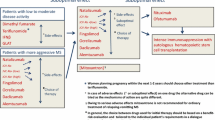
Abstract
Six pharmacological agents are currently approved for the treatment of multiple sclerosis (MS).However, all established substances are only partially effective in reducing disease progression or relapse rates. In addition, they have potentially serious side effects. Thus, significant efforts are being made to develop new agents or to optimize current therapies. The latter includes modifications of dose, route of administration or the time point of treatment initiation. In this review, we provide an update on the most important clinical phase II/III trials on approved and novel immunotherapeutic strategies in MS reported during the last two years. Pharmacotherapies include agents that target chemoattraction, cell migration, chemotherapies, and antigen-based therapies.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Achiron A, Gabbay U, Gilad R, Hassin- Baer S, Barak Y, Gornish M, Elizur A, Goldhammer Y, Sarova-Pinhas I (1998) Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in multiple sclerosis. Effect on relapses. Neurology 50:398–402
Achiron A, Kishner I, Sarova-Pinhas I, Raz H, Faibel M, Stern Y, Lavie M, Gurevich M, Dolev M, Magalashvili D, Barak Y (2004) Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment following the first demyelinating event suggestive of multiple sclerosis: a randomized, doubleblind, placebo-controlled trial. Arch Neurol 61:1515–1520
Achiron A, Lavie G, Kishner I, Stern Y, Sarova-Pinhas I, Ben-Aharon T, Barak Y, Raz H, Lavie M, Barliya T, Faibel M, Cohen IR, Mandel M (2004) T cell vaccination in multiple sclerosis relapsing- remitting nonresponders patients. Clin Immunol 113:155–160
Aktas O, Waiczies S, Smorodchenko A, Dorr J, Seeger B, Prozorovski T, Sallach S, Endres M, Brocke S, Nitsch R, Zipp F (2003) Treatment of relapsing paralysis in experimental encephalomyelitis by targeting Th1 cells through atorvastatin. J Exp Med 197:725–733
Baggiolini M (1998) Chemokines and leukocyte traffic. Nature 392:565–568
Bar-Or A, Antel J, Bodner CA (2006) Antigen-specific immunomodulation in multiple sclerosis patients treated with MBP encoding DNA plasmid (BHT-3009) alone or combined with atorvastatin. Neurology 66 (5) (Suppl):A62–A62
Barbero P, Bergui M, Versino E, Ricci A, Zhong JJ, Ferrero B, Clerico M, Pipieri A, Verdun E, Giordano L, Durelli L (2006) Every-other-day interferon beta-1b versus once-weekly interferon beta-1a for multiple sclerosis (INCOMIN Trial) II: analysis of MRI responses to treatment and correlation with Nab. Mult Scler 12:72–76
Baumhackl U, Fodermair S (1990) Enzymtherapie bei Multipler Sklerose. Allgemeinmedizin 19:169–172
Baumhackl U, Kappos L, Radue EW, Freitag P, Guseo A, Daumer M, Mertin J (2005) A randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study of oral hydrolytic enzymes in relapsing multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 11:166–168
Ben-Nun A, Cohen IR (1981) Vaccination against autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE): attenuated autoimmune T lymphocytes confer resistance to induction of active EAE but not to EAE mediated by the intact T lymphocyte line. Eur J Immunol 11:949–952
Bielekova B, Goodwin B, Richert N, Cortese I, Takayuki K, Afshar G, Gran B, Antel J, Franck JA, McFarland HF, Martin R (2000) Encephalitogenic potential of the myelin basic protein peptide (amino acids 83–99) in multiple sclerosis: Results of a phase II clinical trial with an altered peptide ligand. Nat Med 6:1167–1175
Birnbaum G, Altafullah I (2005) Neurology Volume 64 (6) (Suppl. 1):A385, P306. 158
Bitsch A, Schuchardt J, Bunkowski S, Kuhlmann T, Bruck W (2000) Acute axonal injury in multiple sclerosis. Correlation with demyelination and inflammation. Brain 123 (Pt 6):1174–1183
Brex PA, Ciccarelli O, O’Riordan JI, Sailer M, Thompson AJ, Miller DH (2002) A longitudinal study of abnormalities on MRI and disability from multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 346:158–164
Brinkmann V, Davis MD, Heise CE, Albert R, Cottens S, Hof R, Bruns C, Prieschl E, Baumruker T, Hiestand P, Foster CA, Zollinger M, Lynch KR (2002) The immune modulator FTY720 targets sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors. J Biol Chem 277:21453–21457
