Abstract
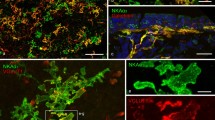
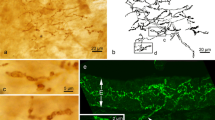
The laminar nerve endings are distributed in the laryngeal mucosa, and described as sensory receptors evoked by laryngeal pressure changes. The present study aimed to determine detailed morphological characteristics of the laryngeal laminar endings of the rat. Immunohistochemistry for Na+-K+-ATPase, α3 subunit, showed that laminar endings were distributed in the entire laryngeal surface of the epiglottis. The parent axons of the endings were thick in diameter, and they were branched and continued to the endings. In some cases, several endings from different parent axons fused into a large complex structure of 500 μm in width. The laminar endings were also immunoreactive for vesicular glutamate transporter 1 (vGLUT1) and vGLUT2, but not for P2X3 purinoceptor. Around the laminar endings, terminal Schwann cells with immunoreactivity for S-100 protein were closely associated with axon terminals. Use of scanning electron microscopy with alkaline maceration method showed that the terminal Schwann cells consisted of a rounded perinuclear region and lamellar cytoplasmic processes. Ultrastructurally, axon terminals with numerous mitochondria were partly covered with Schwann cell sheath, and some terminals intruded into the epithelial layer. Clear vesicles of 50 nm in diameter were also observed especially in small cytoplasmic processes of 400 nm to 1 μm in size. The results in the present study suggested that the laminar endings in epiglottic mucosa have morphological characteristics of slowly adapting mechanoreceptors and contribute to sensation of laryngeal pressure via mucosal tension.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andres KH, von Düring M (1973) Morphology of cutaneous receptors. In: Iggo A (ed) Handbook of sensory physiology, vol II, Somatosensory system. Springer, Berlin, pp 3–28
Arystarkhova E, Sweadner KJ (1996) Isoform-specific monoclonal antibodies to Na, K-ATPase α subunits: Evidence for a tissue-specific post-translational modification of the α3 subunit. J Biol Chem 271:23407–23417
Bewick GS, Reid B, Richardson C, Banks RW (2005) Autogenic modulation of mechanoreceptor excitability by glutamate release from synaptic-like vesicles: evidence from the rat muscle spindle primary sensory ending. J Physiol 562:381–394
Blanco G, Mercer RW (1998) Isozymes of the Na-K-ATPase: heterogeneity in structure, diversity in function. Am J Physiol 275:F633–F650
Blanco G, Sánchez G, Mercer RW (1995) Comparison of the enzymatic properties of the Na, K-ATPase α3β1 and α3β2 isozymes. Biochemistry 34:9897–9903
Brouns I, Pintelon I, De Proost I, Alewaters R, Timmermans J-P, Adriaensen D (2006) Neurochemical characterisation of sensory receptors in airway smooth muscle: comparison with pulmonary neuroepithelial bodies. Histochem Cell Biol 125:351–367
Brouns I, Oztay F, Pintelon I, De Proost I, Lembrechts R, Timmermans J-P, Adriaensen D (2009) Neurochemical pattern of the complex innervation of neuroepithelial bodies in mouse lungs. Histochem Cell Biol 131:55–74
Burnstock G (2009) Purinergic mechanosensory transduction and visceral pain. Mol Pain 5:69. doi:10.1186/1744-8069-5-69
Cahusac PMB, Mavulati SC (2009) Non-competitive metabotropic glutamate 1 receptor antagonists block activity of slowly adapting type 1 mechanoreceptor units in the rat sinus hair follicle. Neuroscience 163:933–941
Cahusac PMB, Senok SS, Hitchcock IS, Genever PG, Baumann KI (2005) Are unconventional NMDA receptors involved in slowly adapting type I mechanoreceptor responses? Neuroscience 133:763–773
Chiba T, Watanabe S, Shin T (1985) Ultrastructure of the glomerular corpuscular nerve endings in the subepithelium of human epiglottis. Arch Histol Jpn 48:213–221
Dobretsov M, Hastings SL, Stimers JR (1999) Non-uniform expression of α subunit isoforms of the Na+/K+ pump in rat dorsal root ganglia neurons. Brain Res 821:212–217
Dobretsov M, Hastings SL, Sims TJ, Stimers JR, Romanovsky D (2003) Stretch receptor-associated expression of α3 isoform of the Na+, K+-ATPase in rat peripheral nervous system. Neuroscience 116:1069–1080
Ewald P, Neuhuber WL, Raab M (2006) Vesicular glutamate transporter 1 immunoreactivity in extrinsic and intrinsic innervation of the rat esophagus. Histochem Cell Biol 125:377–395
