
Hutchinson TM, Bakulin AV, Rakhmanov AS, Martin RB, Steele CR, Arnaud SB (2001) Effects of chair restraint on the strength of the tibia in rhesus monkeys. J Med Primatol 30:313–321
Kiebzak GM, Box JH, Box P (1999) Decreased ulnar bending stiffness in osteoporotic Caucasian women. J Clin Densitom 2:143–152
Lohman TG, Roche AF, Martorell R (1988) Anthropometric standardization reference manual, Human Kinetics Books, Champaign, pp 55–70
Lowet G, Van Audekercke R, Vander P, Geusans P, Dequejers J, Lammens J (1991) The relation between resonant frequencies and torsional stiffness of long bones in vitro. Validation of a simple beam model. J Biomech 26:689–696
Martin RB, Ishida J (1989) The relative effects of collagen fiber orientation, porosity, density, and mineralization on bone strength. J Biomech 22:419–426
McCabe F, Zhou L-Z, Steele CR, Marcus R (1991) Noninvasive assessment of ulnar bending stiffness in women. J Bone Miner Res 6:53–59
Myburgh K, Charette S, Zhou L-Z, Steele CR, Arnaud SB, Marcus R (1993) Influence of recreational activity and muscle strength on ulnar bending stiffness in healthy men. Med Sci Sports Exerc 25:592–596
Risser WL, Lee EJ, LeBlanc A, Pointdexer JM, Risser JM, Schneider V (1990) Bone density in eumenorrheic female college athletes. Med Sci Sports Exerc 33:570–574
Roberts SG, Steele CR (1995) End flexibility incorporated into a model of a vibrating human tibia for non-invasive measurement of bone properties. Ad In Bioeng Proc Intl Mech Eng Congr Expo 31:345–346
Roberts SG, Hutchinson T, Arnaud SB, Kiratli BJ, Martin RB, Steele CR (1996) Noninvasive determination of bone mechanical properties using vibration response: a refined model and validation in vivo. J Biomech 29(1):91–98
Rubin CT, Lanyon LE (1987) Osteoregulatory nature of mechanical stimuli: function as a determinant for adaptive remodeling in bone. J Orthop Res 5:300–310
Smith SR, Burshell A, Bober M, Smetherman D (1994) Adaptation of bone in a kindred with osteogenesis imperfecta. J Bone Miner Res 9:S424
Snow-Harter CM, Bouxsien M, Lewis B, Charette S, Weinstein P, Marcus R (1990) Muscle strength as a predictor of bone mineral density in young women. J Bone Miner Res 5(6):589–595
Steele CR, Zhou L-Z, Guido D, Marcus R, Heinrichs WL, Cheema C (1988) Noninvasive determination of ulnar stiffness from mechanical response—in vivo comparison of stiffness and bone mineral content in humans. J Biomech Eng 110:87–96
Taafe DR, Robinson TL, Snow CM, Marcus R (1997) High impact exercise promotes bone gain in well trained female athletes. J Bone Miner Res 12:255–260
Weinstein RS (2000) True strength. J Bone Miner Res 15:621–625
Young DR, Howard WH, Cann C, Steele CR (1979) Noninvasive measures of bone bending rigidity in the monkey (M. Nemestrina). Calcif Tissue Int 27:109–115
Acknowledgements
We gratefully acknowledge the generosity of the coaches and athletes who took the time to participate in our study. This study is partially supported by a NIH grant No. 5 S0 GM053933-06 and NASA No. SAA2-401535
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liang, M.T.C., Arnaud, S.B., Steele, C.R. et al. Ulnar and tibial bending stiffness as an index of bone strength in synchronized swimmers and gymnasts. Eur J Appl Physiol 94, 400–407 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-005-1351-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00421-005-1351-2