Budde K, Schmouder RL, Brunkhorst R, Nashan B, Lucker PW, Mayer T, Choudhury S, Skerjanec A, Kraus G, Neumayer HH (2002) First human trial of FTY720, a novel immunomodulator, in stable renal transplant patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 13:1073–1083
Caon C, Din M, Ching W, Tselis A, Lisak R, Khan O (2006) Clinical course after change of immunomodulating therapy in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurol 13:471–474
Charo IF, Ransohoff RM (2006) The many roles of chemokines and chemokine receptors in inflammation. N Engl J Med 354:610–621
Chiba K (2005) FTY720, a new class of immunomodulator, inhibits lymphocyte egress from secondary lymphoid tissues and thymus by agonistic activity at sphingosine 1-phosphate receptors. Pharmacol Ther 108:308–319
Chunduru SK, Sutherland RM, Stewart GA, Doms RW, Paterson Y (1996) Exploitation of the Vbeta8. 2 T cell receptor in protection against experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis using a live vaccinia virus vector. J Immunol 156:4940–4945
Cohen JA, Cutter GR, Fischer JS, Goodman AD, Heidenreich FR, Kooijmans MF, Sandrock AW, Rudick RA, Simon JH, Simonian NA, Tsao EC, Whitaker JN (2002) Benefit of interferon beta-1a on MSFC progression in secondary progressive MS. Neurology 59:679–687
Cohen JA, Rovaris M, Goodman AD, Ladkani D, Wynn D, Filippi M (2007) Randomized, double-blind, dose-comparison study of glatiramer acetate in relapsing-remitting MS. Neurology 68:939–944
Coles A, Group TCS (2007) Efficacy of Alemtuzumab in Treatment-Naive Relapsing- Remitting Multiple Sclerosis: Analysis after Two Years of Study CAMMS223 Neurology 68(Suppl 1):A100
Coles AJ, Cox A, Le Page E, Jones J, Trip SA, Deans J, Seaman S, Miller DH, Hale G, Waldmann H, Compston DA (2006) The window of therapeutic opportunity in multiple sclerosis: evidence from monoclonal antibody therapy. J Neurol 253:98–108
Comi G, Abramsky O, Arbizu T, Boiko A, Gold R, Havrdova E, Komoly S, Selmaj K, Sharrack B, Filippi M (2007) The Effekt of Two Doses of Laquinimod on MRI-Monitored Disease Activity in Patients with Relaspsing-Remitting Multiple Sclerosis: A Multi-Center, Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo- Controlled Study. Neurology 68 (Suppl 1):A84
Comi G, Filippi M, Barkhof F, Durelli L, Edan G, Fernandez O, Hartung H, Seeldrayers P, Sorensen PS, Rovaris M, Martinelli V, Hommes OR (2001) Effect of early interferon treatment on conversion to definite multiple sclerosis: a randomised study. Lancet 357:1576–1582
Comi G, Filippi M, Wolinsky JS (2001) European/Canadian multicenter, double- blind, randomized, placebo-controlled study of the effects of glatiramer acetate on magnetic resonance imaging–measured disease activity and burden in patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis. European/Canadian Glatiramer Acetate Study Group. Ann Neurol 49:290–297
Cree BA, Lamb S, Morgan K, Chen A, Waubant E, Genain C (2005) An open label study of the effects of rituximab in neuromyelitis optica. Neurology 64:1270–1272
Cross AH, Stark JL, Lauber J, Ramsbottom MJ, Lyons JA (2006) Rituximab reduces B cells and T cells in cerebrospinal fluid of multiple sclerosis patients. J Neuroimmunol 180:63–70
Durelli L (2003) Dose and frequency of interferon treatment matter–INCOMIN and OPTIMS. J Neurol 250 (Suppl 4):IV9–IV14
Durelli L, Verdun E, Barbero P, Bergui M, Versino E, Ghezzi A, Montanari E, Zaffaroni M (2002) Every-other-day interferon beta-1b versus once-weekly interferon beta-1a for multiple sclerosis: results of a 2-year prospective randomised multicentre study (INCOMIN). Lancet 359:1453–1460
Ebers GC (2004) Natural history of primary progressive multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 10 Suppl 1:S8–13; discussion S13–15
Elices MJ (2002) BX-471 Berlex. Curr Opin Investig Drugs 3:865–869
Faria AM, Weiner HL (2005) Oral tolerance. Immunol Rev 206:232–259
Fazekas F, Barkhof F, Filippi M, Grossman RI, Li DKB, McDonald WI, McFarland HF, Paty DW, Simon JH, Wolinsky JS, Miller DH (1999) The contribution of magnetic resonance imaging to the diagnosis of multiple sclerosis. Neurology 53:448–456
Fazekas F, Deisenhammer F, Strasser- Fuchs S, Nahler G, Mamoli B (1997) Randomised placebo-controlled trial of monthly intravenous immunoglobulin therapy in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Lancet 349:589–593
