Abstract
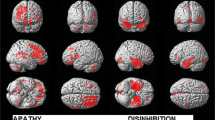
Apathy is a neurocognitive syndrome of reduced goal-directed behaviour and is an important cause of disability in neurodegenerative disorders. Frontal–subcortical dysfunction is thought to be important in apathy, but the contribution of individual brain regions to different aspects of the apathy syndrome is poorly understood. We aimed to test the hypotheses that apathy in two distinct neurodegenerative disorders would be associated with frontal lobe atrophy and that reduced initiative and emotional blunting would be associated with distinct patterns of atrophy in functionally relevant brain areas. Seventeen patients with progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) and 17 patients with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) underwent structural MRI scanning at 3 T to provide data for voxel based morphometric analysis. Apathy was defined using Robert’s 2009 diagnostic criteria and specific symptoms were assessed with the Apathy Inventory. Patients with and without apathy were matched for important demographic and clinical characteristics. Apathy was associated with atrophy of the ventromedial orbitofrontal cortex and left insula in both AD and PSP. Reduced initiative was specifically associated with atrophy of the anterior cingulate and ventrolateral orbitofrontal cortex whilst emotional blunting was specifically associated with atrophy of the left insula. These findings provide further support for the role of medial frontal regions and insular cortex in apathy and suggest that behavioural and emotional aspects of the apathy syndrome may have distinct neuroanatomical bases.



Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Brown RG, Pluck G (2000) Negative symptoms: the ‘pathology’ of motivation and goal-directed behaviour. Trends Neurosci 23:412–417
Starkstein SE, Leentjens AF (2008) The nosological position of apathy in clinical practice. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 79:1088–1092
Davis JD, Tremont G (2007) Impact of frontal systems behavioral functioning in dementia on caregiver burden. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 19:43–49
Zawacki TM, Grace J, Paul R, Moser DJ, Ott BR, Gordon N, Cohen RA (2002) Behavioral problems as predictors of functional abilities of vascular dementia patients. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 14:296–302
Chase TN (2011) Apathy in neuropsychiatric disease: diagnosis, pathophysiology, and treatment. Neurotox Res 19:266–278
Marin RS (1991) Apathy: a neuropsychiatric syndrome. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 3:243–254
Lau HC, Rogers RD, Ramnani N, Passingham RE (2004) Willed action and attention to the selection of action. Neuroimage 21:1407–1415
Murphy FC, Nimmo-Smith I, Lawrence AD (2003) Functional neuroanatomy of emotions: a meta-analysis. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 3:207–233
Passingham RE, Bengtsson SL, Lau HC (2010) Medial frontal cortex: from self-generated action to reflection on one’s own performance. Trends Cogn Sci 14:16–21
Fusar-Poli P, Placentino A, Carletti F, Landi P, Allen P, Surguladze S, Benedetti F, Abbamonte M, Gasparotti R, Barale F, Perez J, McGuire P, Politi P (2009) Functional atlas of emotional faces processing: a voxel-based meta-analysis of 105 functional magnetic resonance imaging studies. J Psychiatry Neurosci 34:418–432
Cummings JL (1993) Frontal–subcortical circuits and human behavior. Arch Neurol 50:873–880
Apostolova LG, Akopyan GG, Partiali N, Steiner CA, Dutton RA, Hayashi KM, Dinov ID, Toga AW, Cummings JL, Thompson PM (2007) Structural correlates of apathy in Alzheimer’s disease. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 24:91–97
Lavretsky H, Ballmaier M, Pham D, Toga A, Kumar A (2007) Neuroanatomical characteristics of geriatric apathy and depression: a magnetic resonance imaging study. Am J Geriatr Psychiatry 15:386–394
