Abstract
Objective
To investigate the risk factors for musculoskeletal injuries in military personnel.
Methods
A systematic literature search was carried out in August 2019 and updated in July 2020 without language or time filters. The inclusion criteria were prospective studies that investigated the risk factors for injuries in military personnel. Only risk factors analyzed by at least ten studies were selected for the meta-analysis. For data analysis, the RevMan5.3 program was used to compare the number of participants with injuries between high- or low-risk groups. The measurement of dichotomous variables was one of the selected parameters for the analysis, as well as the Mantel–Haenszel statistical method, random-effects model, and analysis with a relative risk (RR) and 95% confidence interval for the included studies.
Results
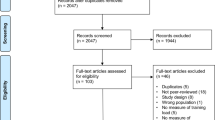
A total of 2,629 studies were identified through databases. Thirty-four studies met the inclusion criteria. The groups considered at risk were the oldest [RR = 1.22; (95% CI 1.06–1.41)], with overweight or obesity [RR = 1.27; (95% CI 1.08–1, 48)], with previous injuries [RR = 1.15; (95% CI 1.01–1.30)], and with the worst performance in running tests of 1,600–3,200 m [RR = 1.87; (95% CI 1.28–2.71)]. Gender, ethnicity, and smoking were not associated with injuries. However, a subgroup analysis showed that among studies with a follow-up of fewer than 12 months, women presented RR = 2.44 (95% CI 1.65–3.60) more likely to develop injuries.
Conclusion
Age, overweight or obesity, previous injuries, and performance in the 1600–3200 m run are associated with an increased risk of injury in the military.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material:
Complementary materials can be found in the Appendix.
References
Abt JP, Perlsweig K, Nagai T et al (2016) Effects of age and military service on strength and physiological characteristics of US. Army Soldiers Mil Med 181:173–179. https://doi.org/10.7205/MILMED-D-15-00036
Age EG, Heir T (1996) Age, body composition, aerobic fitness and health condition as risk factors for musculoskeletal injuries in conscripts. Scand J Med Sci Sport 6:222–227
Alvar B, Sell K, Deuster P (2017) NSCA ’ s essentials of tactical strength and conditioning
Amako M, Yato Y, Yoshihara Y et al (2018) Epidemiological patterns of traumatic musculoskeletal injuries and non-traumatic disorders in Japan Self-Defense Forces. Inj Epidemiol. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40621-018-0150-2
Andersen KA, Grimshaw PN, Kelso RM, Bentley DJ (2016) Musculoskeletal lower limb injury risk in army populations. Sport Med Open. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40798-016-0046-z
Anderson MK, Grier T, Canham-chervak M et al (2015) Occupation and other risk factors for injury among enlisted US. Army Soldiers Public Health 129:531–538. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.puhe.2015.02.003
Armstrong DW, Rue JH, Wilckens JH, Frassica FJ (2004) Stress fracture injury in young military men and women. Bone 35:806–816. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bone.2004.05.014
Bader CE, Giordano NA, Mcdonald CC et al (2018) Musculoskeletal pain and headache in the active duty military population: an integrative review. Worldviews Evid Based Nurs 15:264–271. https://doi.org/10.1111/wvn.12301
Bedno S, Hauret K, Loringer K et al (2014) Effects of personal and occupational stress on injuries in a young, physically active population: a survey of military personnel. Mil Med 179:1311–1318. https://doi.org/10.7205/MILMED-D-14-00080
Bell NS, Mangione TW, Hemenway D et al (2000) High injury rates among female army trainees a function of gender? Am J Prev Med 18:141–146
Bergeron MF, Nindl BC, Deuster PA et al (2011) Consortium for health and military performance and American College of sports medicine consensus paper on extreme conditioning programs in military personnel. Curr Sports Med Rep 10:383–389. https://doi.org/10.1249/JSR.0b013e318237bf8a
Blacker SD, Wilkinson DM, Rayson MP (2009) Gender differences in the physical demands of British Army recruit training. Mil Med 174:811–816. https://doi.org/10.7205/MILMED-D-01-3708