Fazekas F, Freedman M, Hartung HP, Li D, Lublin F, Rieckmann P, Soelberg- Sorensen P, Maas-Enriquez M, Sommerauer B, Anderesi M (2006) Prevention of relapse with intravenous immunoglobulin study: initial results of a dose-finding trial in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 253:101
Fazekas F, Sorensen PS, Filippi M, Ropele S, Lin X, Koelmel HW, Fernandez O, Pozzilli C, O’Connor P, Enriquez MM, Hommes OR (2005) MRI results from the European Study on Intravenous Immunoglobulin in Secondary Progressive Multiple Sclerosis (ESIMS). Mult Scler 11:433–440
Fergusson D, Hutton B, Sharma M, Tinmouth A, Wilson K, Cameron DW, Hebert PC (2005) Use of intravenous immunoglobulin for treatment of neurologic conditions: a systematic review. Transfusion 45:1640–1657
Filippi M, Rovaris M, Rocca MA, Sormani MP, Wolinsky JS, Comi G (2001) Glatiramer acetate reduces the proportion of new MS lesions evolving into “black holes”. Neurology 57:731–733
Filippi M, Wolinsky JS, Comi G (2006) Effects of oral glatiramer acetate on clinical and MRI-monitored disease activity in patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis: a multicentre, doubleblind, randomised, placebo-controlled study. Lancet Neurol 5:213–220
Fox RJ, Ransohoff RM (2004) New directions in MS therapeutics: vehicles of hope. Trends Immunol 25:632–636
Francis G, Evans A, Panitch H (1997) MRI results of a phase III trial of oral myelin in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis [abstract]. Ann Neurol 42:467
Freedman M, Polman C, Kappos L, Edan G, Hartung HP, Miller D, Montalban X, Barkhof F, Bauer L, Dahms S, Pohl C, Sandbrink R (2007) Betaseron in Newly Emerging Multiple Sclerosis for Initial Treatment (BENEFIT): Effects of Immediate vs. Early Onset of Interferon Beta-1b Treatment. Neurology 68 (Suppl 1):A85
Freedman MS, Francis GS, Sanders EA, Rice GP, O’Connor P, Comi G, Duquette P, Metz L, Murray TJ, Bouchard JP, Abramsky O, Pelletier J, O’Brien F (2005) Randomized study of onceweekly interferon beta-1a therapy in relapsing multiple sclerosis: three-year data from the OWIMS study. Mult Scler 11:41–45
Frohman EM, Havrdova E, Lublin F, Barkhof F, Achiron A, Sharief MK, Stuve O, Racke MK, Steinman L, Weiner H, Olek M, Zivadinov R, Corboy J, Raine C, Cutter G, Richert J, Filippi M (2006) Most patients with multiple sclerosis or a clinically isolated demyelinating syndrome should be treated at the time of diagnosis. Arch Neurol 63:614–619
Fujino M, Funeshima N, Kitazawa Y, Kimura H, Amemiya H, Suzuki S, Li XK (2003) Amelioration of experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis in Lewis rats by FTY720 treatment. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 305:70–77
Gaupp S, Pitt D, Kuziel WA, Cannella B, Raine CS (2003) Experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis (EAE) in CCR2(-/-) mice: susceptibility in multiple strains. Am J Pathol 162:139–150
Genain CP, Cannella B, Hauser SL, Raine CS (1999) Identification of autoantibodies associated with myelin damage in multiple sclerosis. Nat Med 5:170–175
Gold R, Havrdova E, Kappos L, Limmroth V, Miller D, Polman C, Yang M, Eraksoy M, Meluzinova E, Rektor I, O’Neill GN (2006) Safety of a novel oral single-agent fumarate, BG00012, in patients with relapsing-remitting mutiple sclerosis: results of a phase 2 study. J Neurol 253:144
Goodkin DE, Group NASS (2000) The North American Study of interferon beta-1b in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis. 52nd Annual Meeting of the American Academy of Neurology, San Diego, CA, 2000 Abstract #LBN 0. 002
Gray O, McDonnell GV, Forbes RB (2003) Intravenous immunoglobulins for multiple sclerosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev:CD002936
Greenwood J, Steinman L, Zamvil SS (2006) Statin therapy and autoimmune disease: from protein prenylation to immunomodulation. Nat Rev Immunol 6:358–370
Haas J (2000) High dose IVIg in the post partum period for prevention of exacerbations in MS. Multiple Sclerosis 6:18–20
Hafler DA, Weiner HL (1995) Immunologic mechanisms and therapy in multiple sclerosis. Immunol Rev 144:75–107
Hartung HP (2005) Early treatment and dose optimisation BENEFIT and BEYOND. J Neurol 252 (Suppl 3):iii44–iii50
Hass J, Firzlaff M (2005) Twenty-fourmonth comparison of immunomodulatory treatments–a retrospective open label study in 308 RRMS patients treated with beta interferons or glatiramer acetate (Copaxone). Eur J Neurol 12:425–431