Rosen HJ, Allison SC, Schauer GF, Gorno-Tempini ML, Weiner MW, Miller BL (2005) Neuroanatomical correlates of behavioural disorders in dementia. Brain 128:2612–2625
Bruen PD, McGeown WJ, Shanks MF, Venneri A (2008) Neuroanatomical correlates of neuropsychiatric symptoms in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain 131:2455–2463
Reijnders JS, Scholtissen B, Weber WE, Aalten P, Verhey FR, Leentjens AF (2010) Neuroanatomical correlates of apathy in Parkinson’s disease: a magnetic resonance imaging study using voxel-based morphometry. Mov Disord 25:2318–2325
Massimo L, Powers C, Moore P, Vesely L, Avants B, Gee J, Libon DJ, Grossman M (2009) Neuroanatomy of apathy and disinhibition in frontotemporal lobar degeneration. Dement Geriatr Cogn Disord 27:96–104
Zamboni G, Huey ED, Krueger F, Nichelli PF, Grafman J (2008) Apathy and disinhibition in frontotemporal dementia: insights into their neural correlates. Neurology 71:736–742
Tunnard C, Whitehead D, Hurt C, Wahlund LO, Mecocci P, Tsolaki M, Vellas B, Spenger C, Kloszewska I, Soininen H, Lovestone S, Simmons A (2011) Apathy and cortical atrophy in Alzheimer’s disease. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 26:741–748
Litvan I, Bhatia KP, Burn DJ, Goetz CG, Lang AE, McKeith I, Quinn N, Sethi KD, Shults C, Wenning GK (2003) Movement Disorders Society Scientific Issues Committee report: sIC Task Force appraisal of clinical diagnostic criteria for Parkinsonian disorders. Mov Disord 18:467–486
Litvan I, Agid Y, Jankovic J, Goetz C, Brandel JP, Lai EC, Wenning G, D’Olhaberriague L, Verny M, Chaudhuri KR, McKee A, Jellinger K, Bartko JJ, Mangone CA, Pearce RK (1996) Accuracy of clinical criteria for the diagnosis of progressive supranuclear palsy (Steele-Richardson-Olszewski syndrome). Neurology 46:922–930
Litvan I (2001) Diagnosis and management of progressive supranuclear palsy. Semin Neurol 21:41–48
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Stadlan EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA Work Group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer’s disease. Neurology 34:939–944
Molloy DW, Standish TI (1997) A guide to the standardized Mini-Mental State Examination. Int Psychogeriatr 9(Suppl 1):87–94
van Marwijk HW, Wallace P, de Bock GH, Hermans J, Kaptein AA, Mulder JD (1995) Evaluation of the feasibility, reliability and diagnostic value of shortened versions of the geriatric depression scale. Br J Gen Pract 45:195–199
Martinez-Martin P, Gil-Nagel A, Gracia LM, Gomez JB, Martinez-Sarries J, Bermejo F (1994) Unified Parkinson’s Disease Rating Scale characteristics and structure. The cooperative multicentric group. Mov Disord 9:76–83
Leentjens AF, Dujardin K, Marsh L, Martinez-Martin P, Richard IH, Starkstein SE, Weintraub D, Sampaio C, Poewe W, Rascol O, Stebbins GT, Goetz CG (2008) Apathy and anhedonia rating scales in Parkinson’s disease: critique and recommendations. Mov Disord 23:2004–2014
Schrag A (2011) Apathy and depression scales in Parkinson’s disease: are they good enough? J Neurol Sci 310:216–219
Robert P, Onyike CU, Leentjens AF, Dujardin K, Aalten P, Starkstein S, Verhey FR, Yessavage J, Clement JP, Drapier D, Bayle F, Benoit M, Boyer P, Lorca PM, Thibaut F, Gauthier S, Grossberg G, Vellas B, Byrne J (2009) Proposed diagnostic criteria for apathy in Alzheimer’s disease and other neuropsychiatric disorders. Eur Psychiatry 24:98–104
Drijgers RL, Dujardin K, Reijnders JS, Defebvre L, Leentjens AF (2010) Validation of diagnostic criteria for apathy in Parkinson’s disease. Parkinsonism Relat Disord 16:656–660
Marin RS, Biedrzycki RC, Firinciogullari S (1991) Reliability and validity of the Apathy Evaluation Scale. Psychiatry Res 38:143–162
Cummings JL, Mega M, Gray K, Rosenberg-Thompson S, Carusi DA, Gornbein J (1994) The Neuropsychiatric Inventory: comprehensive assessment of psychopathology in dementia. Neurology 44:2308–2314
Robert PH, Clairet S, Benoit M, Koutaich J, Bertogliati C, Tible O, Caci H, Borg M, Brocker P, Bedoucha P (2002) The Apathy Inventory: assessment of apathy and awareness in Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease and mild cognitive impairment. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 17:1099–1105
