Abstract
Background
For ischemic stroke patients with concomitant unruptured aneurysm, intravenous thrombolysis therapy (IVT) remains a disputable decision. We hence performed a meta-analysis to identify the related brain hemorrhage rate of unruptured aneurysms and the risk ratio for their rupture comparing to stroke patients who do not have aneurysms.
Methods
A comprehensive search was conducted to identify the studies from the online database from 2000 to September 1st, 2022. Cohort studies were included and assessed by Newcastle–Ottawa Scale (NOS) for quality. The research procedures were subjected to the Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses guidelines. Fixed-effects model was used based on the heterogeneity tests.
Results
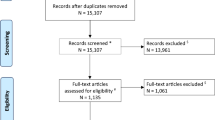
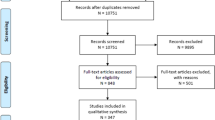
In 10 eligible studies, 7238 ischemic stroke patients were screened, a total of 302 patients with 348 aneurysms were included. 10 studies were eligible for ICH rate analysis, 8 for SAH rate analysis and 7 for risk ratio of stroke patients with unruptured aneurysms. The pooled any ICH rate was 16% (95% CI 11–21%), symptomatic ICH rate was 4% (95% CI 1–7%, I2 = 0.00%, p = 0.90), and 0% (95% CI 0–1%) for aneurysm-related ICH. Subarachnoid hemorrhage was as low as 2% (95% CI 0–5%), while 0% (95% CI 0–2%) directly related to the aneurysm rupture. The risk ratio of ICH in stroke patients with aneurysms was 1.18 (95% CI 0.79–1.77). Additionally, the hemorrhage rate difference was not evident between saccular and fusiform aneurysms due to a lack of details.
Conclusions
IVT is unlikely to induce hemorrhage of pre-existing unruptured aneurysms in stroke patients. Further randomized control studies are warranted to validate these conclusions.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of supporting data
The clinical data used in this study can be provided via the corresponding authors upon reasonable request.
References
Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T et al (2019) Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: 2019 update to the 2018 guidelines for the early management of acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 50(12):e344–e418. https://doi.org/10.1161/str.0000000000000211
Powers WJ, Rabinstein AA, Ackerson T et al (2018) Guidelines for the early management of patients with acute ischemic stroke: a guideline for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 49(3):e46–e110. https://doi.org/10.1161/str.0000000000000158
Virta JJ, Strbian D, Putaala J, Korja M (2021) Risk of aneurysm rupture after thrombolysis in patients with acute ischemic stroke and unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Neurology 97(18):e1790–e1798. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000012771
Ding J, Han J, Jing Z, Jiang Y (2016) Is it dangerous to treat acute ischemic stroke by thrombolytic therapy in patients with comorbid intracranial aneurysms? Am J Emerg Med 34(3):636–642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajem.2015.12.025
Chen F, Yan S, Jin X, Lin C, Cao J (2014) Post-thrombolysis hemorrhage risk of unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Eur Neurol 73(1–2):37–43. https://doi.org/10.1159/000366200
Chen H, Zeng X, Gao C, Cheng Y, Ren S, Zhao Q (2014) The safety among acute ischemic stroke patients with asymptomatic intracranial aneurysm after the administration of intravenous thrombolysis. Chin J Neurol 47(9):643–647. https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.issn.1006-7876.2014.09.009
Bernardo F, Nannoni S, Strambo D, Bartolini B, Michel P, Sirimarco G (2019) Intravenous thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke due to intracranial artery dissection: a single-center case series and a review of literature. J Thromb Thrombolysis 48(4):679–684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11239-019-01918-6
Chiu WT, Hong CT, Chi NF, Hu CJ, Hu HH, Chan L (2017) The risk of intravenous thrombolysis-induced intracranial hemorrhage in Taiwanese patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysm. PLoS ONE 12(6):e0180021. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0180021
Mowla A, Singh K, Mehla S, et al. Is acute reperfusion therapy safe in acute ischemic stroke patients who harbor unruptured intracranial aneurysm? Stroke. 2015;46(SUPPL. 1)American Heart Association/American Stroke Association 2015 International Stroke Conference and State-of-the-Science Stroke Nursing Symposium. Nashville, TN United States. (var.pagings)
Zhang C-H, Li C, Wang Y-X et al (2015) Efficacy and safety of intravenous thrombolysis for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke patients with saccular intracranial aneurysms of a parts per thousand currency sign3 mm. Cell Biochem Biophys 72(3):889–893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0557-0