Hauser SL, Waubant E, Douglas A, Vollmer T, Antel J, Fox R, Bar-Or A, Sarkar N, Langer-Gould A, Panzara M, Smith C (2007) A Phase II Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Multicenter Trial of Rituximab in Adults with Relapsing Remitting Multiple Sclerosis (RRMS). Neurology 68(Suppl 1):A99
Hemmer B, Vergelli M, Tranquill L, Conlon P, Ling N, McFarland HF, Martin R (1997) Human T-cell response to myelin basic protein peptide (83–99): extensive heterogeneity in antigen recognition, function, and phenotype. Neurology 49:1116–1126
Hohlfeld R, Wekerle H (2004) Autoimmune concepts of multiple sclerosis as a basis for selective immunotherapy: from pipe dreams to (therapeutic) pipelines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 101 Suppl 2:14599–14606
Hohlfeld R, Wiendl H (2001) The ups and downs of multiple sclerosis therapeutics. Ann Neurol 49:281–284
Hommes OR, Sorensen PS, Fazekas F, Enriquez MM, Koelmel HW, Fernandez O, Pozzilli C, O’Connor P (2004) Intravenous immunoglobulin in secondary progressive multiple sclerosis: randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 364:1149–1156
Imitola J, Chitnis T, Khoury SJ (2006) Insights into the molecular pathogenesis of progression in multiple sclerosis: potential implications for future therapies. Arch Neurol 63:25–33
Jacobs LD, Beck RW, Simon JH, Kinkel RP, Brownscheidle CM, Murray TJ, Simonian NA, Slasor PJ, Sandrock AW (2000) Intramuscular interferon beta- 1a therapy initiated during a first demyelinating event in multiple sclerosis. CHAMPS Study Group. N Engl J Med 343:898–904
Jiang H, Kashleva H, Xu LX, Forman J, Flaherty L, Pernis B, Braunstein NS, Chess L (1998) T cell vaccination induces T cell receptor Vbeta-specific Qa-1-restricted regulatory CD8(+) T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 95:4533–4537
Johnson KP, Brooks BR, Cohen JA, Ford CC, Goldstein J, Lisak RP, Myers LW, Panitch HS, Rose JW, Schiffer RB (1995) Copolymer 1 reduces relapse rate and improves disability in relapsing- remitting multiple sclerosis: results of a phase III multicenter, doubleblind placebo-controlled trial. The Copolymer 1 Multiple Sclerosis Study Group. Neurology 45:1268–1276
Kappos L, Barkhof F, Desmet A (2005) The effect of oral temsirolimus on new magnetic resonance imaging scan lesions, brain atrophy, and the number of relapses in multiple sclerosis: results from a randomised, controlled clinical trial. J Neurol 252 (Suppl 42):46–46
Kappos L, Miller DH, MacManus DG, Gold R, Havrdova E, Limmroth V, Polman C, Schmierer K, Yousry T, Yang M, Eraksoy M, Meluzinova E, Rektor I, O’Neill G (2006) Efficacy of a novel oral single-agent fumarate, BG00012, in patients with relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: results of a phase 2 study. J Neurol 253:27
Kappos L, Polman CH, Freedman MS, Edan G, Hartung HP, Miller DH, Montalban X, Barkhof F, Bauer L, Jakobs P, Pohl C, Sandbrink R (2006) Treatment with interferon beta-1b delays conversion to clinically definite and McDonald MS in patients with clinically isolated syndromes. Neurology 7:1242–1249
Kappos L, Radu EW, Antel J (2005) Promising results with a novel oral immunomodulator– FTY720–in relapsing multiple sclerosis. Mult Scler 11(Suppl):S13-S13
Keegan M, Konig F, McClelland R, Bruck W, Morales Y, Bitsch A, Panitch H, Lassmann H, Weinshenker B, Rodriguez M, Parisi J, Lucchinetti CF (2005) Relation between humoral pathological changes in multiple sclerosis and response to therapeutic plasma exchange. Lancet 366:579–582
Keegan M, Pineda AA, McClelland RL, Darby CH, Rodriguez M, Weinshenker BG (2002) Plasma exchange for severe attacks of CNS demyelination: predictors of response. Neurology 58:143–146
Kieburtz K, McDermott M (2002) Needed in MS: evidence, not EVIDENCE. Neurology 59:1482–1483
Kim KS, Jacob N, Stohl W (2003) In vitro and in vivo T cell oligoclonality following chronic stimulation with staphylococcal superantigens. Clin Immunol 108:182–189
Kinkel RP, Kollman C, O’Connor P, Murray TJ, Simon J, Arnold D, Bakshi R, Weinstock-Gutman B, Brod S, Cooper J, Duquette P, Eggenberger E, Felton W, Fox R, Freedman M, Galetta S, Goodman A, Guarnaccia J, Hashimoto S, Horowitz S, Javerbaum J, Kasper L, Kaufman M, Kerson L, Mass M, Rammohan K, Reiss M, Rolak L, Rose J, Scott T, Selhorst J, Shin R, Smith C, Stuart W, Thurston S, Wall M (2006) IM interferon beta-1a delays definite multiple sclerosis 5 years after a first demyelinating event. Neurology 66:678–684
