Abstract
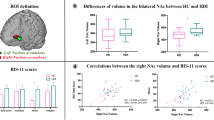
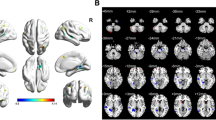
The neural mechanisms of heroin addiction are still incompletely understood, even though modern neuroimaging techniques offer insights into disease-related changes in vivo. While changes on cortical structure have been reported in heroin addiction, evidence from subcortical areas remains underrepresented. Functional imaging studies revealed that the brain reward system and particularly the nucleus accumbens (NAcc) play a pivotal role in the pathophysiology of drug addiction. The aim of this study was to investigate whether there was a volume difference of the NAcc in heroin addiction in comparison to healthy controls. A further aim was to correlate subcortical volumes with clinical measurements on negative affects in addiction. Thirty heroin-dependent patients under maintenance treatment with diacetylmorphine and twenty healthy controls underwent structural MRI scanning at 3T. Subcortical segmentation analysis was performed using FMRIB’s Integrated Registration and Segmentation Tool function of FSL. The State–Trait Anxiety Inventory and the Beck Depression Inventory were used to assess trait anxiety and depressive symptoms, respectively. A decreased volume of the left NAcc was observed in heroin-dependent patients compared to healthy controls. Depression score was negatively correlated with left NAcc volume in patients, whereas a positive correlation was found between the daily opioid dose and the volume of the right amygdala. This study indicates that there might be structural differences of the NAcc in heroin-dependent patients in comparison with healthy controls. Furthermore, correlations of subcortical structures with negative emotions and opioid doses might be of future relevance for the investigation of heroin addiction.


Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Albertson DN, Schmidt CJ, Kapatos G, Bannon MJ (2006) Distinctive profiles of gene expression in the human nucleus accumbens associated with cocaine and heroin abuse. Neuropsychopharmacology 31:2304–2312
Beck AT, Erbaugh J, Ward CH, Mock J, Mendelsohn M (1961) An inventory for measuring depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 4:561
Bewernick BH, Hurlemann R, Matusch A, Kayser S, Grubert C, Hadrysiewicz B, Axmacher N, Lemke M, Cooper-Mahkorn D, Cohen MX, Brockmann H, Lenartz D, Sturm V, Schlaepfer TE (2010) Nucleus accumbens deep brain stimulation decreases ratings of depression and anxiety in treatment-resistant depression. Biol Psychiatry 67:110–116
Blum J, Gerber H, Gerhard U, Schmid O, Petitjean S, Riecher-Rossler A, Wiesbeck GA, Borgwardt SJ, Walter M (2013) Acute effects of heroin on emotions in heroin-dependent patients. Am J Addict 22:598–604
Bookstein FL (2001) “Voxel-based morphometry” should not be used with imperfectly registered images. Neuroimage 14:1454–1462
Bremner JD, Narayan M, Anderson ER, Staib LH, Miller HL, Charney DS (2000) Hippocampal volume reduction in major depression. Am J Psychiatry 157:115–118
Carlezon WA Jr, Thomas MJ (2009) Biological substrates of reward and aversion: a nucleus accumbens activity hypothesis. Neuropharmacology 56(Suppl 1):122–132
de Jong LW, van der Hiele K, Veer IM, Houwing JJ, Westendorp RG, Bollen EL, de Bruin PW, Middelkoop HA, van Buchem MA, van der Grond J (2008) Strongly reduced volumes of putamen and thalamus in Alzheimer’s disease: an MRI study. Brain 131:3277–3285
Fang J, Gu JW, Yang WT, Qin XY, Hu YH (2012) Clinical observation of physiological and psychological reactions to electric stimulation of the amygdaloid nucleus and the nucleus accumbens in heroin addicts after detoxification. Chin Med J 125:63–66
Franken IH, Kroon LY, Wiers RW, Jansen A (2000) Selective cognitive processing of drug cues in heroin dependence. J Psychopharmacol 14:395–400
Gerber H, Borgwardt SJ, Schmid O, Gerhard U, Joechle W, Riecher-Rossler A, Wiesbeck GA, Walter M (2012) The impact of diacetylmorphine on hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis activity and heroin craving in heroin dependence. Eur Addict Res 18:116–123
Hannestad J, Taylor WD, McQuoid DR, Payne ME, Krishnan KR, Steffens DC, Macfall JR (2006) White matter lesion volumes and caudate volumes in late-life depression. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 21:1193–1198
