Abstract
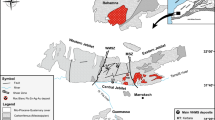
An undated high-pressure low-temperature tectonic mélange in the Elekdağ area (central Pontides, N Turkey) comprises blocks of MORB-derived lawsonite eclogite within a sheared serpentinite matrix. In their outer shells, some of the eclogite blocks contain large (up to 6 cm) tourmaline crystals. ‘Prograde’ inclusions in poikiloblastic garnet from a well-preserved eclogite block are lawsonite, epidote/clinozoisite, omphacite, rutile, glaucophane, chlorite, Ba-bearing phengite, minor actinolite, winchite and quartz. In addition, glaucophane, lawsonite and rutile occur as inclusions in omphacite. These inclusion assemblages document the transition from a garnet-lawsonite-epidote-bearing blueschist to a lawsonite eclogite with the peak assemblage garnet + omphacite I + lawsonite + rutile. Peak metamorphic conditions are not well-constrained but are estimated approximately 400–430°C and >1.35 GPa, based on Fe–Mg exchange between garnet and omphacite and the coexistence of lawsonite + omphacite + rutile. During exhumation of the eclogite–serpentinite mélange in the hanging wall of a subduction system, infiltration of B-rich aqueous fluids into the rims of eclogite blocks caused retrogressive formation of abundant chlorite, titanite and albite, followed by growth of tourmaline at the expense of chlorite. At the same time, omphacite I (XJd=0.24–0.44) became unstable and partially replaced by omphacite II characterized by higher XJd (0.35–0.48), suggesting a relatively low silica activity in the infiltrating fluid. Apart from Fe-rich rims developed at the contact to chlorite, tourmaline crystals are nearly homogeneous. Their compositions correspond to Na-rich dravite, perhaps with a small amount of excess (tetrahedral) boron (~5.90 Si and 3.10 B cations per 31 anions). δ11 B values range from −2.2 to +1.7‰. The infiltrating fluids were most probably derived from subducting altered oceanic crust and sediments.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bebout GE, Nakamura E (2003) Record in metamorphic tourmalines of subduction-zone devolatilization and boron cycling. Geology 31:407–410
Benton LD, Ryan JG, Tera F (2001) Boron isotope systematics of slab fluids as inferred from a serpentinite seamount, Mariana forearc. Earth Planet Sci Lett 187:273–282
Boynton WV (1984) Cosmochemistry of the rare earth elements: meteorite studies. In: Henderson P (ed) rare earth element geochemistry. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 63–114
Brown EH (1977) The crossite content of Ca-amphibole as a guide to pressure of metamorphism. J Petrol 18:53–72
Brunsmann A, Franz G, Heinrich W (2002) Experimental investigation of zoisite-clinozoisite phase equilibria in the system CaO-Fe2O3-Al2O3-SiO2-H2O. Contrib Miner Petrol 143:115–130
Cantanzaro EJ, Champion CE, Garner El, Marinenko G, Sappenfield KM, Shields WR (1970) Boric acid: isotopic and assay standard reference materials. Natl Bureau Stand (US) Spec Publ 260(17):70
Caron JM, Pequignot G (1986) The transition between blueschists and lawsonite-bearing eclogites based on observations from Corsican metabasalts. Lithos 19:205–218
Chakraborty S, Ganguly J (1992) Cation diffusion in aluminosilicate garnets: experimental determination in spessartine-almandine diffusion couples, evaluation of effective binary diffusion coefficients, and applications. Contrib Miner Petrol 111:74–86
Dutrow BL, Foster CT (1992) Constraints on metamorphic fluid from irreversible thermodynamic modeling of tourmaline-rich pseudomorph formation. Geol Soc Am Abstr Progr 24:A218
Dyar MD, Taylor ME, Lutz TM, Francis CA, Guidotti CV, Wise MA (1998) Inclusive chemical characterization of tourmaline: Mössbauer study of Fe valence and site occupancy. Am Miner 83:848–864
Dyar MD, Wiedenbeck M, Robertson D, Cross LR, Delaney JS, Ferguson K, Francis CA, Grew ES, Guidotti CV, Hervig LR, Hughes JM, Husler J, Leeman W, McGuire AV, Rhede D, Rothe H, Paul RL, Richards I, Yates M (2001) Reference minerals for the microanalysis of light elements. Geostand Newslett 25:441–463