Kleinschmidt-DeMasters BK, Tyler KL (2005) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy complicating treatment with natalizumab and interferon beta- 1a for multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 353:369–374
Kleinschnitz C, Meuth SG, Kieseier BC, Wiendl H (2006) Immunotherapeutic Approaches in MS: Update on Pathophysiology and Emerging Agents or Strategies 2006. EMID DT 7:35–63
Koch-Henriksen N, Sorensen PS, Christensen T, Frederiksen J, Ravnborg M, Jensen K, Heltberg A, Kristensen O, Stenager E, Petersen T, Hansen T (2006) A randomized study of two interferon- beta treatments in relapsingremitting multiple sclerosis. Neurology 66:1056–1060
Koralnik IJ (2006) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy revisited: Has the disease outgrown its name? Ann Neurol 60:162–173
Kozik M (1973) Activity of hydrolytic enzymes in a case of subacute multiple sclerosis. Pathol Eur 8:143–147
Kuhlmann T, Lingfeld G, Bitsch A, Schuchardt J, Bruck W (2002) Acute axonal damage in multiple sclerosis is most extensive in early disease stages and decreases over time. Brain 125:2202–2212
Kwak B, Mulhaupt F, Myit S, Mach F (2000) Statins as a newly recognized type of immunomodulator. Nat Med 6:1399–1402
Langer-Gould A, Atlas SW, Green AJ, Bollen AW, Pelletier D (2005) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy in a patient treated with natalizumab. N Engl J Med 353:375–381
Leary SM, Thompson AJ (2005) Primary progressive multiple sclerosis: current and future treatment options. CNS Drugs 19:369–376
Lehmann HC, Hartung HP, Hetzel GR, Stuve O, Kieseier BC (2006) Plasma exchange in neuroimmunological disorders: Part 1: Rationale and treatment of inflammatory central nervous system disorders. Arch Neurol 63:930–935
Lehmann HC, Hartung HP, Hetzel GR, Stuve O, Kieseier BC (2006) Plasma exchange in neuroimmunological disorders: part 2. Treatment of neuromuscular disorders. Arch Neurol 63:1066–1071
Lennon VA, Kryzer TJ, Pittock SJ, Verkman AS, Hinson SR (2005) IgG marker of optic-spinal multiple sclerosis binds to the aquaporin-4 water channel. J Exp Med 202:473–477
Lewanska M, Siger-Zajdel M, Selmaj K (2002) No difference in efficacy of two different doses of intravenous immunoglobulins in MS: clinical and MRI assessment. Eur J Neurol 9:565–572
Lublin FD (2002) When marketing and science intersect: do patients with MS benefit? Neurology 59:1480–1481
Lucchinetti C, Bruck W, Parisi J, Scheithauer B, Rodriguez M, Lassmann H (2000) Heterogeneity of multiple sclerosis lesions: implications for the pathogenesis of demyelination. Ann Neurol 47:707–717
Mao-Draayer Y, Braff S, Pendlebury W, Panitch H (2002) Treatment of steroid-unresponsive tumefactive demyelinating disease with plasma exchange. Neurology 59:1074–1077
Matloubian M, Lo CG, Cinamon G, Lesneski MJ, Xu Y, Brinkmann V, Allende ML, Proia RL, Cyster JG (2004) Lymphocyte egress from thymus and peripheral lymphoid organs is dependent on S1P receptor 1. Nature 427:355–360
Meden H, Mielke S, Marx D, Wuttke W, Kuhn W (1997) Hormonal treatment with sex steroids in women is associated with lower p105 serum concentrations. Anticancer Res 17:3075–3077
Menge T, Hartung HP, Stuve O (2005) Statins–a cure-all for the brain? Nat Rev Neurosci 6:325–331
Miller DH, Khan OA, Sheremata WA, Blumhardt LD, Rice GP, Libonati MA, Willmer-Hulme AJ, Dalton CM, Miszkiel KA, O’Connor PW (2003) A controlled trial of natalizumab for relapsing multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 348:15–23
Monson NL, Cravens PD, Frohman EM, Hawker K, Racke MK (2005) Effect of rituximab on the peripheral blood and cerebrospinal fluid B cells in patients with primary progressive multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 62:258–264
Neuhaus O, Strasser-Fuchs S, Fazekas F, Kieseier BC, Niederwieser G, Hartung HP, Archelos JJ (2002) Statins as immunomodulators: comparison with interferon-beta 1b in MS. Neurology 59:990–997
Niino M, Bodner C, Simard ML, Alatab S, Gano D, Kim HJ, Trigueiro M, Racicot D, Guerette C, Antel JP, Fournier A, Grand’Maison F, Bar-Or A (2006) Natalizumab effects on immune cell responses in multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 59:748–754
Noseworthy JH, Vandervoort MK, Penman M, Ebers G, Shumak K, Seland TP, Roberts R, Yetisir E, Gent M, Taylor DW (1991) Cyclophosphamide and plasma exchange in multiple sclerosis. Lancet 337:1540–1541