Ashburner J, Friston KJ (2005) Unified segmentation. Neuroimage 26:839–851
Jones DK, Symms MR, Cercignani M, Howard RJ (2005) The effect of filter size on VBM analyses of DT-MRI data. Neuroimage 26:546–554
Bullmore ET, Suckling J, Overmeyer S, Rabe-Hesketh S, Taylor E, Brammer MJ (1999) Global, voxel, and cluster tests, by theory and permutation, for a difference between two groups of structural MR images of the brain. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 18:32–42
Lancaster JL, Woldorff MG, Parsons LM, Liotti M, Freitas CS, Rainey L, Kochunov PV, Nickerson D, Mikiten SA, Fox PT (2000) Automated Talairach atlas labels for functional brain mapping. Hum Brain Mapp 10:120–131
Jouvent E, Reyes S, Mangin JF, Roca P, Perrot M, Thyreau B, Herve D, Dichgans M, Chabriat H (2011) Apathy is related to cortex morphology in CADASIL. A sulcal-based morphometry study. Neurology 76:1472–1477
Jenkins IH, Jahanshahi M, Jueptner M, Passingham RE, Brooks DJ (2000) Self-initiated versus externally triggered movements. II. The effect of movement predictability on regional cerebral blood flow. Brain 123 (Pt 6):1216–1228
Robert G, Le JF, Lozachmeur C, Drapier S, Dondaine T, Peron J, Travers D, Sauleau P, Millet B, Verin M, Drapier D (2012) Apathy in patients with Parkinson disease without dementia or depression: a PET study. Neurology 79:1155–1160
Brenneis C, Seppi K, Schocke M, Benke T, Wenning GK, Poewe W (2004) Voxel based morphometry reveals a distinct pattern of frontal atrophy in progressive supranuclear palsy. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 75:246–249
Cordato NJ, Duggins AJ, Halliday GM, Morris JG, Pantelis C (2005) Clinical deficits correlate with regional cerebral atrophy in progressive supranuclear palsy. Brain 128:1259–1266
Schofield EC, Hodges JR, Macdonald V, Cordato NJ, Kril JJ, Halliday GM (2011) Cortical atrophy differentiates Richardson’s syndrome from the parkinsonian form of progressive supranuclear palsy. Mov Disord 26:256–263
Brooks JC, Tracey I (2007) The insula: a multidimensional integration site for pain. Pain 128:1–2
Ihme K, Dannlowski U, Lichev V, Stuhrmann A, Grotegerd D, Rosenberg N, Kugel H, Heindel W, Arolt V, Kersting A, Suslow T (2013) Alexithymia is related to differences in gray matter volume: a voxel-based morphometry study. Brain Res 1491:60–67
Craig AD (2002) How do you feel? Interoception: the sense of the physiological condition of the body. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:655–666
Bechara A, Damasio H, Damasio AR (2000) Emotion, decision making and the orbitofrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 10:295–307
Aalten P, Van Valen E, Clare L, Kenny G, Verhey F (2005) Awareness in dementia: a review of clinical correlates. Aging Ment Health 9:414–422
Eslinger PJ, Dennis K, Moore P, Antani S, Hauck R, Grossman M (2005) Metacognitive deficits in frontotemporal dementia. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 76:1630–1635
Acknowledgments
The study was supported by the Medical Research Council through a Clinical Research Training Fellowship (G0500443) (BS). Author RB receives salary support from the National Institute for Health Research (NIHR) Mental Health Biomedical Research Centre and Dementia Biomedical Research Unit at South London and Maudsley NHS Foundation Trust and King’s College London. The views expressed are those of the authors and not necessarily those of the NHS, the NIHR or the Department of Health.
Conflicts of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stanton, B.R., Leigh, P.N., Howard, R.J. et al. Behavioural and emotional symptoms of apathy are associated with distinct patterns of brain atrophy in neurodegenerative disorders. J Neurol 260, 2481–2490 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-6989-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-013-6989-9