Huang L-C, Greenwood D, Thorne PR, Housley GD (2005) Developmental regulation of neuron specific P2X3 receptor expression in the rat cochlea. J Comp Neurol 484:133–143
Hwang JC, St John WM, Bartlett D Jr (1984) Receptors responding to changes in upper airway pressure. Respir Physiol 55:355–366
Iggo A and Andres KH (1982) Morphology of cutaneous receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci 5:1–31
Inaga S, Katsumoto T, Tanaka K, Kameie T, Nakane H, Naguro T (2007) Platinum blue as an alternative to uranyl acetate for staining in transmission electron microscopy. Arch Histol Cytol 70:43–49
Jeftinija SD, Jeftinija KV (1998) ATP stimulates release of excitatory amino acids from cultured Schwann cells. Neuroscience 82:927–934
Lingrel JB (1992) Na,K-ATPase: isoform structure, function, and expression. J Bioenerg Biomembr 24:263–270
Liu GJ, Werry EL, Bennett MR (2005) Secretion of ATP from Schwann cells in response to uridine triphosphate. Eur J Neurosci 21:151–160
Lund JP, Sadeghi S, Athanassiadis T, Sales NC, Auclair F, Thivierge B, Arsenault I, Rompré P, Westberg K-G, Kolta A (2010) Assessment of the potential role of muscle spindle mechanoreceptor afferents in chronic muscle pain in the rat masseter muscle. PLoS One 5:e11131. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0011131
Maeda T, Sato O, Kobayashi S, Iwanaga T, Fujita T (1989) The ultrastructure of Ruffini endings in the periodontal ligament of rat incisors with special reference to the terminal Schwann cells (K-cells). Anat Rec 223:95–103
Maeda T, Ochi K, Nakakura-Ohshima K, Youn SH, Wakisaka S (1999) The Ruffini endings as the primary mechanoreceptor in the periodontal ligament: its morphology, cytochemical features, regeneration, and development. Crit Rev Oral Biol Med 10:307–327
Mathew OP, Farber JP (1983) Effect of upper airway negative pressure on respiratory timing. Respir Physiol 54:259–268
Mazzone SB, McGovern AE (2008) Immunohistochemical characterization of nodose cough receptor neurons projecting to the trachea of guinea pig. Cough 4:9. doi:10.1186/1745-9974-4-9
Melone M, Burette A, Weinberg RJ (2005) Light microscopic identification and immunocytochemical characterization of glutamatergic synapses in brain sections. J Comp Neurol 492:495–509
Munger BL and Ide C (1988) The structure and function of cutaneous sensory receptors. Arch Histol Cytol 51:1–34
Parekh A, Campbell AJM, Djouhri L, Fang X, McMullan S, Berry C, Acosta C, Lawson SN (2010) Immunostaining for the α3 isoform of the Na+/K+-ATPase is selective for functionally identified muscle spindle afferents in vivo. J Physiol 588:4131–4143
Peng L, Martin-Vasallo P, Sweadner KJ (1997) Isoforms of Na, K-ATPase α and β subunits in the rat cerebellum and in granule cell cultures. J Neurosci 17:3488–3502
Pintelon I, Brouns I, De Proost I, Van Meir F, Timmermans J-P, Adriaensen D (2007) Sensory receptors in the visceral pleura. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 36:541–551
Ploschko A (1897) Die Nervenendigungen und Gaglien der Respirationsorgane. Anat Anz 13:12–22
Raab M, Neuhuber WL (2004) Intraganglionic laminar endings and their relationships with nuronal and glial structures of myenteric ganglia in the esophagus of rat and mouse. Histochem Cell Biol 122:445–459
Rousse I, Robitaille R (2006) Calcium signaling in Schwann cells at synaptic and extra-synaptic sites: active glial modulation of neuronal activity. Glia 54:691–699
Ryan S, McNicholas WT, O’Regan RG, Nolan P (2001) Reflex respiratory response to changes in upper airway pressure in the anaesthetized rat. J Physiol 537:251–265
Sant’Ambrogio G, Mathew OP, Fisher JT, Sant’Ambrogio FB (1983) Laryngeal receptors responding to transmural pressure, airflow and local muscle activity. Respir Physiol 54:317–330
Sato O, Maeda T, Kobayashi S, Iwanaga T, Fujita T, Takahashi Y (1988) Innervation of periodontal ligament and dental pulp in the rat incisor: an immunohistochemical investigation of neurofilament protein and glia-specific S-100 protein. Cell Tissue Res 251:13–21
Schoultz TW, Swett JE (1974) Ultrastructural organization of the sensory fibers innervating the Golgi tendon organ. Anat Rec 179:147–162
Sekizawa S, Tsubone H (1991) The respiratory activity of the superior laryngeal nerve in the rat. Respir Physiol 86:335–368
Soiza-Reilly M, Commons KG (2011) Quantitative analysis of glutamatergic innervation of the mouse dorsal raphe nucleus using array tomography. J Comp Neurol 519:3802–3814