Bliekendaal S, Goossens L, Stubbe JH (2017) Incidence and risk factors of injuries and their impact on academic success: a prospective study in PETE students. Scand J Med Sci Sport 27:1978–1985. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.12838
Carow SD, Haniuk EM, Cameron KL et al (2016) Risk of lower extremity injury in a military cadet population after a supervised injury-prevention program. J Athl Train 51:905–918. https://doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-49.5.22
Cosio-lima LM, Reynolds KL, Knapik JJ et al (2013) US coast guard academy injury and risk factor study. Br J Med Med Res 3:914–927
Cowan DN, Bedno SA, Urban N et al (2011) Musculoskeletal injuries among overweight army trainees : incidence and health care utilization. Occup Med (Chic Ill) 61:247–252. https://doi.org/10.1093/occmed/kqr028
Ferguson CJ (2009) An effect size primer: a guide for clinicians and researchers. Prof Psychol Res Pract 40:532–538. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0015808
Finestone A, Milgrom C, Evans R et al (2008) Overuse injuries in female infantry recruits during low-intensity basic training. Med Sci Sport Exerc. https://doi.org/10.1249/MSS.0b013e3181892ff9
Geary KG, Croft AM (2007) Acute knee injuries in military personnel: a case–control study of the effectiveness of direct-access magnetic resonance imaging in a primary care setting. Mil Med 172:436–439
George SZ, Childs JD, Teyhen DS et al (2012) Predictors of occurrence and severity of first time low back pain episodes : findings from a military inception cohort. PLoS ONE 7:e30597. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0030597
Gilchrist J, Kimsey CD (2000) Exercise-related injuries among women strategies for prevention from civilian and military studies. Recomm reports 49:13–33
Glavač B, Dopsaj M, Nikić MD et al (2015) Changing body structure components and motor skills in Military High School students within one year. Vojnosanit Pregl 72:677–682. https://doi.org/10.2298/VSP140205067G
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R et al (2011a) GRADE guidelines: 8. Rating the quality of evidence—indirectness. J Clin Epidemiol 64:1303–1310. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2011.04.014
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R et al (2011b) GRADE guidelines: 7. Rating the quality of evidence—inconsistency. J Clin Epidemiol 64:1294–1302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2011.03.017
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Kunz R et al (2011c) GRADE guidelines 6. Rating the quality of evidence—imprecision. J Clin Epidemiol 64:1283–1293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2011.01.012
Guyatt GH, Oxman AD, Montori V et al (2011d) GRADE guidelines: 5. Rating the quality of evidence—Publication bias. J Clin Epidemiol 64:1277–1282. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2011.01.011
Hägglund M, Waldén M, Bahr R, Ekstrand J (2005) Methods for epidemiological study of injuries to professional football players: developing the UEFA model. Br J Sports Med 39:340–346. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsm.2005.018267
Hägglund M, Waldén M, Ekstrand J (2006) Previous injury as a risk factor for injury in elite football: a prospective study over two consecutive seasons. Br J Sports Med 40:767–772. https://doi.org/10.1136/bjsm.2006.026609
Hauschild VD, Schuh-renner A, Lee T et al (2019) Journal of Science and Medicine in Sport Using causal energy categories to report the distribution of injuries in an active population: an approach used by the US. Army J Sci Med Sport 22:997–1003. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2019.04.001
Heir T, Eide G (1997) Injury proneness in intantry conscripts undergoing a physical training programme: smokeless tobacco use, higher age, and low levels of physical fitness are risk factors. Scand J Med Sci Sport 7:304–311
Henderson NE, Knapik JJ, Scott CPT et al (2000) Injuries and injury risk factors among men and women in US army combat medic advanced individual training. Mil Med 9:647–652
