Abstract
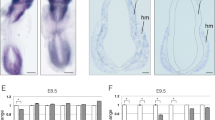
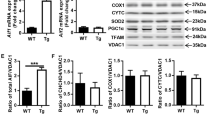
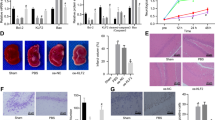
The aim of this study was to clarify the mechanism of apoptosis seen in the cortex of neural cell-specific hypoxia inducible factor-1α (HIF-1α)-deficient embryos. A previous study showed that the neural cells in the cortical area of the mutant embryos underwent apoptosis coincident with vascular regression. Through histological, immunohistochemical, and electron microscopic technique, two kinds of apoptotic cells were detected in the mutant embryonal cortex. Apoptotic cells of one type were clustered in small round structures, 10–20 μm in diameter, whereas the others, present in large numbers, were distributed in a group at the cortical plate located more to the outer side than the round structures. The histochemical and electron microscopic findings indicate that the former represented the appearance of macrophages, in which cellular fragments including vascular cells underwent oxidative stress-related, TNF receptor-mediated, caspase-2-induced apoptosis, while the latter showed c-Myc-related, caspase-3-activated apoptosis of the neural cells. These results suggest that two pathways of apoptosis are induced in neuronal and vascular cells of the cortex in the neural cell-specific HIF-1α-deficient mouse.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad M, Srinivasula SM, Wang L, Talanian RV, Litwack G, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES (1997) CRADD, a novel human apoptotic adaptor molecule for caspase and FasL/tumor necrosis factor receptor-interacting protein RIP. Cancer Res 57:615–619
Akakura N, Kobayashi M, Horiuchi I, Suzuki A, Wang J, Chen J, Niizaki H, Kawamura KI, Hosokawa M, Asaka M (2001) Constitutive expression of hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha renders pancreatic cancer cells resistant to apoptosis induced by hypoxia and nutrient deprivation. Cancer Res 61:6548–6554
Botchkina GI, Meistrell ME III, Botchkina IL, Tracey KJ (1997) Expression of TNF and TNF receptors (p55 and p75) in the rat brain after focal cerebral ischemia. Mol Med 3:765–781
Carmeliet P, Tessier-Lavigne M (2005) Common mechanisms of nerve and blood vessel wiring. Rev Nat 436:193–200
Carmeliet P, Dor Y, Herbert JM, Fukumura D, Brusselmans K, Dewerchin M, Neeman M, Bono F, Abramovitch R, Maxwell P, Koch CJ, Ratcliffe P, Moons L, Jain RK, Collen D, Keshert E (1998) Role of HIF-1 alpha in hypoxia-mediated apoptosis, cell proliferation and tumor angiogenesis. Nature 394:485–490
Dang CV, Resar LMS, Emison E, Kim S, Li Q, Prescott JE, Wonsey D, Zeller K (1999) Function of the c-Myc oncogenic transcription factor. Exp Cell Res 253:63–77
Duan H, Dixit VM (1997) RAIDD is a new 7death adaptor molecule. Nature 385:86–89
Evan GI, Wyllie AH, Gilbert CS, Littlewood TD, Land H, Brooks M, Waters CM, Penn LZ, Hancock DC (1992) Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell 69:119–128
Firth JD, Ebert BL, Ratcliffe PJ (1995) Hypoxic regulation of lactate dehydrogenase A. Interaction between hypoxia-inducible factor 1 and cAMP response elements. J Biol Chem 270:21021–21027
Fu Y-C, Chi C-S, Yin S-C, Hwang B, Chiu Y-T, Hsu S-L (2004) Norepinephrine induces apoptosis in neonatal rat cardiomyocytes through a reactive oxygen species-TNFα-caspase signaling pathway. Cardiovasc Res 62:558–567
Gergeron L, Perez GI, Macdonald G, Shi L, Sun Y, Jurisicova A, Varmuza S, Latham KE, Flaws JA, Salter JC, Hara H, Moskowitz MA, Li E, Greenberg A, Tilly JL, Yuan J (1998) Defects in regulation of apoptosis in caspase-2-deficient mice. Genes Dev 12:1304–1314
Gregersen R, Lambertsen K, Finsen B (2000) Microglia and macrophages are the major source of tumor necrosis factor in permanent middle cerebral artery occlusion in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:53–65
Guo Y, Srinivasula SM, Druilhe A, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Alnemri ES (2002) Caspase-2 induces apoptosis by releasing proapoptotic proteins from mitochondria. J Biol Chem 277:13430–13437