Zhang PL, Wang YX, Chen Y et al (2015) Analysis on the correlation factors for hemorrhagic transformation after intravenous thrombolytic therapy. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 19(6):1001–1008
Goyal N, Tsivgoulis G, Zand R et al (2015) Systemic thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms. Neurology 85(17):1452–1458. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000002068
Mittal MK, Seet RC, Zhang Y, Brown RD Jr, Rabinstein AA (2013) Safety of intravenous thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke patients with saccular intracranial aneurysms. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis 22(5):639–643. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2012.01.009
Sheth KN, Shah N, Morovati T, Hermann LD, Cronin CA (2012) Intravenous rt-PA is not associated with increased risk of hemorrhage in patients with intracranial aneurysms. Neurocrit Care 17(2):199–203. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12028-012-9734-9
Kim JT, Park MS, Yoon W, Cho KH (2012) Detection and significance of incidental unruptured cerebral aneurysms in patients undergoing intravenous thrombolysis for acute ischemic stroke. J Neuroimaging 22(2):197–200. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1552-6569.2010.00560.x
Fugate JE, Rabinstein AA (2015) Absolute and relative contraindications to IV rt-PA for acute ischemic stroke. Neurohospitalist. 5(3):110–121. https://doi.org/10.1177/1941874415578532
Sheth KN, Shah N, Morovati T, Hermann LD, Cronin CA. Intravenous RT-PA is not associated with increased risk of symptomatic hemorrhage in patients with intracranial aneurysms. Stroke. 2012;43(2 Meeting Abstracts)2012 International Stroke Conference and Nursing Symposium. New Orleans, LA United States. (var.pagings)
Cumpston M, Li T, Page MJ, et al. Updated guidance for trusted systematic reviews: a new edition of the Cochrane Handbook for Systematic Reviews of Interventions. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2019;10:000142. https://doi.org/10.1002/14651858.Ed000142
Egger M, Davey Smith G, Schneider M, Minder C (1997) Bias in meta-analysis detected by a simple, graphical test. BMJ (Clinical research ed) 315(7109):629–634. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmj.315.7109.629
Duval S, Tweedie R (2000) Trim and fill: a simple funnel-plot-based method of testing and adjusting for publication bias in meta-analysis. Biometrics 56(2):455–463. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.0006-341x.2000.00455.x
Rücker G, Schwarzer G, Carpenter JR, Binder H, Schumacher M (2011) Treatment-effect estimates adjusted for small-study effects via a limit meta-analysis. Biostatistics (Oxford, England) 12(1):122–142. https://doi.org/10.1093/biostatistics/kxq046
Virta JJ, Strbian D, Putaala J, Kaprio J, Korja M (2022) Characteristics and outcomes of thrombolysis-treated stroke patients with and without saccular intracranial aneurysms. Stroke 53(12):3616–3621. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.122.040151
Mowla A, Singh K, Mehla S et al (2015) Is acute reperfusion therapy safe in acute ischemic stroke patients who harbor unruptured intracranial aneurysm? Int J Stroke 10(A100):113–118. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijs.12616
Zhang CH, Li C, Wang YX et al (2015) Efficacy and safety of intravenous thrombolysis for the treatment of acute ischemic stroke patients with saccular intracranial aneurysms of <=3 mm. Cell Biochem Biophys 72(3):889–893. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12013-015-0557-0
Edwards NJ, Kamel H, Josephson SA (2012) The safety of intravenous thrombolysis for ischemic stroke in patients with pre-existing cerebral aneurysms a case series and review of the literature. Stroke 43(2):412–416. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.111.634147
(2000) Effect of intravenous recombinant tissue plasminogen activator on ischemic stroke lesion size measured by computed tomography. NINDS; The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Stroke 31(12):2912–9. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.31.12.2912
(1997) A systems approach to immediate evaluation and management of hyperacute stroke. Experience at eight centers and implications for community practice and patient care. The National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke (NINDS) rt-PA Stroke Study Group. Stroke 28(8):1530–40. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.str.28.8.1530
