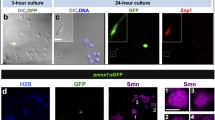
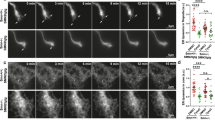
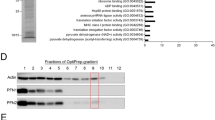
Abstract
Reduced levels of the SMN (survival of motoneuron) protein cause spinal muscular atrophy, the main form of motoneuron disease in children and young adults. In cultured motoneurons, reduced SMN levels lead to disturbed axon growth that correlates with reduced actin mRNA and protein in growth cones, indicating that anterograde transport and local translation of β-actin mRNA are altered in this disease. However, it is not fully understood how local translation of the β-actin mRNA is regulated in SMN-deficient motoneurons. Here, we established a lentiviral GFP-based reporter construct to monitor local translation of β-actin mRNA. Time-lapse imaging of fluorescence recovery after photobleaching (FRAP) in living motoneurons revealed that β-actin is locally translated in the growth cones of embryonic motoneurons. Interestingly, local translation of the β-actin reporter construct was differentially regulated by various Laminin isoforms, indicating that Laminins provide extracellular cues for the regulation of local translation in growth cones. Notably, local translation of β-actin mRNA was deregulated in motoneurons from a mouse model for the most severe form of SMA (Smn −/− ;SMN2). Taken together our findings suggest that local translation of β-actin in growth cones of motoneurons is regulated by Laminin signalling and that this signalling is disturbed in SMA.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aakalu G, Smith WB, Nguyen N, Jiang C, Schuman EM (2001) Dynamic visualization of local protein synthesis in hippocampal neurons. Neuron 30(2):489–502
Andreassi C, Riccio A (2009) To localize or not to localize: mRNA fate is in 3′UTR ends. Trends Cell Biol 19(9):465–474. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2009.06.001
Bassell GJ, Warren ST (2008) Fragile X syndrome: loss of local mRNA regulation alters synaptic development and function. Neuron 60(2):201–214. doi:10.1016/j.neuron.2008.10.004
Bassell GJ, Zhang H, Byrd AL, Femino AM, Singer RH, Taneja KL, Lifshitz LM, Herman IM, Kosik KS (1998) Sorting of beta-actin mRNA and protein to neurites and growth cones in culture. J Neurosci 18(1):251–265
Bowerman M, Anderson CL, Beauvais A, Boyl PP, Witke W, Kothary R (2009) SMN, profilin IIa and plastin 3: a link between the deregulation of actin dynamics and SMA pathogenesis. Mol Cell Neurosci 42(1):66–74
Bowerman M, Shafey D, Kothary R (2007) Smn depletion alters profilin II expression and leads to upregulation of the RhoA/ROCK pathway and defects in neuronal integrity. J Mol Neurosci 32(2):120–131
Campbell DS, Holt CE (2001) Chemotropic responses of retinal growth cones mediated by rapid local protein synthesis and degradation. Neuron 32(6):1013–1026
Cheever TR, Li B, Ervasti JM (2012) Restricted morphological and behavioral abnormalities following ablation of beta-actin in the brain. PLoS One 7(3):e32970
Cheever TR, Olson EA, Ervasti JM (2011) Axonal regeneration and neuronal function are preserved in motor neurons lacking ss-actin in vivo. PLoS One 6(3):e17768
Condeelis J, Singer RH (2005) How and why does beta-actin mRNA target? Eur Cell Biol Org 97(1):97–110
Crawford TO, Pardo CA (1996) The neurobiology of childhood spinal muscular atrophy. Neurobiol Dis 3(2):97–110. doi:10.1006/nbdi.1996.0010
Garber KB, Visootsak J, Warren ST (2008) Fragile X syndrome. Eur J Hum Genet 16(6):666–672