Ernst WG (1979) Coexisting sodic and calcic amphiboles from high-pressure metamorphic belts and the stability of barroisitic amphibole. Mineral Mag 43:269–278
Frondel C, Collette RL (1957) Synthesis of tourmaline by reaction of mineral grains with NaCl-H2BO3 solution, and its implications in rock metamorphism. Am Mineral 42:754–758
Fuchs Y, Lagache M (1994) La transformation chlorite-tourmaline en milieu hydrothermal, exemples naturels et approche expérimentale. C R Acad Sci Paris Sér II 319:907–913
Gao J, Klemd R (2001) Primary fluids entrapped at blueschist to eclogite transition: evidence from the Tianshan meta-subduction complex in northeastern China. Contrib Miner Petrol 142:1–14
Ghent ED, Stout MZ, Erdmer P (1993) Pressure-temperature evolution of lawsonite-bearing eclogites, Pinchi Lake, British Columbia. J Metamorphic Geol 11:279–290
Gómez-Pugnaire MT, Karsten L, Sánchez-Vizcíno VL (1997) Phase relationships and P-T conditions of coexisting eclogite-blueschists and their transformations to greenschist-facies rocks in the Nerkau complex (Northern Urals). Tectonophysics 276:195–216
Hacker BR, Abers GA, Peacock SM (2003a) Subduction factory. 1. Theoretical mineralogy, densities, seismic wave speeds, and H2O contents. J Geophys Res 108: DOI 10.1029/2001JB001127, ESE 10-1 to 10-26
Hacker BR, Peacock SM, Abers GA, Holloway SD (2003b) Subduction factory. 2. Are intermediate-depth earthquakes in subducting slabs linked to metamorphic dehydration reactions? J Geophys Res 108: DOI 10.1029/2001JB001129, ESE 11-1 to 11-16
Hattori KH, Guillot S (2003) Volcanic fronts form as a consequence of serpentinite dehydration in the forearc mantle wedge. Geology 31:525–528
Heinrich W, Althaus E (1988) Experimental determination of the reactions 4 lawsonite+1 albite=1 paragonite+2 zoisite+2 quartz+6 H2O and 4 lawsonite+1 jadeite=1 paragonite+2 zoisite+1 quartz+6 H2O. N Jb Miner Mh 1988:516–528
Hellman PL, Green TH (1979) The role of sphene as an accessory phase in the high-pressure partial melting of hydrous mafic compositions. Earth Planet Sci Lett 42:191–201
Helmstaedt H, Schulze DJ (1988) Eclogite-facies ultramafic xenoliths from Colorado Plateau diatreme breccias: comparison with eclogites in crustal environments, evaluation of the subduction hypothesis, and implications for eclogite xenoliths from diamondiferous kimberlites. In: Smith DC (ed) Eclogites and Eclogite-Facies Rocks. Developments in Petrology, vol 12. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 387–450
Henry DJ, Dutrow BI (1996) Metamorphic tourmaline and its petrologic applications. In: Anowitz LM, Grew ES (eds) Boron: mineralogy, petrology and geochemisty. Min Soc Am Rev in Mineralogy, vol 33, pp 502–537
Hervig RL, Moore GM, Williams LB, Peacock SM, Holloway JR, Roggensack K (2002) Isotopic and elemental fractionation of boron between hydrous fluid and silicate melt. Am Miner 87:769–774
Himmelberg GR, Papike JJ (1969) Coexisting amphiboles from blueschist-facies metamorphic rocks. J Petrol 10:102–114
Hofmann AW (1988) Chemical differentiation of the Earth: the relationship between mantle, continental crust, and oceanic crust. Earth Planet Sci Lett 90:297–314
Hofmann AW, Jochum KP, Seufert M, White WM (1986) Nb and Pb in oceanic basalts: new constraints on mantle evolution. Earth Planet Sci Lett 79:33–45
Holland TJB, Powell R (1998) An internally consistent thermodynamic data set for phases of petrological interest. J Metamorphic Geol 16:309–343
Ishikawa T, Tera F (1997) Source, composition and distribution of fluid in the Kurile mantle wedge: constraints from across-arc variations of B/Nb and B isotopes. Earth Planet Sci Lett 152:123–138
Ishikawa T, Tera T, Nakazawa T (2001) Boron isotope and trace element systematics of the three volcanic zones in the Kamchatka arc. Geochim Cosmochim Acta 65:4523–4537