Song X, Gao X, Guo D, Yu Q, Guo W, He C, Burnstock G, Xiang Z (2011) Expression of P2X2 and P2X3 receptors in the rat carotid sinus, aortic arch, vena cava, and heart, as well as petrosal and nodose ganglia. Purin Signal. doi:10.1007/s11302-011-9249-4
Spencer PS, Schaumburg HH (1973) An ultrastructural study of the inner core of the Pacinian corpuscle. J Neurocytol 2:217–235
Stevens B, Fields RD (2000) Response of Schwann cells to action potentials in development. Science 287:2267–2271
Takahashi-Iwanaga H (2000) Three-dimensional microanatomy of longitudinal lanceolate endings in rat vibrissae. J Comp Neurol 426:259–269
Takahashi-Iwanaga H, Fujita T (1986) Application of an NaOH maceration method to a scanning electron microscopic observation of Ito cells in the rat liver. Arch Histol Jpn 49:349–357
Takahashi-Iwanaga H, Habara Y (2004) Oscillatory calcium responses mediated by P2Y2 purinergic receptors in terminal Schwann cells of longitudinal lanceolate endings isolated from rat vibrissae. J Comp Neurol 475:416–425
Takahashi-Iwanaga H, Maeda T, Abe K (1997) Scanning and transmission electron microscopy of Ruffini endings in the periodontal ligament of rat incisors. J Comp Neurol 389:177–184
Todd AJ, Hughes DI, Polgár E, Nagy GG, Mackie M, Ottersen OP, Maxwell DJ (2003) The expression of vesicular glutamate transporters VGLUT1 and VGLUT2 in neurochemically defined axonal populations in the rat spinal cord with emphasis on the dorsal horn. Eur J Neurosci 17:13–27
Tsubone H, Mathew OP, Sant’Ambrogio G (1987) Respiratory activity in the superior laryngeal nerve of the rabbit. Respir Physiol 69:195–207
van Lunteren E, van de Graaff WB, Parker DM, Mitra J, Haxhiu MA, Strohl KP, Cherniack NS (1984) Nasal and laryngeal reflex responses to negative upper airway pressure. J Appl Physiol 56:746–752
Vulchanova L, Riedl MS, Shuster SJ, Buell G, Surprenant A, North RA, Elde R (1997) Immunohistochemical study of the P2X2 and P2X3 receptor subunits in rat and monkey sensory neurons and their central terminals. Neuropharmacology 36:1229–1242
Wang ZJ, Neuhuber WL (2003) Intraganglionic laminar endings in the rat esophagus contain purinergic P2X2 and P2X3 receptor immunoreactivity. Anat Embryol 207:363–371
Wu S-X, Koshimizu Y, Feng Y-P, Okamoto K, Fujiyama F, Hioki H, Li Y-Q, Kaneko T, Mizuno N (2004) Vesicular glutamate transporter immunoreactivity in the central and peripheral endings of muscle-spindle afferents. Brain Res 1011:247–251
Xu GY and Huang LY (2004) Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II potentiates ATP responses by promoting trafficking of P2X receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:11868–11873
Yamamoto Y, Hayashi M, Atoji Y, Suzuki Y (1994) Vagal afferent nerve endings in the trachealis muscle of the dog. Arch Histol Cytol 57:473–480
Yamamoto Y, Hosono I, Atoji Y, Suzuki Y (1997) Morphological study of the vagal afferent nerve endings in the laryngeal mucosa of the dog. Ann Anat 179:65–73
Yamamoto Y, Atoji Y, Kuramoto H, Suzuki Y (1998) Calretinin-immunoreactive laminar nerve endings in the laryngeal mucosa of the rat. Cell Tissue Res 292:613–617
Yamamoto Y, Atoji Y, Suzuki Y (2000) Calbindin D28k-immunoreactive afferent nerve endings in the laryngeal mucosa. Anat Rec 259:237–247
Yamamoto Y, Atoji Y, Hobo S, Yoshihara T, Suzuki Y (2001) Morphology of the nerve endings in laryngeal mucosa of the horse. Equine Vet J 33:150–158
Yasaka T, Thiong SYX, Hughes DI, Riddell JS, Todd AJ (2010) Populations of inhibitory and excitatory interneurons in lamina II of the adult rat spinal dorsal horn revealed by a combined electrophysiological and anatomical approach. Pain 151:475–488
Yu J (2005) Airway mechanoreceptors. Resp Physiol Neurobiol 148:217–243
Yu J, Wang F, Zhang JW (2003) Structure of slowly adapting pulmonary stretch receptors in the lung periphery. J Appl Physiol 95:385–393
Zhang X, Bruce EN (1998) Response of breathing pattern to flow and pressure in the upper airway of rats. Respir Physiol 113:191–200
Acknowledgments
The authors thank Dr. Misuzu Yamaguchi-Yamada for valuable comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Soda, Y., Yamamoto, Y. Morphology and chemical characteristics of subepithelial laminar nerve endings in the rat epiglottic mucosa. Histochem Cell Biol 138, 25–39 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-012-0939-y
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-012-0939-y