O'Connor P (2003) The effects of intramuscular interferon beta-Ia in patients at high risk for development of multiple sclerosis: a post hoc analysis of data from CHAMPS. Clin Ther 25:2865–2874
O'Connor P, Antel J, Comi G (2006) Oral FTY720 in relapsing MS: Results of the dose-blinded, active drug extension phase of a phase II study. Neurology 66 (5)(Suppl):A123–A123
Osterberg L, Blaschke T (2005) Adherence to medication. N Engl J Med 353:487–497
Ota K, Matsui M, Milford EL, Mackin GA, Weiner HL, Hafler DA (1990) Tcell recognition of an immunodominant myelin basic protein epitope in multiple sclerosis. Nature 346:183–187
OWIMS (1999) Evidence of interferon beta-1a dose response in relapsingremitting MS: the OWIMS Study. The Once Weekly Interferon for MS Study Group. Neurology 53:679–686
Paintlia AS, Paintlia MK, Khan M, Vollmer T, Singh AK, Singh I (2005) HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor augments survival and differentiation of oligodendrocyte progenitors in animal model of multiple sclerosis. Faseb J 19:1407–1421
Panitch H, Francis G, and the Oral Myelin Study Group (1997) Clinical results of a phase III trial of oral myelin in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Ann Neurol 42:459
Panitch H, Goodin D, Francis G, Chang P, Coyle P, O'Connor P, Li D, Weinshenker B (2005) Benefits of high-dose, high-frequency interferon beta-1a in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis are sustained to 16 months: final comparative results of the EVIDENCE trial. J Neurol Sci 239:67–74
Panitch H, Goodin DS, Francis G, Chang P, Coyle PK, O'Connor P, Monaghan E, Li D, Weinshenker B (2002) Randomized, comparative study of interferon beta-1a treatment regimens in MS: The EVIDENCE Trial. Neurology 59:1496–1506
Patti F, Pappalardo A, Florio C, Politi G, Fiorilla T, Reggio E, Reggio A (2006) Effects of interferon beta-1a and –1b over time: 6-year results of an observational head-to-head study. Acta Neurol Scand 113:241–247
Pittock SJ, Weinshenker BG, Noseworthy JH, Lucchinetti CF, Keegan M, Wingerchuk DM, Carter J, Shuster E, Rodriguez M (2006) Not every patient with multiple sclerosis should be treated at time of diagnosis. Arch Neurol 63:611–614
Polman C, Barkhof F, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Linde A, Nordle O, Nederman T (2005) Treatment with laquinimod reduces development of active MRI lesions in relapsing MS. Neurology 64:987–991
Polman CH, Kappos L, Freedman MS, Edan G, Hartung HP, Miller DH, Montalban X, Barkhof F, Bauer L, Dahms S, Pohl C, Sandbrink R, group obotBs (2006) Betaferon in newly emerging multiple sclerosis for initial treatment (BENEFIT): subgroup analyses. Neurology Suppl. 2:103
Polman CH, O’Connor PW, Havrdova E, Hutchinson M, Kappos L, Miller DH, Phillips JT, Lublin FD, Giovannoni G, Wajgt A, Toal M, Lynn F, Panzara MA, Sandrock AW (2006) A randomized, placebo-controlled trial of natalizumab for relapsing multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 354:899–910
Poser CM, Brinar VV (2001) Diagnostic criteria for multiple sclerosis. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 103:1–11
Ransohoff RM (2005) Natalizumab and PML. Nat Neurosci 8:1275
Rizvi SA, Bashir K (2004) Other therapy options and future strategies for treating patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology 63(12 Suppl 6):S47–54
Roach ES (2006) Early multiple sclerosis: to treat or not to treat? Arch Neurol 63:619
Rosen H, Goetzl EJ (2005) Sphingosine 1-phosphate and its receptors: an autocrine and paracrine network. Nat Rev Immunol 5:560–570
Rovaris M, Cohen J, Goodman A, Comi G, Filippi M (2006) Results of a randomised, double-blind, parallelgroup study assessing safety and efficacy of 40 mg vs. 20 mg of glatiramer acetate on MRI-measured disease activity in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. J Neurol 253 (Suppl 2):144
Rudick RA, Cutter GR, Baier M, Weinstock- Guttman B, Mass MK, Fisher E, Miller DM, Sandrock AW (2005) Estimating long-term effects of diseasemodifying drug therapy in multiple sclerosis patients. Mult Scler 11:626–634
Rudick RA, Stuart WH, Calabresi PA, Confavreux C, Galetta SL, Radue EW, Lublin FD, Weinstock-Guttman B, Wynn DR, Lynn F, Panzara MA, Sandrock AW (2006) Natalizumab plus interferon beta-1a for relapsing multiple sclerosis. N Engl J Med 354:911–923