Iwamori H (1998) Transportation of H2O and melting in subduction zones. Earth Planet Sci Lett 160:65–80
Kalt A, Schreyer W, Ludwig T, Prowatke S, Bernhardt H-J, Ertl A (2001) Complete solid solution between magnesian schorl and lithian excess-boron olenite in a pegmatite from the Koralpe (eastern Alps, Austria). Eur J Miner 13:1191–1205
Kerrick DM, Connolly JAD (2001a) Metamorphic devolatilization of subducted oceanic metabasalts: implications for seismicity, arc magmatism and volatile recycling. Earth Planet Sci Lett 189:19–29
Kerrick DM, Connolly JAD (2001b) Metamorphic devolatilization of subducted marine sediments and the transport of volatiles into the Earth’s mantle. Nature 411:293–296
Kopf A, Deyhle A (2002) Back to the roots: boron geochemistry of mud volcanoes and its implications for mobilization depth and global B cycling. Chem Geol 192:195–210
Krogh Ravna E (2000) The garnet-clinopyroxene Fe2+ -Mg geothermometer: an updated calibration. J Metamorphic Geol 18:211–219
Krogh Ravna EJ, Terry MP (2001) Geothermobarometry of phengite-kyanite-quartz/coesite eclogites. In: 11th Annual V. M. Goldschmidt Conf Abstr#3754. LPI Contribution No. 3154, Lunar and Planetary Institute, Houston (CD-ROM)
Krogh EJ, Oh CW, Liou JG (1994) Polyphase and anticlockwise P-T evolution for Franciscan eclogites and blueschsists from Jenner, California, USA. J Metamorphic Geol 12:121–134
Leeman WP, Sisson VB (2002) Geochemistry of boron and its implications for crustal and mantle processes. In: Grew ES, Anovitz LM (eds) Boron: mineralogy, petrology and geochemistry. Mineralogical Soc Am Rev in Mineralogy, vol 33, 2nd edn, pp 645–708
Leeman WP, Tonarini S (2001) Boron isotopic analysis of proposed borosilicate mineral reference samples. Geostand Newslett 25:399–403
Manning CE, Bohlen SR (1991) The reaction titanite+kyanite=anorthite+rutile and titanite–rutile barometry in eclogites. Contrib Miner Petrol 109:1–9
Marschall H, Altherr R, Ludwig T, Kalt A (2003) Syros tourmaline: evidence for very high-δ11 B fluids in subduction zones. Ber DMG Beih 1 Eur J Mineral 15:127
Marschall H, Ertl A, Hughes JM, McCammon C (2004a) Metamorphic Na- and OH-rich disordered dravite with tetrahedral boron, associated with omphacite, from Syros, Greece: chemistry and structure. Eur J Mineral (in press)
Marschall H, Altherr R, Ludwig T, Kalt A (2004b) Evidence for subduction related fluids and their boron isotopic composition from metasomatic zones in high-pressure metamorphic rocks from Syros, Greece. Geophys Res Abstr 6:3865
Morgan GB, London D (1989) Experimental reactions of amphibolite with boron-bearing aqueous fluids at 200 MPa: implications for tourmaline stability and partial melting in mafic rocks. Contrib Miner Petrol 102:281–297
Morimoto N, Fabries J, Ferguson AK, Ginzburg IV, Ross M, Seifert FA, Zussman J, Akio K, Gottardi G (1988) Nomenclature of pyroxenes. Am Miner 73:1123–1133
Mottana A, Carswell DA, Chopin C, Oberhänsli R (1990) Eclogite facies mineral parageneses. In: Carswell DA (ed) Eclogite facies rocks, Chapman and Hall, New York, pp 14–52
Nakano T, Nakamura E (2001) Boron isotope geochemistry of metasedimentary rocks and tourmalines in a subduction zone metamorphic suite. Phys Earth Planet Int 127:233–352
Okay AI (2000) Was the late Triassic orogeny in Turkey caused by the collision of an oceanic plateau? In: Bozkurt E, Winchester JA, Piper JDA (eds) Tectonics and Magmatism in Turkey and surrounding area. Geol Soc London Spec Publ 173, pp 25–41
Okay AI, Şahintürk Ö (1997) Geology of the Eastern Pontides. In: Robertson AG (ed) Regional and petroleum geology of the Black Sea and surrounding region. AAPG Memoir 68:291–311
Okay AI, Satır M, Maluski H, Siyako M, Monié P, Metzger R, Akyüz S (1996) Palaeo- and Neo-Tethyan events in northwest Turkey. In: Yin E, Harrison M (eds) Tectonics of Asia, Cambridge University Press, pp 420–441,
Okay AI, Monod O, Monié P (2002) Triassic blueschists and eclogites from northwest Turkey: vestiges of the Paleo-Tethyan subduction. Lithos 64:155–178
