Abstract
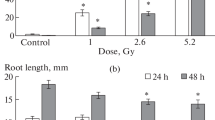
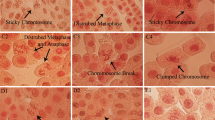
The induction of chromosome aberrations in tobacco root tip cells was measured after exposure to either 18 MeV/n carbon ions or 2 MeV electrons. The RBE value for acute exposure was found to be about 10. Splitting the dose into two fractions did not produce any significant effect on the yield of aberrations following carbon-ion exposure, whereas a clear decrease was observed after exposure to electrons thereby indicating an induction/activation of error-free repair after the first fraction. Moreover, this decrease appeared to be independent of the types of chromosome aberrations. On the other hand, it was suggested that the lack of any significant effect on the yield of aberrations is either due to a lack of error-free repair or to a less efficient damage repair after exposure to carbon ions.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 26 February 2001 / Accepted: 28 June 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shimono, K., Shikazono, N., Inoue, M. et al. Effect of fractionated exposure to carbon ions on the frequency of chromosome aberrations in tobacco root cells. Radiat Environ Biophys 40, 221–226 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004110100105
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004110100105