Hattori Y, Nishigori C, Tanaka T, Uchida K, Nikaido O, Osawa T, Hiai H, Imamura S, Toyokuni S (1997) 8-hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine is increased in epidermal cells of hairless mice after chronic ultraviolet B exposure. J Invest Dermatol 107:733–737
Helton R, Cui J, Scheel JR, Ellison JA, Ames C, Gibson C, Blouw B, Ouyang L, Dragatsis I, Zeitlin S, Johnson RS, Lipton SA, Barlow C (2005) Brain-specific knock-out of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α reduces rather than increases hypoxic–ischemic damage. J Neurosci 25:4099–4107
Iritani BM, Eisenman RN (1999) c-Myc enhances protein synthesis and cell size during B lymphocyte development. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96:13180–13185
Iyer NY, Kotch LE, Agami F, Leung SW, Laughner E, Wenger RH, Gassmann M, Georhart JD, Lawler AM, Yu AY, Semenza GL (1998) Cellular and developmental control of O2 homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1 alpha. Genes Dev 12:149–162
Kotch LE, Iyer NV, Laughner E, Semenza GL (1999) Defective vascularization of HIF-1α-null embryos is not associated with VEGF deficiency but with mesenchymal cell death. Dev Biol 209:254–267
Kuida K, Lippke JA, Ku G, Harding MW, Livingston DJ, Su MSS, Flavell RA (1995) Altered cytokine export and apoptosis in mice deficient in interleukin-1-beta converting enzyme. Science 267:2000–2003
Lassus P, Opitz-Araya X, Lazebnik Y (2002) Requirement for caspase-2 in stress-induced apoptosis before mitochondrial permeabilization. Science 297:1352–1354
Liu T, Clark RK, McDonnell PC, Young PR, White MS, Barone FC, Feuerstein GZ (1994) Tumor necrosis factor-α expression in ischemic neurons. Stroke 25:1481–1487
Liu T, Brouha B, Grossman D (2004) Rapid induction of mitochondrial events and caspase-independent apoptosis in survivin-targeted melanoma cells. Oncogene 23:39–48
Mancini M, Machamer CE, Roy S, Nicholson DW, Thornberry NA, Casciola-Rosen LA, Rosen A (2000) Caspase-2 is localized at the Golgi complex and cleaves golgin-160 during apoptosis. J Cell Biol 149:603–612
Martinet W, Knaapen MWM, De Mayer GRY, Herman AG, Kockx MM (2003) Overexpression of the anti-apoptotic caspase-2 short isoform in macrophage-derived foam cells of human atherosclerotic plaques. Am J Pathol 162:731–736
Minamino T, Yujiri T, Terada N, Taffet GE, Michael LH, Johnson GL, Schneider MD (2002) MEKK1 is essential for cardiac hypertrophy and dysfunction induced by Gq. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:3322–3327
Namura S, Zhu J, Fink K, Endres M, Srinivasan A, Tomaselli KJ, Yuan J, Moskowitz MA (1998) Activation and cleavage of caspase-3 in apoptosis induced by experimental cerebral ischemia. J Neurosci 18:3659–3668
Nilsson JA, Cleveland IL (2003) Myc pathways provoking cell suicide and cancer. Oncogene 22:9007–9021
Packham G, Cleveland IL (1995) c-Myc and apoptosis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1242:11–28
Paroni G, Henderson C, Schneider C, Brancolini C (2001) Caspase-2-induced apoptosis is dependent on caspase-9, but its processing during UV- or tumor necrosis factor-dependent cell death requires caspase-3. J Biol Chem 276:21907–21915
Qi Y, Gregory MA, Li Z, Brousal JP, West K, Hann SR (2004) p19ARF directly and differentially controls the functions of c-Myc independently of p53. Nature 431:712–717
Qin X, Zhang S, Nakatsuru Y, Oda H, Yamazaki Y, Nikaido O, Ishikawa T (1994) Detection of active UV-photoproduct repair in monkey skin in vivo by quantitative immunohistochemistry. Cancer Lett 83:291–298
Rosenfeld ME, Prichard L, Shiojiri N, Fausto N (2000) Prevention of hepatic apoptosis and embryonic lethality in RelA/TNFR-1 double knockout mice. Am J Pathol 156:997–1007
Ryan HE, Lo J, Johnson RS (1998) HIF-1 alpha is required for solid tumor formation and embryonic vascularization. EMBO J 17:3005–3015
Semenza GL (1998) Hypoxia-inducible factor 1: master regulator of O2 homeostasis. Curr Opin Genet Dev 8:588–594