Okay AI, Tüysüz O, Satır M, Eren RH (2003) Tectonic imbrication of Paleo- and Neo-Tethyan accretionary complexes in the central Pontides, Turkey. Eur Geophys Soc Geophys Res Abstr 5:3493
Ottolini L, Bottazi P, Vannucci R (1993) Quantification of lithium, beryllium, and boron in silicates by secondary ion mass spectrometry using energy filtering. Anal Chem 65:1960–1968
Palmer MR, Swihart GH (2002) Boron isotope geochemistry: an overview. In: Grew ES, Anovitz LM (eds) Boron: Mineralogy, Petrology and Geochemistry. Min Soc Am, Rev in Mineralogy 33, 2nd edition, pp 709–744
Palmer MR, London D, Morgan GB, Babb HA (1992) Experimental determination of fractionation of 11 B/10 B between tourmaline and aqueous vapor: a temperature- and pressure-dependant isotopic system. Chem Geol 101:123–129
Paquin J, Altherr R, Ludwig T (2004) Li-Be-B systematics in the ultrahigh-pressure garnet peridotite from Alpe Arami (Central Swiss Alps): implications for slab-to-mantle wedge transfer. Earth Planet Sci Lett 218:507–519
Peacock SM (1990a) Fluid processes in subduction zones. Science 248:329–337
Peacock SM (1990b) Numerical simulation of metamorphic pressure-temperature-time paths and fluid production in subducting slabs. Tectonics 9:1197–1211
Peacock SM (1993) The importance of blueschist —-> eclogite dehydration reactions in subducting oceanic crust. Geol Soc Am Bull 105:684–694
Peacock SM, Hervig RL (1999) Boron isotopic composition of subduction-zone metamorphic rocks. Chem Geol 160:281–290
Peacock SM, Wang K (1999) Seismic consequences of warm versus cool subduction metamorphism: examples from southwest and northwest Japan. Science 286:937–939
Pearce NJG, Perkins WT, Westgate JA, Gorton MP, Jackson SE, Neal CR, Chenery SP (1997) A compilation of new and published major and trace element data for NIST SRM 610 and NIST SRM 612 glass reference materials. Geostand Newslett 21:115–144
Pognante U, Kienast JR (1987) Blueschist and eclogite transformations in Fe-Ti gabbros: a case from the Western Alps ophiolites. Contrib Miner Petrol 28:271–292
Poli S, Schmidt MW (2002) Petrology of subducted slabs. Ann Rev Earth Planet Sci 30:207–235
Pouchou JL, Pichoir F (1984) A new model for quantitative analyses. I. Application to the analysis of homogeneous samples. La Recherche Aérospatiale 3:13–38
Pouchou JL, Pichoir F (1985) “PAP” φ(ρZ) correction procedure for improved quantitative microanalysis. In: Armstrong JT (ed) Microbeam Analysis, San Francisco Press, pp 104–106
Reynard B, Ballèvre M (1988) Coexisting amphiboles in the eclogite from the Western Alps: new constraints on the miscibility gap between sodic and calcic amphiboles. J Metamorphic Geol 6:333–350
Rollinson H (1993) Using geochemical data: evaluation, presentation, interpretation. Longman Scientific and Technical, Singapore
Ryan J, Morris J, Bebout GE, Leeman B (1996) Describing chemical fluxes in subduction zones: insights from ‘depth-profiling’ studies of arc and forearc rocks. In: Bebout GE, Scholl DW, Kirby SH, Platt JP (eds) Subduction top to bottom. Geopyhs Monogr Series 96, Am Geophys Union, Washington, pp 263–268
Scambelluri M, Philippot P (2001) Deep fluids in subduction zones. Lithos 55:213–227
Schmidt MW, Poli S (1998) Experimentally based water budgets for dehydrating slabs and consequences for arc magma generation. Earth Planet Sci Lett 163:361–379
Schumacher JC (1997) The estimation of ferric iron in electron microprobe analysis of amphiboles. Eur J Miner 9:643–651
Shibakusa H, Maekawa H (1997) Lawsonite-bearing eclogitic metabasites in the Cazadero area, northern California. Miner Petrol 61:163–180
Sun S-S, McDonough WF (1989) Chemical and isotopic systematics of oceanic basalts: implications for mantle composition and processes. In: Saunders AD, Norry MJ (eds) Magmatism in the Ocean Basins. Geol Soc Lond Spec Publ 42:313–345
Tüysüz O (1990) Tectonic evolution of a part of the Tethyside orogenic collage: The Kargı massif, northern Turkey. Tectonics 9:141–160