Herman DC, Riveros D, Jacobs K et al (2019) Previous high school participation in varsity sport and jump-landing biomechanics in adult recreational athletes. J Athl Train 54:1089–1094. https://doi.org/10.4085/1062-6050-412-18
Higgins J, Green S (2008) Cochrane handbook for systematic reviews of intervenions. Chichester: The Cochrane Collaboration
Higgins JPT, Thompson SG, Deeks JJ, Altman DG (2003) Measuring inconsistency in meta-analyses. Br Med J 327:557–560. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.327.7414.557
Hollander NA, Finestone AS, Yofe V et al (2020) The association between increased body mass index and overuse injuries in israel defense forces conscripts. Obes Facts 13:152–165. https://doi.org/10.1159/000505836
Holsteen KK, Choi YS, Bedno SA et al (2018) Gender differences in limited duty time for lower limb injury. Occup Med (Lond) 68:18–25. https://doi.org/10.1093/occmed/kqx169
Hruby A, Bulathsinhala L, Mckinnon CJ et al (2015) BMI and lower extremity injury in US army soldiers, 2001–2011. Am J Prev Med. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2015.10.015
Jensen AE, Laird LTM, Jameson JT, Kelly KR (2019) Prevalence of musculoskeletal injuries sustained during marine corps recruit training. Mil Med 184:511–520. https://doi.org/10.1093/milmed/usy387
Jones B, Cowan D, Tomlinson P, Robinson J et al (1993a) Epidemiology of injuries associated with physical training among young men in the Army. Med Sci Sport Exerc 197–203
Jones BH, Bovee MW, Mca J et al (1993b) Intrinsic risk factors for exercise-related injuries among male and female army trainees. Am J Sports Med 21:705–710
Jones BH, Canham-Chervak M, Sleet DA (2010) An evidence-based public health approach to injury priorities and prevention recommendations for the US military. Am J Prev Med 38:S1–S10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amepre.2009.10.001
Kelly KR, Jameson JT (2016) Preparing for combat readiness for the fight: physical performance profile of female US Marines. J Strength Cond Res 30:595–604. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000001269
Knapik JJ, Jones SB, Darakjy S et al (2007) Injury rates and injury risk factors among US army wheel vehicle mechanics. Mil Med 172:988–996
Knapik JJ, Hauret KG, Canada S et al (2011) Association between ambulatory physical activity and injuries during United States army basic combat training. J Phys Act Heal 8:496–502
Knapik JJ, Graham B, Cobbs J et al (2013) A prospective investigation of injury incidence and risk factors among army recruits in combat engineer training. J Occup Med Toxicol 8:1. https://doi.org/10.1186/1745-6673-8-5
Koury JC, Daleprane JB, Pitaluga-Filho MV et al (2016) Aerobic conditioning might protect against liver and muscle injury caused by short-term military training. J Strength Cond Res 30:454–460. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000001102
Kyrolainen H, Pihlainen K, Vaara JP et al (2018) Optimising training adaptations and performance in military environment. J Sci Med Sport 21:1131–1138. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jsams.2017.11.019
Lappe JM, Stegman MR, Recker RR (2001) International original article the impact of lifestyle factors on stress fractures in female army recruits. Osteoporos Int 12:35–42
Leppänen M, Aaltonen S, Parkkari J et al (2014) Interventions to prevent sports related injuries: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. Sport Med 44:473–486. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40279-013-0136-8
Lisman PJ, De La Motte SJ, Gribbin TC et al (2017) A systematic review of the association between physical fitness and musculoskeletal injury risk: part 1-cardiorespiratory endurance. J Strength Cond Res 31:1744–1757. https://doi.org/10.1519/JSC.0000000000001855
Lovalekar M, Johnson CD, Eagle S et al (2018) Epidemiology of musculoskeletal injuries among US air force special tactics operators: an economic cost perspective. BMJ Open Sport Exerc Med 4:e000471. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjsem-2018-000471
Matilla V, Niva M, Kiuru M, Pihlajamaki H (2007) Risk factors for bone stress injuries: a follow-up study of 102,515 person-years. Med Sci Sports Exerc. https://doi.org/10.1249/01.mss.0b013e318053721d