Hilkens NA, Algra A, Diener HC et al (2021) Balancing benefits and risks of long-term antiplatelet therapy in noncardioembolic transient ischemic attack or stroke. Stroke 52(10):3258–3265. https://doi.org/10.1161/strokeaha.120.031755
van Gijn J, Kerr RS, Rinkel GJE (2007) Subarachnoid haemorrhage. Lancet 369(9558):306–318. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0140-6736(07)60153-6
Beneš V 3rd, Jurák L, Jedlička J, Dienelt J, Suchomel P (2019) Fatal intracranial aneurysm rupture after thrombolytic treatment for ischemic stroke: a case report and literature review. Acta Neurochir (Wien) 161(7):1337–1341. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-019-03931-3
Kim Y, Choi CH, Lee TH et al (2017) Endovascular stenting for symptomatic carotid dissection with hemodynamic insufficiency. World Neurosurg 102:598–607. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2017.03.086
Glenn J, Strecker-McGraw M, McGraw I, Jabbar K, James NA, Stone CK (2017) Rupture of an occult intracranial mycotic aneurysm after intravenous thrombolysis with recombinant tissue plasminogen activator for acute ischemic stroke. J Emerg Med 53(5):717–721. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jemermed.2017.08.032
Haji F, van Adel B, Avery M, Megyesi J, Young GB (2014) Intracranial aneurysm rupture following intravenous thrombolysis for stroke. Can J Neurol Sci 41(1):95–98. https://doi.org/10.1017/s0317167100016358
Rammos SK, Neils DM, Fraser K, Klopfenstein JD (2012) Anterior communicating artery aneurysm rupture after intravenous thrombolysis for acute middle cerebral artery thromboembolism: case report. Neurosurgery 70(6):E1603–E1607. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e31822e1097
Shi H, Wee CK, John S (2019) Post-thrombolysis rupture of small lenticulostriate aneurysms: a report of 2 consecutive cases. J Clin Neurosci 60:148–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2018.10.087
Cai X, Han S, Feske SK, Chou SH (2013) Pearls and oy-sters: small but consequential: intracerebral hemorrhage caused by lenticulostriate artery aneurysm. Neurology 80(9):e89-91. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0b013e31828406a2
Heck O, Anxionnat R, Bracard S (2013) Pearls & oy-sters: small but consequential: intracerebral hemorrhage caused by lenticulostriate artery aneurysm. Neurology 81(21):1881. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000435757.50996.ae
Lama S, Dolati P, Sutherland GR (2014) Controversy in the management of lenticulostriate artery dissecting aneurysm: a case report and review of the literature. World Neurosurg 81(2):441.e1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2012.12.006
Figueroa-Sánchez JA, Caro-Osorio E, Martínez-Rodríguez HR, Herrera-Castro JC (2020) Diagnostic and therapeutic challenge in intracerebral hemorrhage due to aneurysm of distal lenticulostriate artery. Cir Cir 88(3):366–369. https://doi.org/10.24875/ciru.19001026. (Reto diagnóstico y terapéutico en la hemorragia intracerebral por aneurisma de la arteria lenticuloestriada distal)
Yaghi S, Willey JZ, Cucchiara B et al (2017) Treatment and outcome of hemorrhagic transformation after intravenous alteplase in acute ischemic stroke: a scientific statement for healthcare professionals from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association. Stroke 48(12):e343–e361. https://doi.org/10.1161/str.0000000000000152
Kim H, Kang D, Kwon SU, Kim JS, Jeon S-B (2017) Aneurysmal subarachnoid hemorrhage following intravenous thrombolysis in acute ischemic stroke. J Neurocrit Care 10(2):107–111. https://doi.org/10.18700/jnc.170015
Acknowledgements
None.
Funding
Dr. Dingke Wen is supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 82201450). The sponsors had no role in the design or conduct of this research. Dr. Lu Ma received financial support from the National Key R&D Program of China (numbers 2018YFA 0108604 and 2018YFA0108603) and the Clinical Incubation Program of West China Hospital, SCU (2018HXFU008).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Consent for publication
All authors have agreed to publish this article and this article in part and whole has not been considered for publication elsewhere.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary figure 1.
Publications bias assessment of studies reporting SAH data. (TIF 4441 kb)
Supplementary figure 2.
Publications bias assessment of studies reporting ICH cohort data. (TIF 4441 kb)
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wen, D., Chen, Y., Zhu, W. et al. Cerebral hemorrhage after thrombolysis in stroke patients with unruptured intracranial aneurysms: a systemic review and meta-analysis. J Neurol 270, 1931–1944 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-022-11533-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-022-11533-w