Abstract
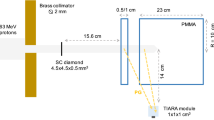
For real-time monitoring of the longitudinal position of the Bragg-peak during an ion therapy treatment, a novel non-invasive technique has been recently proposed that exploits the detection of prompt γ-rays issued from nuclear fragmentation. Two series of experiments have been performed at the GANIL and GSI facilities with 95 and 305 MeV/u 12C6+ ion beams stopped in PMMA and water phantoms. In both experiments, a clear correlation was obtained between the carbon ion range and the prompt photon profile. Additionally, an extensive study has been performed to investigate whether a prompt neutron component may be correlated with the carbon ion range. No such correlation was found. The present paper demonstrates that a collimated set-up can be used to detect single photons by means of time-of-flight measurements, at those high energies typical for ion therapy. Moreover, the applicability of the technique both at cyclotron and at synchrotron facilities is shown. It is concluded that the detected photon count rates provide sufficiently high statistics to allow real-time control of the longitudinal position of the Bragg-peak under clinical conditions.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnabà O, Chen YB, Musitelli G, Nardò R, Raselli GL, Rossella M, Torre P (1998) A full-integrated pulse shape discriminator for liquid scintillator counters. Nucl Instr Meth A410:220–228
Enghardt W, Parodi K, Crespo P, Fiedler F, Pawelke J, Pönisch F (2004) Dose quantification from in-beam positron emission tomography. Radioth Oncol 73:96–98
Gunzert-Marx K, Iwase H, Schardt D, Simon RS (2008) Secondary beam fragments produced by 200 MeV/u 12C ions in water and their dose contributions in carbon ion radiotherapy. New J Phys 10:075003
Kraemer M, Jakel O, Haberer T, Kraft G, Schardt D, Weber U (2000) Treatment planning for heavy-ion radiotherapy: physical beam model and dose optimization. Phys Med Biol 45:3299–3317
Kraft G (2000) Tumor therapy with heavy charged particles. Prog Part Nucl Phys 45:S473–S544
Le Foulher F, Bajard M, Chevallier M, Dauvergne D, Freud N, Henriquet P, Karkar S, Létang JM, Plescak R, Ray C, Schardt D, Testa E, Testa M (2010) Monte Carlo simulations of prompt-gamma emission during carbon ion irradiation. Accepted for publication in IEEE Transactions on Nuclear Science
Min C-H, Kim CH, Youn M-Y, Kim J-W (2006) Prompt gamma measurements for locating the dose falloff region in proton therapy. Appl Phys Lett 89:183517
Normand S, Mouandab B, Haana S, Louvel M (2002) Discrimination methods between neutron and gamma rays for boron loaded plastic scintillators. Nucl Instr Meth A 484:342–350
Parodi K, Bortfeld T, Enghardt W, Fiedler F, Knopf A, Paganetti H, Pawelke J, Shakirin G, Shih H (2008) PET imaging for treatment verification of ion therapy: Implementation and experience at GSI Darmstadt and MGH Boston. Nucl Instr Meth A 591:282–286
Riess S (1989) Exclusive photon yields from peripheral collisions of 40Ar + 158Gd at 44 MeV/u. Nucl Phys A49(5):49c–56c
Sommerer F, Parodi K, Ferrari A, Poljanc K, Enghardt W, Aiginger H (2006) Investigating the accuracy of the FLUKA code for transport of therapeutic ion beams in matter. Phys Med Biol 51:4385–4398
Testa E, Bajard M, Chevallier M, Dauvergne D, Le Foulher F, Freud N, Létang J-M, Poizat J-C, Ray C, Testa M (2008) Monitoring the Bragg peak location of 73 MeV/u carbon ions by means of prompt gamma ray measurements. Appl Phys Lett 93:093506
Testa E, Bajard M, Chevallier M, Dauvergne D, Le Foulher F, Freud N, Létang J-M, Poizat J-C, Ray C, Testa M (2009) Dose profile monitoring with carbon ions by means of prompt-gamma measurements. Nucl Instr Meth Phys Res B 267:993–996
Acknowledgments
Part of this work was funded by the Rhône-Alpes regional research program for ion therapy ETOILE.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
This manuscript is based on a contribution given at the Heavy Ions in Therapy and Space Symposium 2009, July 6–10, 2009, Cologne (Germany).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Testa, M., Bajard, M., Chevallier, M. et al. Real-time monitoring of the Bragg-peak position in ion therapy by means of single photon detection. Radiat Environ Biophys 49, 337–343 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-010-0276-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00411-010-0276-2