Mattila VM, Kuronen P, Pihlajama H (2007) Nature and risk factors of injury hospitalization in young adults: a follow-up of 135, 987 military conscripts. Scand J Public Health 35:418–423. https://doi.org/10.1080/14034940601181439
Monnier A, Djupsjöbacka M, Larsson H et al (2016) Risk factors for back pain in marines; a prospective cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 17:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-016-1172-y
Moola S, Zachary M, Sears K et al (2015) Conducting systematic reviews of association (etiology): the Joanna Briggs Institute’s approach. Int J Evid Based Healthc 13:163–169. https://doi.org/10.1097/XEB.0000000000000064
Opar DA, Serpell BG (2014) Is there a potential relationship between prior hamstring strain injury and increased risk for future anterior cruciate ligament injury ? Arch Phys Med Rehabil 95:401–405. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2013.07.028
Opar DA, Williams MD, Shield AJ (2012) Hamstring strain injuries factors that lead to injury and re-injury. Sport Med 42:209–226
Page MJ, Higgins JPT, Sterne JAC (2019) Chapter 13: Assessing risk of bias due to missing results in a synthesis. Cochrane Collab
Pihlajamaki H, Parviainen M, Kyrolainen H et al (2019) Regular physical exercise before entering military service may protect young adult men from fatigue fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 20:126. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-019-2513-4
Popovich RM, Gardner JW, Potter R et al (2000) Effect of rest from running on overuse injuries in army basic training. Am J Prev Med 18:147–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0749-3797(99)00167-1
Radzak KN, Putnam AM, Tamura K et al (2017) Asymmetry between lower limbs during rested and fatigued state running gait in healthy individuals. Gait Posture 51:268–274
Rauh M, Macera C, Trone D et al (2006) Epidemiology of stress fracture and lower-extremity overuse injury in female recruits. Med Sci Sports Exerc. https://doi.org/10.1249/01.mss.0000227543.51293.9d
Reynolds KL, White JS, Knapik JJ et al (1999) Injuries and risk factors in a 100-mile (161-km) infantry road march. Prev Med (Baltim) 28:167–173
Roy TC, Lopez HP, Piva SR (2013) Loads worn by soldiers predict episodes of low back pain during deployment to afghanistan. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 38:1310–1317. https://doi.org/10.1097/BRS.0b013e31829265c4
Roy TC, Ritland BM, Sharp MA (2017) A description of injuries in men and women while serving in Afghanistan. Mil Med 180:126–131. https://doi.org/10.7205/MILMED-D-14-00321
Santtila M, Kyröläinen H, Vasankari T et al (2006) Physical fitness profiles in young Finnish men during the years 1795–2004. Med Sci Sports Exerc 38:1990–1994. https://doi.org/10.1249/01.mss.0000232023.28984.78
Santtila M, Pihlainen K, Koski H et al (2019) Physical fitness and body anthropometrics profiles of the female recruits entering to voluntary military service. Mil Med 184:E200–E205. https://doi.org/10.1093/milmed/usy145
Schoenfeld AJ, Goodman GP, Burks R et al (2014) The influence of musculoskeletal conditions, behavioral health diagnoses, and demographic factors on injury-related outcome in a high-demand population. J Bone Jt Surg Am 106:1–8
Shaffer RA, Rauh MJ, Brodine SK et al (2006) Predictors of stress fracture susceptibility in young female recruits. Am J Sports Med 34:108–115. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546505278703
Sharma J, Golby J, Greeves J, Spears IR (2011) Biomechanical and lifestyle risk factors for medial tibia stress syndrome in army recruits: a prospective study. Gait Posture 33:361–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gaitpost.2010.12.002
Sharma J, Greeves JP, Byers M et al (2015) Musculoskeletal injuries in British Army recruits: a prospective study of diagnosis-specific incidence and rehabilitation times epidemiology of musculoskeletal disorders. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 16:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-015-0558-6