Semenza GL (1999) Regulation of mammalian O2 homeostasis by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 15:551–578
Semenza GL, Roth PH, Fang H-M, Wang GL (1994) Transcriptional regulation of genes encoding glycolytic enzymes by hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem 269:23757–23763
Semenza GL, Jiang B-H, Leung SW, Passantino R, Concordet J-P, Maire P, Giallongo A (1996) Hypoxia response elements in the aldolase A, enolase 1, and lactate dehydrogenase A gene promoters contain essential binding sites for hypoxia-inducible factor 1. J Biol Chem 271:32529–32537
Serini G, Bussolino F (2004) Common cues in vascular and axon guidance. Physiology 19:348–354
Shim H, Chun YS, Lewis BC, Dang CV (1998) A unique glucose-dependent apoptotic pathway induced by c-Myc. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:1511–1516
Srinivasula SM, Datta P, Fan X-J, Fernandes-Alnemri T, Huang Z, Alnemri ES (2000) Molecular determinants of the caspase-promoting activity of smac/DIABLO and its role in the death receptor pathway. J Biol Chem 275:36152–36157
Suzuki T, Nakamoto T, Ogawa S, Seo S, Matsumura T, Tachibana K, Morimoto C, Hirai H (2002) MICAL, a novel CasL interacting molecule, associates with vimentin. J Biol Chem 277:14933–14941
Tomita S, Ueno M, Sakamoto M, Kitahama Y, Ueki M, Maekawa N, Sakamoto H, Gassmann M, Kageyama R, Ueda N, Gonzalez FJ, Takahama Y (2003) Defective brain development in mice lacking the Hif-1α gene in neural cells. Mol Cell Biol 23:6739–6749
Troy CM, Salvesen GS (2002) Caspases on the brain. J Neurosci Res 69:145–150
Troy CM, Rabacchi SA, Hohl JB, Angelastro JM, Greene LA, Shelanski ML (2001) Death in the balance: alternative participation of the caspase-2 and -9 pathways in neuronal death induced by nerve growth factor deprivation. J Neurosci 21:5007–5016
Tufro A, Norwood VF, Carey RM, Gomez RA (1999) Vascular endothelial growth factor induces nephrogenesis and vasculogenesis. J Am Soc Nephrol 10:2125–2134
Uno H, Matsuyama T, Akita H, Nishimura H, Sugita M (1997) Induction of tumor necrosis factor-α in the mouse hippocampus following transient forebrain ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17:491–499
Vielhauer V, Stavrakis G, Mayadas TN (2005) Renal cell-expressed TNF receptor 2, not receptor 1, is essential for the development of glomerulonephritis. J Clin Invest 115:1199–1209
Wang S, Miura M, Jung Y-K, Zhu H, Yuan J (1998) Murine caspase-11, an ICE-interacting protease, is essential for the activation of ICE. Cell 92:501–509
Yu EZ, Li Y-Y, Liu X-H, Kagan E, MaCarron RM (2004) Antiapoptotic action of hypoxia-inducible factor-1α in human endothelial cells. Lab Invest 84:553–561
Zheng TS, Hunot S, Kuida K, Momoi T, Srinivasan A, Nicholson DW, Lazebnik Y, Flavell RA (2000) Deficiency in caspase-9 or caspase-3 induces compensatory caspase activation. Nat Med 6:1241–1247
Zhu B, Luo L, Chen Y, Paty DW, Cynader MS (2002) Intrathecal Fas ligand infusion strengthens immunoprivilege of central nervous system and suppresses experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 169:1561–1569
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to express their appreciation to Dr. S. Adachi, Kyoto University, for critical comments, Dr. T. Nakagawa, Mr. H. Miyanaka, Ms. C. Ishikawa, and Ms. S. Fuke, Kagawa University, for technical assistance and Ms. Y. Fujiwara and Ms. A. Kimura, for editorial assistance. This research was supported by a grant-in-aid for encouragement of young scientists (15790171) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan. We have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ueno, M., Tomita, S., Ueki, M. et al. Two pathways of apoptosis are simultaneously induced in the embryonal brains of neural cell-specific HIF-1α-deficient mice. Histochem Cell Biol 125, 535–544 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-005-0101-1
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-005-0101-1