Abstract
Background
Given the increasing popularity of optical coherence tomography in the diagnosis of glaucoma, we aimed to assess agreement between StratusOCT and stereophotography in measuring the vertical cup-to-disc ratio (VCDR) and examine whether it can be improved by changing the StratusOCT cup-offset.
Methods
In group 1 (79 eyes), VCDR measurements obtained by StratusOCT (using the default cup-offset of 150 μm above the retinal pigment epithelium) and stereophotography were compared. For each eye, the cup-offset was moved upward or downward until the difference disappeared and an adjusted cup-offset was identified. In group 2 (41 eyes), the stereophotography VCDR was compared to the StratusOCT value obtained by using the mean adjusted cup-offset. StratusOCT was used to classify optic disc cups as shallow or deep.
Results
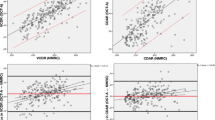
In group 1, StratusOCT overestimated VCDR in optic discs with deep cups and underestimated it in those with shallow cups (p < 0.0001). Mean adjusted cup-offsets were 72.8 ± 92 μm and 191.6 ± 70 μm for eyes with deep and shallow cups. The 95% limits of agreement (LOA) ranged from −0.21 to 0.17. In group 2, the adjusted cup-offsets enabled us to eliminate the statistical differences in VCDR measurements and improve the 95% LOA (from −0.13 to 0.14).
Conclusion
Adjusting the StratusOCT cup-offset according to the cup depth improves agreement between StratusOCT and stereophotography in measuring the VCDR.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schuman JS, Wollstein G, Farra T, Hertzmark E, Aydin A, Fujimoto JG, Paunescu LA (2003) Comparison of optic nerve head measurements obtained by optical coherence tomography and confocal laser ophthalmoscopy. Am J Ophthalmol 135:504–512, doi:10.1016/S0002-9394(02)02093-7
Iliev ME, Meyenberg A, Garweg JG (2006) Morphometric assessment of normal, suspect and glaucomatous optic discs with StratusOCT and HRTII. Eye 20:1288–1299, doi:10.1038/sj.eye.6702101
Kamppeter BA, Schubert KV, Budde WM, Degenring RF, Jonas JB (2006) Optical coherence of the optic nerve head: interindividual reproducibility. J Glaucoma 15:248–254, doi:10.1097/01.ijg.0000212205.02771.b7
Huang ML, Chen HY, Lin JC (2007) Rule extraction for glaucoma detection with summary data from StratusOCT. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48:244–250, doi:10.1167/iovs.06-0320
Manassakorn A, Nouri-Mahdavi K, Caprioli J (2006) Comparison of retinal nerve fiber layer thickness and optic disk algorithms with optical coherence tomography to detect glaucoma. Am J Ophthalmol 141:105–115, doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2005.08.023
Naithani P, Sihota R, Sony P, Dada T, Gupta V, Kondal D, Pandey RM (2007) Evaluation of optical coherence tomography and Heidelberg retinal tomography parameters in detecting early and moderate glaucoma. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 48:3138–3145, doi:10.1167/iovs.06-1407
Medeiros FA, Zangwill LM, Bowd C, Vessani RM, Susanna R, Weinreb RN (2005) Evaluation of retinal nerve fiber layer, optic nerve head, and macular thickness measurements for glaucoma detection using optical coherence tomography. Am J Ophthalmol 139:44–55, doi:10.1016/j.ajo.2004.08.069
Arthur SN, Aldridge AJ, De León-Ortega J, McGwin G, Xie A, Girkin CA (2006) Agreement in assessing cup-to-disc ratio measurement among stereoscopic optic nerve head photographs, HRT II, and Stratus OCT. J Glaucoma 15:183–189, doi:10.1097/01.ijg.0000212216.19804.ee
Bland JM, Altman DG (1986) Statistical methods for assessing agreement between two methods of clinical measurement. Lancet 1(8476):307–310
Altman DG, Bland JM (1983) Measurement in medicine: the analysis of method comparison studies. Statistician 32:307–317, doi:10.2307/2987937
Leung CK, Chan W, Hui Y, Yung WH, Woo J, Tsang MK, Tse KK (2005) Analysis of retinal nerve fiber layer and optic nerve head in glaucoma with different reference plane offsets, using optical coherence tomography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 46:891–899, doi:10.1167/iovs.04-1107
Ramakrishnan R, Kader MA, Budde WM (2005) Optic disc morphometry with optical coherence tomography: Comparison with planimetry of fundus photographs and influence of parapapillary atrophy and pigmentary conus. Indian J Ophthalmol 53:187–191
Jayasundera T, Danesh-Meyer HV, Donaldson M, Gamble G (2005) Agreement between stereoscopic photographs, clinical assessment, Heidelberg retina tomography and digital stereoscopic optic disc camera in estimating vertical cup:disc ratio. Clin Exp Ophthalmol 33:259–263, doi:10.1111/j.1442-9071.2005.01000.x
Sung VC, Bhan A, Vernon SA (2002) Agreement in assessing optic disc camera (Discam) and Heidelberg retina tomography. Br J Ophthalmol 86:196–202, doi:10.1136/bjo.86.2.196
Correnti AJ, Wollstein G, Price LL, Schuman JS (2003) Comparison of optic nerve head assessment with a digital stereoscopic camera (Discam), scanning laser ophthalmoloscopy, and stereophotography. Ophthalmology 110:1499–1505, doi:10.1016/S0161-6420(03)00496-2
Sheen NJ, Morgan JE, Poulsen JL, North RV (2004) Digital stereoscopic analysis of the optic disc. Ophthalmology 111:1873–1879
Ikram MK, Borger PH, Assink JJ, Jonas JB, Hofman A, de Jong PT (2002) Comparing ophthalmoscopy, slide viewing and semiautomated systems in optic disc morphometry. Ophthalmology 109:486–493, doi:10.1016/S0161-6420(01)00983-6
Funding support
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Savini, G., Espana, E.M., Acosta, A.C. et al. Agreement between optical coherence tomography and digital stereophotography in vertical cup-to-disc ratio measurement. Graefes Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 247, 377–383 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-008-0968-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00417-008-0968-3