Sharma J, Heagerty R, Dalal S et al (2019) Risk factors associated with musculoskeletal injury: a prospective study of British infantry recruits. Curr Rheumatol Rev 15:50–58. https://doi.org/10.2174/1573397114666180430103855
Smith GS, Dannenberg AL, Amoroso PJ (2000) Hospitalization due to injuries in the military—evaluation of current data and recommendations on their use for injury prevention. Am J Prev Med 18:41–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0749-3797(99)00171-3
Stroup DF, Berlin JA, Morton SC et al (2000) Meta-analysis of observational studies. JAMA 283:2008–2012
Taanila H, Suni J, Pihlajamäki H et al (2010) Aetiology and risk factors of musculoskeletal disorders in physically active conscripts: a follow-up study in the Finnish Defence Forces. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 11:146. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2474-11-146
Taanila H, Suni JH, Kannus P et al (2015) Risk factors of acute and overuse musculoskeletal injuries among young conscripts: a population-based cohort study. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 16:104. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-015-0557-7
Teyhen D, Bergeron MF, Deuster P et al (2014) Consortium for health and military performance and American College of Sports Medicine Summit: utility of functional movement assessment in identifying musculoskeletal injury risk. Curr Sports Med Rep 13:52–63. https://doi.org/10.1249/JSR.0000000000000023
Teyhen DS, Shaffer SW, Butler RJ et al (2015) What risk factors are associated with musculoskeletal injury in US army rangers? A prospective prognostic study. Clin Orthop Relat Res. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-015-4342-6
Trone DW, Cipriani DJ, Raman R et al (2014) Self-reported smoking and musculoskeletal overuse injury among male and female US. Mar Corps recruits Mil Med 197:735–743. https://doi.org/10.7205/MILMED-D-13-00516
Uhorchak JM, Scoville CR, Williams GN et al (2003) Risk factors associated with noncontact injury of the anterior cruciate ligament—a prospective four-year evaluation of 859 west point cadets. Am J Sports Med 31:831–842
Vaara JP, Santtila M, Vasankari T et al (2019) Cardiorespiratory and muscular fitness in young adult Finnish men between 2003 and 2015. Scand J Med Sci Sport. https://doi.org/10.1111/sms.13619
Waterman BR, Belmont PJ, Cameron KL et al (2010) Epidemiology of ankle sprain at the United States military academy. Am J Sports Med 38:797–803. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546509350757
Wearing SC, Hennig EM, Byrne NM et al (2006) Musculoskeletal disorders associated with obesity: a biomechanical perspective. Obes Rev 7:239–250. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1467-789X.2006.00251.x
Wells GA, Shea B, Connell DO, et al (2000) The Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS ) for assessing the quality of nonrandomised studies in meta-analyses. http://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp. Accessed 16 Oct 2017
Yates B, Fcpod S, White S (2004) The incidence and risk factors in the development of medial tibial stress syndrome among naval recruits. Am J Sports Med 32:772–780. https://doi.org/10.1177/0095399703258776
Zhang Y, Coello PA, Guyatt G et al (2018) GRADE Guidelines: 20. Assessing the certainty of evidence in the importance of outcomes outcomes or values and preferences—inconsistency, imprecision, and other domains. J Clin Epidemiol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinepi.2018.05.011
Funding
There was no funding related to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors report the absence of conflicts of interest related to this publication.
Consent for publication
The authors authorize the publication of this systematic review study in the International Archives of Occupational and Environmental Health.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
dos Santos Bunn, P., de Oliveira Meireles, F., de Souza Sodré, R. et al. Risk factors for musculoskeletal injuries in military personnel: a systematic review with meta-analysis. Int Arch Occup Environ Health 94, 1173–1189 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-021-01700-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00420-021-01700-3