Ruprecht K, Klinker E, Dintelmann T, Rieckmann P, Gold R (2004) Plasma exchange for severe optic neuritis: treatment of 10 patients. Neurology 63:1081–1083
Sandberg-Wollheim M, Bever C, Carter J, Farkkila M, Hurwitz B, Lapierre Y, Chang P, Francis GS (2005) Comparative tolerance of IFN beta-1a regimens in patients with relapsing multiple sclerosis. The EVIDENCE study. J Neurol 252:8–13
Schilling S, Linker RA, Konig FB, Koziolek M, Bahr M, Muller GA, Paulus W, Gartner J, Bruck W, Chan A, Gold R (2006) [Plasma exchange therapy for steroid-unresponsive multiple sclerosis relapses: Clinical experience with 16 patients, ]. Nervenarzt 77:430–438
Schwid SR, Thorpe J, Sharief M, Sandberg-Wollheim M, Rammohan K, Wendt J, Panitch H, Goodin D, Li D, Chang P, Francis G (2005) Enhanced benefit of increasing interferon beta- 1a dose and frequency in relapsing multiple sclerosis: the EVIDENCE Study. Arch Neurol 62:785–792
Sehgal SN (2003) Sirolimus: its discovery, biological properties, and mechanism of action. Transplant Proc 35:7S–14S
Sorensen PS, Fazekas F, Lee M (2002) Intravenous immunoglobulin G for the treatment of relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis: a meta-analysis. Eur J Neurol 9:557–563
Sorensen PS, Wanscher B, Jensen CV, Schreiber K, Blinkenberg M, Ravnborg M, Kirsmeier H, Larsen VA, Lee ML (1998) Intravenous immunoglobulin G reduces MRI activity in relapsing multiple sclerosis. Neurology 50:1273–1281
Sorensen TL, Tani M, Jensen J, Pierce V, Lucchinetti C, Folcik VA, Qin S, Rottman J, Sellebjerg F, Strieter RM, Frederiksen JL, Ransohoff RM (1999) Expression of specific chemokines and chemokine receptors in the central nervous system of multiple sclerosis patients. J Clin Invest 103:807–815
Sospedra M, Martin R (2005) Antigen- specific therapies in multiple sclerosis. Int Rev Immunol 24:393–413
SPECTRIMS SG (2001) Randomized controlled trial of interferon-beta-1a in secondary progressive MS: Clinical results. Neurology 56:1496–1504
Steinman L (2005) Blocking adhesion molecules as therapy for multiple sclerosis: natalizumab. Nat Rev Drug Discov 4:510–518
Steinman L (2006) The coming of age for antigen-specific therapy of multiple sclerosis. Eur J Neurol 13:793–794
Steinman L (2001) Immunotherapy of multiple sclerosis: the end of the beginning. Curr Opin Immunol 13:597–600
Steinman L, Zamvil SS (2005) Virtues and pitfalls of EAE for the development of therapies for multiple sclerosis. Trends Immunol 26:565–571
Storch MK, Piddlesden S, Haltia M, Iivanainen M, Morgan P, Lassmann H (1998) Multiple sclerosis: in situ evidence for antibody- and complement- mediated demyelination. Ann Neurol 43:465–471
Stuve O, Cepok S, Elias B, Saleh A, Hartung HP, Hemmer B, Kieseier BC (2005) Clinical stabilization and effective B-lymphocyte depletion in the cerebrospinal fluid and peripheral blood of a patient with fulminant relapsing- remitting multiple sclerosis. Arch Neurol 62:1620–1623
Stuve O, Marra CM, Jerome KR, Cook L, Cravens PD, Cepok S, Frohman EM, Phillips JT, Arendt G, Hemmer B, Monson NL, Racke MK (2006) Immune surveillance in multiple sclerosis patients treated with natalizumab. Ann Neurol 59:743–747
Stuve O, Youssef S, Weber MS, Nessler S, von Budingen HC, Hemmer B, Prod’homme T, Sobel RA, Steinman L, Zamvil SS (2006) Immunomodulatory synergy by combination of atorvastatin and glatiramer acetate in treatment of CNS autoimmunity. J Clin Invest 116:1037–1044
Sun D, Qin Y, Chluba J, Epplen JT, Wekerle H (1988) Suppression of experimentally induced autoimmune encephalomyelitis by cytolytic T-T cell interactions. Nature 332:843–845
Van Assche G, Van Ranst M, Sciot R, Dubois B, Vermeire S, Noman M, Verbeeck J, Geboes K, Robberecht W, Rutgeerts P (2005) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy after natalizumab therapy for Crohn’s disease. N Engl J Med 353:362–368
Vandenbark AA (2005) TCR peptide vaccination in multiple sclerosis: boosting a deficient natural regulatory network that may involve TCRspecific CD4+ CD25+ Treg cells. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy 4:217–229
Vartanian T (2003) An examination of the results of the EVIDENCE, INCOMIN, and phase III studies of interferon beta products in the treatment of multiple sclerosis. Clin Ther 25:105–118
Vollmer T, Key L, Durkalski V, Tyor W, Corboy J, Markovic-Plese S, Preiningerova J, Rizzo M, Singh I (2004) Oral simvastatin treatment in relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis. Lancet 363:1607–1608