Hengst U, Deglincerti A, Kim HJ, Jeon NL, Jaffrey SR (2009) Axonal elongation triggered by stimulus-induced local translation of a polarity complex protein. Nat Cell Biol 11(8):1024–1030
Holt CE, Bullock SL (2009) Subcellular mRNA localization in animal cells and why it matters. Science 326(5957):1212–1216. doi:10.1126/science.1176488
Jablonka S, Beck M, Lechner BD, Mayer C, Sendtner M (2007) Defective Ca2+ channel clustering in axon terminals disturbs excitability in motoneurons in spinal muscular atrophy. J Cell Biol 179(1):139–149. doi:10.1083/jcb.200703187
Jablonka S, Rossoll W, Schrank B, Sendtner M (2000) The role of SMN in spinal muscular atrophy. J Neurol 247(Suppl 1):I37–I42
Kabouridis PS, Magee AI, Ley SC (1997) S-acylation of LCK protein tyrosine kinase is essential for its signalling function in T lymphocytes. EMBO J 16(16):4983–4998. doi:10.1093/emboj/16.16.4983
Kiebler MA, Bassell GJ (2006) Neuronal RNA granules: movers and makers. Neuron 51(6):685–690
Kislauskis EH, Zhu X, Singer RH (1994) Sequences responsible for intracellular localization of beta-actin messenger RNA also affect cell phenotype. J Cell Biol 127(2):441–451
Leung KM, van Horck FP, Lin AC, Allison R, Standart N, Holt CE (2006) Asymmetrical beta-actin mRNA translation in growth cones mediates attractive turning to netrin-1. Nat Neurosci 9(10):1247–1256
Lin AC, Holt CE (2008) Function and regulation of local axonal translation. Curr Opin Neurobiol 18(1):60–68. doi:10.1016/j.conb.2008.05.004
Lois C, Hong EJ, Pease S, Brown EJ, Baltimore D (2002) Germline transmission and tissue-specific expression of transgenes delivered by lentiviral vectors. Science 295(5556):868–872. doi:10.1126/science.1067081
McGovern VL, Gavrilina TO, Beattie CE, Burghes AH (2008) Embryonic motor axon development in the severe SMA mouse. Human Mol Genet 17(18):2900–2909
Monani UR, Sendtner M, Coovert DD, Parsons DW, Andreassi C, Le TT, Jablonka S, Schrank B, Rossoll W, Prior TW, Morris GE, Burghes AH (2000) The human centromeric survival motor neuron gene (SMN2) rescues embryonic lethality in Smn(−/−) mice and results in a mouse with spinal muscular atrophy. Human Mol Genet 9(3):333–339
Murray LM, Lee S, Baumer D, Parson SH, Talbot K, Gillingwater TH (2010) Pre-symptomatic development of lower motor neuron connectivity in a mouse model of severe spinal muscular atrophy. Human Mol Genet 19(3):420–433
Noakes PG, Gautam M, Mudd J, Sanes JR, Merlie JP (1995) Aberrant differentiation of neuromuscular junctions in mice lacking s-laminin/laminin beta 2. Nature 374(6519):258–262. doi:10.1038/374258a0
Oleynikov Y, Singer RH (2003) Real-time visualization of ZBP1 association with beta-actin mRNA during transcription and localization. Curr Biol 13(3):199–207
Patton BL, Miner JH, Chiu AY, Sanes JR (1997) Distribution and function of laminins in the neuromuscular system of developing, adult, and mutant mice. J Cell Biol 139(6):1507–1521
Piazzon N, Rage F, Schlotter F, Moine H, Branlant C, Massenet S (2008) In vitro and in cellulo evidences for association of the survival of motor neuron complex with the fragile X mental retardation protein. J Biol Chem 283(9):5598–5610. doi:10.1074/jbc.M707304200
Plantman S, Patarroyo M, Fried K, Domogatskaya A, Tryggvason K, Hammarberg H, Cullheim S (2008) Integrin-laminin interactions controlling neurite outgrowth from adult DRG neurons in vitro. Mol Cell Neurosci 39(1):50–62. doi:10.1016/j.mcn.2008.05.015
Porter BE, Sanes JR (1995) Gated migration: neurons migrate on but not onto substrates containing S-laminin. Developmental Biol 167(2):609–616. doi:10.1006/dbio.1995.1052
