Abstract
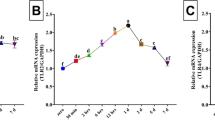
This study was performed to clarify whether interleukin-10 messenger RNA (IL-10 mRNA) could be a possible indicator for the distinction between intravital wounds and postmortem damage. After incision, mice were sacrificed from 0 to 180 min. The initial amount of IL-10 mRNA in each skin specimen was evaluated using the reverse transcriptase-polymerase chain reaction (RT-PCR). After 15 min there was a rapid increase in IL-10 mRNA which peaked at 60 min. A significant increase in IL-10 mRNA occurred between 30 and 180 min. During the 5 day postmortem interval the increase in time-dependent IL-10 mRNA expression was maintained and no significant increase in IL-10 mRNA expression occurred in the postmortem control. The increased expression of IL-10 mRNA could be considered a vital reaction in skin specimens with postmortem change. This study demonstrated the possible use of mRNA analysis for forensic wound examination because mRNA was detectable by RT-PCR over a longer postmortem time course.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 1 December 1997 / Received in revised form: 15 January 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ohshima, T., Sato, Y. Time-dependent expression of interleukin-10 (IL-10) mRNA during the early phase of skin wound healing as a possible indicator of wound vitality. Int J Leg Med 111, 251–255 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004140050163
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004140050163