Abstract
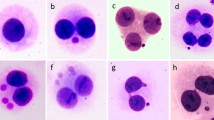
Micronuclei can be used as markers of past radiation exposure, but only few studies have dealt with uranium miners. In this paper, we report on micronuclei in lymphocytes from individuals currently working at Rožná, Czech Republic, the last functioning uranium mine in the European Union. A modified micronucleus-centromere test was applied to assess the occurrence of micronuclei in stimulated lymphocytes, as well as their content in terms of whole chromosomes or fragments. Compared with unexposed individuals, the miners had higher frequencies of micronucleus-containing lymphocytes and higher percentages of micronuclei without centromeres, and the differences were significant for both parameters (0.74 ± 0.60 vs. 0.50 ± 0.42, p = 0.017 and 49 ± 44 vs. 12 ± 21, p = 0.0002; means ± standard deviations). There were also significant correlations between one or other of these parameters on the one hand and various dose values on the other, in particular with a ‘retrievable’ dose, that is, a dose whose effect should still be recognisable in lymphocytes assuming a half-life of 3 years. The ‘retrievable’ dose at which a doubling of the micronucleus frequency was observed was around 35 mSv, corresponding to a total dose of 90 mSv received while working in the mines. Altogether, our data show that the micronucleus-centromere test is a valuable tool for the assessment of past radiation exposure in uranium miners. The scatter in the data is of course far too great to allow individual dosimetry, but for groups of a few dozen exposed individuals, the method can be used to monitor doses clearly below 100 mSv.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abend M, Blakely WF, van Beuningen D (1995) Simplified and optimised kinetochore detection: cytogenetic marker for late-G2 cells. Mutat Res 334:39–47
Bejarano LA, Bolivar J, Valdivia MM (1993) Anticentromere antibody specific to human cells directed against the CENP-B autoantigen. Cytogenet Cell Genet 63:54–58
Chang WP, Tsai MS, Hwang JS, Lin YP, Hsieh WH, Sbal-yi H (1999) Follow-up in the micronucleus frequencies and its subsets in human population with chronic low-dose γ-irradiation exposure. Mutat Res 428:99–105
Earnshaw WC, Sullivan KF, Machlin PS, Cooke CA, Kaiser DA, Pollard TD, Rothfield NF, Cleveland DW (1987) Molecular cloning of cDNA for CENP-B, the major human centromere autoantigen. J Cell Biol 104:817–829
Fenech M, Morley AA (1985) Measurement of micronuclei in lymphocytes. Mutat Res 147:29–36
Fenech M, Denham J, Francis W, Morley A (1990) Micronuclei in cytokinesis-blocked lymphocytes of cancer patients following fractionated partial-body radiotherapy. Int J Radiat Biol 57:373–383
Johannes C, Dixius A, Pust M, Hentschel R, Buraczewska I, Staaf E, Brehwens K, Haghdoost S, Nievaart S, Czub J, Braziewicz J, Wojcik A (2010) The yield of radiation-induced micronuclei in early and late-arising binucleated cells depends on radiation quality. Mutat Res 701:80–85
Kryscio A, Ulrich Müller WU, Wojcik A, Kotschy N, Grobelny S, Streffer C (2001) A cytogenetic analysis of the long-term effect of uranium mining on peripheral lymphocytes using the micronucleus-centromere assay. Int J Radiat Biol 77:1087–1093
Lindholm C (1998) Persistence of translocations after accidental exposure to ionizing radiation. Int J Radiat Biol 74:565–571
Marsh JW, Blanchardon E, Gregoratto D, Hofmann W, Karcher K, Nosske D, Tomašek L (2011) Dosimetric calculations for uranium miners for epidemiological studies. Radiat Prot Dosim. doi:10.1093/rpd/ncr310
Marušiaková M, Gregor Z, Tomášek L (2011) A review of exposures to radon, long-lived radionuclides and external gamma at the Czech uranium mine. Radiat Prot Dosim 145:248–251
Müller WU, Streffer C (1994) Micronucleus assays. In: Obe G (ed) Advances in mutagenesis research. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–134
Natarajan AT, Kesavan PC (2005) Cytogenetics for dosimetry in cases of radiation accidents and assessing the safety of irradiated food material. Curr Sci 89:360–365
Norppa H, Falck GCM (2003) What do human micronuclei contain? Mutagenesis 18:221–233
Norppa H, Renzi L, Lindholm C (1993) Detection of whole chromosomes in micronuclei of cytokinesis-blocked human lymphocytes by antikinetochore staining and in situ hybridization. Mutagenesis 8:519–525
Reddy MM, Goh KO, Hempelmann LH (1980) Induction of micronuclei in PHA-stimulated human lymphocyte cultures by therapeutic radiation. Experientia 36:343–344
Tarazi RC (1985) Pulmonary blood volume. Eur Heart J 6(Supplement C):43
Thierens H, Vral A (2009) The micronucleus assay in radiation accidents. Ann Ist Super Sanita 45:260–264
Thierens H, Vral A, Morthier R, Aousalah B, De Ridder L (2000) Cytogenetic monitoring of hospital workers occupationally exposed to ionizing radiation using the micronucleus centromere assay. Mutagenesis 15:245–249
Thomson EJ, Perry PE (1988) The identification of micronucleated chromosomes: a possible assay for aneuploidy. Mutagenesis 3:415–418
Vral A, Thierens H, De Ridder L (1997) In vitro micronucleus-centromere assay to detect radiation-damage induced by low doses in human lymphocytes. Int J Radiat Biol 71:61–68
Wojcik A, Kowalska M, Bouzyk E, Buraczewska I, Kobialko G, Jarocewicz N, Szumiel I (2000) Validation of the micronucleus-centromere assay for biological dosimetry. Genet Mol Biol 23:25–30
Zeni O, Chiavoni AS, Sannino A, Antolini A, Forigo D, Bersani F, Scarfì MR (2003) Lack of genotoxic effects (micronucleus induction) in human lymphocytes exposed in vitro to 900 MHz electromagnetic fields. Radiat Res 160:152–158
Zölzer F, Freitinger-Skalická Z, Havránková R, Hon Z, Navrátil L, Rosina J, Škopek J (2011) Enhanced frequency of micronuclei in lymphocytes from current as opposed to former uranium miners. J Appl Biomed 9:151–156
Acknowledgments
We thank Ing. Mrs Hana Placakova for reliable technical assistance and Ing. Ladislav Beránek, CSc., MBA, for help with the statistics. These investigations have been supported by the Czech Ministry of Education, Youth and Sports within the framework of the National Research Program II (NPV II, project 2B08001).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zölzer, F., Hon, Z., Skalická, Z.F. et al. Micronuclei in lymphocytes from currently active uranium miners. Radiat Environ Biophys 51, 277–282 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-012-0422-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-012-0422-0