Ustaömer T (1993) Pre-Late Jurassic tectonic-sedimentary evolution of North Tethys: Central Pontides, N. Turkey. PhD thesis, University of Edinburg, p 391
Ustaömer T, Robertson AHF (1997) Tectonic-sedimentary evolution of the North-Tethyan active margin in the Central Pontides of Northern Turkey. In: Robinson AG (ed) Regional and Petroleum Geology of the Black Sea Region. AAPG Mem 68, pp 245–290
Ustaömer T, Robertson AHF (1999) Geochemical evidence used to test alternative plate tectonic models for pre-Late Jurassic (Palaeotethyan) units in the Central Pontides, N Turkey. Geol J 34:25–54
Usui T, Nakamura E, Kobayashi K, Maruyama S, Helmstaedt H (2003) Fate of the subducted Farallon plate inferred from eclogite xenoliths in the Colorado Plateau. Geology 31:589–592
Van Keken PE, Kiefer B, Peacock SM (2002) High-resolution models of subduction zones: implications for mineral dehydration reactions and the transport of water into the deep mantle. Geochem Geophys Geosyst 3: DOI 10.1029/2001GC000256
Vielzeuf D, Schmidt MW (2001) Melting relations in hydrous systems revisited: application to metapelites, metagreywackes and metabasalts. Contrib Miner Petrol 141:251–267
Watanabe T, Leitch E, Fanning M (1997) The age and tectonic significance of lawsonite eclogite and high temperature eclogite blocks in serpentinite melange from the southern New England Fold Belt, eastern Australia. In: 5th International eclogite conference
Watson KD, Morton DM (1969) Eclogite inclusions in kimberlite pipes at Garnet Ridge, northeastern Arizona. Am Mineral 54:267–285
Weisbrod A, Polak C, Roy D (1986) Experimental study of tourmaline solubility in the system Na-Mg-Al-Si-B-O-H: applications to the boron content of natural hydrothermal fluids and tourmalinization processes. Int Symp Exp Miner Abstr 1:140–141
Yılmaz Y, Şengör AMC (1985) Palaeo-Tethyan ophiolites in northern Turkey: petrology and tectonic setting. Ofioliti 10:485–504
Yılmaz Y, Tüysüz O, Yiğitbaş E, Genç SC, Şengör AMC (1997) Geology and tectonic evolution of the Pontides. In: Robinson AG (ed) Regional and Petroleum Geology of the Black Sea and Surrounding Region. Am Ass Petrol Geol Mem 68:183–226
You C-F, Spivack AJ, Smith JH, Gieskes JM (1993) Mobilization of boron in convergent margins: implications for the boron geochemical cycle. Geology 21:207–210
You C-F, Chan LH, Spivack AJ, Gieskes JM (1995) Lithium, boron, and their isotopes in sediments and pore waters of Ocean Drilling Program Site 808, Nankai Trough: implications for fluid expulsion in accretionary prisms. Geology 23:37–40
You C-F, Castillo PR, Gieskes JM, Chan LH, Spivack AJ (1996) Trace element behavior in hydrothermal experiments: implications for fluid processes at shallow depths in subduction zones. Earth Planet Sci Lett 140:41–52
Zack T, Rivers T, Brumm R, Kronz A (2004) Cold subduction of oceanic crust: implications from a lawsonite eclogite from the Dominican Republic. Eur J Mineral (in press)
Acknowledgements
This paper benefited from discussions with Aral I. Okay, Timur Ustaömer, Cüneyt Şen, Muharrem Satır and Cemal Göncüoğlu on the geology of the Pontides. Constructive and valuable reviews by Reiner Klemd and Johann G. Raith helped to substantially improve the manuscript. We thank Murat Kayıkçı for cutting the rock slices, Ilona Fin and Oliver Wienand for preparing high quality polished thin sections, and Hans-Peter Meyer and Alexander Varychev for assistance during EPMA and SEM work. The companionship of Abdurrahman Dokuz during field work is greatly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Altherr, R., Topuz, G., Marschall, H. et al. Evolution of a tourmaline-bearing lawsonite eclogite from the Elekdağ area (Central Pontides, N Turkey): evidence for infiltration of slab-derived B-rich fluids during exhumation. Contrib Mineral Petrol 148, 409–425 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-004-0611-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00410-004-0611-1