Rehberg M, Lepier A, Solchenberger B, Osten P, Blum R (2008) A new non-disruptive strategy to target calcium indicator dyes to the endoplasmic reticulum. Cell Calcium 44(4):386–399
Rodriguez AJ, Czaplinski K, Condeelis JS, Singer RH (2008) Mechanisms and cellular roles of local protein synthesis in mammalian cells. Curr Opin Cell Biol 20(2):144–149
Rossoll W, Jablonka S, Andreassi C, Kroning AK, Karle K, Monani UR, Sendtner M (2003) Smn, the spinal muscular atrophy-determining gene product, modulates axon growth and localization of beta-actin mRNA in growth cones of motoneurons. J Cell Biol 163(4):801–812. doi:10.1083/jcb.200304128
Sanes JR, Lichtman JW (2001) Induction, assembly, maturation and maintenance of a postsynaptic apparatus. Nat Rev Neurosci 2(11):791–805
Sasaki Y, Welshhans K, Wen Z, Yao J, Xu M, Goshima Y, Zheng JQ, Bassell GJ (2010) Phosphorylation of zipcode binding protein 1 is required for brain-derived neurotrophic factor signaling of local beta-actin synthesis and growth cone turning. J Neurosci 30(28):9349–9358. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0499-10.2010
Smith WB, Aakalu G, Schuman EM (2001) Local protein synthesis in neurons. Curr Biol 11(22):R901–R903
Tiruchinapalli DM, Oleynikov Y, Kelic S, Shenoy SM, Hartley A, Stanton PK, Singer RH, Bassell GJ (2003) Activity-dependent trafficking and dynamic localization of zipcode binding protein 1 and beta-actin mRNA in dendrites and spines of hippocampal neurons. J Neurosci 23(8):3251–3261
Twiss JL, Fainzilber M (2009) Ribosomes in axons—scrounging from the neighbors? Trends Cell Biol 19(5):236–243. doi:10.1016/j.tcb.2009.02.007
Verkerk AJ, Pieretti M, Sutcliffe JS, Fu YH, Kuhl DP, Pizzuti A, Reiner O, Richards S, Victoria MF, Zhang FP et al (1991) Identification of a gene (FMR-1) containing a CGG repeat coincident with a breakpoint cluster region exhibiting length variation in fragile X syndrome. Cell 65(5):905–914
Wiese S, Herrmann T, Drepper C, Jablonka S, Funk N, Klausmeyer A, Rogers ML, Rush R, Sendtner M (2010) Isolation and enrichment of embryonic mouse motoneurons from the lumbar spinal cord of individual mouse embryos. Nat Protoc 5(1):31–38
Wu KY, Hengst U, Cox LJ, Macosko EZ, Jeromin A, Urquhart ER, Jaffrey SR (2005) Local translation of RhoA regulates growth cone collapse. Nature 436(7053):1020–1024
Yao J, Sasaki Y, Wen Z, Bassell GJ, Zheng JQ (2006) An essential role for beta-actin mRNA localization and translation in Ca2+-dependent growth cone guidance. Nat Neurosci 9(10):1265–1273. doi:10.1038/nn1773
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Regine Sendtner and Nicole Elflein for excellent technical assistance and Anna Maria Musti for helpful comments on the manuscript. Author contributions: R.B., M.S. designed research; R.R., R.B. performed research, S.H. supported cloning, N.F. did the statistical analysis for best-fit of FRAP curves, R.R. analyzed data, R.R., R.B., M.S. wrote the paper. This work was supported by grants from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft SFB581, project B1 and B24 and from the Hermann und Lilly Schilling Stiftung im Stifterverband der Deutschen Wissenschaft.
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rathod, R., Havlicek, S., Frank, N. et al. Laminin induced local axonal translation of β-actin mRNA is impaired in SMN-deficient motoneurons. Histochem Cell Biol 138, 737–748 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-012-0989-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-012-0989-1