Waisman A, Ruiz PJ, Hirschberg DL, Gelman A, Oksenberg JR, Brocke S, Mor F, Cohen IR, Steinman L (1996) Suppressive vaccination with DNA encoding a variable region gene of the T-cell receptor prevents autoimmune encephalomyelitis and activates Th2 immunity. Nat Med 2:899–905
Warren KG, Catz I, Ferenczi LZ, Krantz MJ (2006) Intravenous synthetic peptide MBP8298 delayed disease progression in an HLA Class IIdefined cohort of patients with progressive multiple sclerosis: results of a 24-month double-blind placebocontrolled clinical trial and 5 years of follow-up treatment. Eur J Neurol 13:887–895
Warren KG, Catz I, Wucherpfennig KW (1997) Tolerance induction to myelin basic protein by intravenous synthetic peptides containing epitope P85 VVHFFKNIVTP96 in chronic progressive multiple sclerosis. J Neurol Sci 152:31–38
Webb M, Tham CS, Lin FF, Lariosa- Willingham K, Yu N, Hale J, Mandala S, Chun J, Rao TS (2004) Sphingosine 1-phosphate receptor agonists attenuate relapsing-remitting experimental autoimmune encephalitis in SJL mice. J Neuroimmunol 153:108–121
Weber MS, Prod’homme T, Steinman L, Zamvil SS (2005) Drug Insight: using statins to treat neuroinflammatory disease. Nat Clin Pract Neurol 1:106–112
Weiner HL, Mackin GA, Matsui M, Orav EJ, Khoury SJ, Dawson DM, Hafler DA (1993) Double-blind pilot trial of oral tolerization with myelin antigens in multiple sclerosis. Science 259:1321–1324
Weinshenker BG, O’Brien PC, Petterson TM, Noseworthy JH, Lucchinetti CF, Dodick DW, Pineda AA, Stevens LN, Rodriguez M (1999) A randomized trial of plasma exchange in acute central nervous system inflammatory demyelinating disease. Ann Neurol 46:878–886
Weissert R, Wiendl H, Pfrommer H, Storch MK, Schreiner B, Barth S, Seifert T, Melms A, Dichgans J, Weller M (2003) Action of treosulfan in myelin-oligodendrocyte-glycoprotein- induced experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and human lymphocytes. J Neuroimmunol 144:28–37
Wiendl H, Hohlfeld R (2002) Therapeutic approaches in multiple sclerosis: lessons from failed and interrupted treatment trials. BioDrugs 16:183–200
Wiendl H, Kieseier BC, Weissert R, Mylius HA, Pichlmeier U, Hartung HP, Melms A, Kuker W, Weller M (2007) Treatment of active secondary progressive multiple sclerosis with treosulfan. J Neurol 254(7):884–889
Wolinsky JS (2004) The PROMiSe trial: baseline data review and progress report. Mult Scler 10 (Suppl 1):S65–71; discussion S71–62
Wucherpfennig KW, Sette A, Southwood S, Oseroff C, Matsui M, Strominger JL, Hafler DA (1994) Structural requirements for binding of an immunodominant myelin basic protein peptide to DR2 isotypes and for its recognition by human T cell clones. J Exp Med 179:279–290
Yousry TA, Major EO, Ryschkewitsch C, Fahle G, Fischer S, Hou J, Curfman B, Miszkiel K, Mueller-Lenke N, Sanchez E, Barkhof F, Radue EW, Jager HR, Clifford DB (2006) Evaluation of patients treated with natalizumab for progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. N Engl J Med 354:924–933
Youssef S, Stuve O, Patarroyo JC, Ruiz PJ, Radosevich JL, Hur EM, Bravo M, Mitchell DJ, Sobel RA, Steinman L, Zamvil SS (2002) The HMG-CoA reductase inhibitor, atorvastatin, promotes a Th2 bias and reverses paralysis in central nervous system autoimmune disease. Nature 420:78–84
Zamvil SS, Steinman L (2003) Diverse targets for intervention during inflammatory and neurodegenerative phases of multiple sclerosis. Neuron 38:685–688
Zipp F, Hartung HP, Hillert J, Schimrigk S, Trebst C, Stangel M, Infante- Duarte C, Jakobs P, Wolf C, Sandbrink R, Pohl C, Filippi M (2006) Blockade of chemokine signaling in patients with multiple sclerosis. Neurology 67:1880–1883
Zipp F, Hartung HP, Hillert J, Schimrigk S, Trebst C, Stangel M, Pohl C, Filippi M (2005) Blockade of chemokine receptor in multiple sclerosis patients. Mult Scler 11(1):S13
Zwibel HL (2006) Glatiramer acetate in treatment-naive and prior interferon- beta-1b-treated multiple sclerosis patients. Acta Neurol Scand 113: 378–386
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kleinschnitz, C., Meuth, S.G., Stüve, O. et al. Multiple sclerosis therapy: An update on recently finished trials. J Neurol 254, 1473–1490 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-007-0684-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-007-0684-7