Hesse M (2006) The Beck Depression Inventory in patients undergoing opiate agonist maintenance treatment. Br J Clin Psychol 45:417–425
Koob GF (2009) Dynamics of neuronal circuits in addiction: reward, antireward, and emotional memory. Pharmacopsychiatry 42(Suppl 1):S32–S41
Lai CH, Wu YT (2011) Duloxetine’s modest short-term influences in subcortical structures of first episode drug-naive patients with major depressive disorder and panic disorder. Psychiatry Res 194:157–162
LaLumiere RT, Kalivas PW (2008) Glutamate release in the nucleus accumbens core is necessary for heroin seeking. J Neurosci 28:3170–3177
Li Q, Li W, Wang H, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Zhu J, Zheng Y, Zhang D, Wang L, Li Y, Yan X, Chang H, Fan M, Li Z, Tian J, Gold MS, Wang W, Liu Y (2014) Predicting subsequent relapse by drug-related cue-induced brain activation in heroin addiction: an event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Addict Biol. doi:10.1111/adb.12182
Li Q, Wang Y, Zhang Y, Li W, Yang W, Zhu J, Wu N, Chang H, Zheng Y, Qin W, Zhao L, Yuan K, Liu J, Wang W, Tian J (2012) Craving correlates with mesolimbic responses to heroin-related cues in short-term abstinence from heroin: an event-related fMRI study. Brain Res 1469:63–72
Liu H, Hao Y, Kaneko Y, Ouyang X, Zhang Y, Xu L, Xue Z, Liu Z (2009) Frontal and cingulate gray matter volume reduction in heroin dependence: optimized voxel-based morphometry. Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 63:563–568
Liu H, Li L, Hao Y, Cao D, Xu L, Rohrbaugh R, Xue Z, Hao W, Shan B, Liu Z (2008) Disrupted white matter integrity in heroin dependence: a controlled study utilizing diffusion tensor imaging. Am J Drug Alcohol Abuse 34:562–575
Liu X, Matochik JA, Cadet JL, London ED (1998) Smaller volume of prefrontal lobe in polysubstance abusers: a magnetic resonance imaging study. Neuropsychopharmacology 18:243–252
Lyoo IK, Pollack MH, Silveri MM, Ahn KH, Diaz CI, Hwang J, Kim SJ, Yurgelun-Todd DA, Kaufman MJ, Renshaw PF (2006) Prefrontal and temporal gray matter density decreases in opiate dependence. Psychopharmacology 184:139–144
Ma N, Liu Y, Fu XM, Li N, Wang CX, Zhang H, Qian RB, Xu HS, Hu X, Zhang DR (2011) Abnormal brain default-mode network functional connectivity in drug addicts. PLoS One 6:e16560
Ma N, Liu Y, Li N, Wang CX, Zhang H, Jiang XF, Xu HS, Fu XM, Hu X, Zhang DR (2010) Addiction related alteration in resting-state brain connectivity. Neuroimage 49:738–744
Machado-de-Sousa JP, de Lima Osorio F, Jackowski AP, Bressan RA, Chagas MH, Torro-Alves N, Depaula AL, Crippa JA, Hallak JE (2014) Increased amygdalar and hippocampal volumes in young adults with social anxiety. PLoS One 9:e88523
Mayberg HS, Brannan SK, Tekell JL, Silva JA, Mahurin RK, McGinnis S, Jerabek PA (2000) Regional metabolic effects of fluoxetine in major depression: serial changes and relationship to clinical response. Biol Psychiatry 48:830–843
Meredith GE, Baldo BA, Andrezjewski ME, Kelley AE (2008) The structural basis for mapping behavior onto the ventral striatum and its subdivisions. Brain Struct Funct 213:17–27
Nestler EJ, Malenka RC (2004) The addicted brain. Sci Am 290:78–85
Nugent AC, Luckenbaugh DA, Wood SE, Bogers W, Zarate CA Jr, Drevets WC (2012) Automated subcortical segmentation using first: test–retest reliability, interscanner reliability, and comparison to manual segmentation. Hum Brain Mapp 34:2313–2329
Oviedo-Joekes E, Brissette S, Marsh DC, Lauzon P, Guh D, Anis A, Schechter MT (2009) Diacetylmorphine versus methadone for the treatment of opioid addiction. N Engl J Med 361:777–786
Patenaude B, Smith SM, Kennedy DN, Jenkinson M (2011) A bayesian model of shape and appearance for subcortical brain segmentation. Neuroimage 56:907–922
Qiu Y, Jiang G, Su H, Lv X, Zhang X, Tian J, Zhuo F (2013) Progressive white matter microstructure damage in male chronic heroin dependent individuals: a DTI and TBSS study. PLoS One 8:e63212
Qiu YW, Han LJ, Lv XF, Jiang GH, Tian JZ, Zhuo FZ, Su HH, Lin CL, Zhang XL (2011) Regional homogeneity changes in heroin-dependent individuals: resting-state functional MR imaging study. Radiology 261:551–559
Qiu YW, Jiang GH, Su HH, Lv XF, Tian JZ, Li LM, Zhuo FZ (2013) The impulsivity behavior is correlated with prefrontal cortex gray matter volume reduction in heroin-dependent individuals. Neurosci Lett 538:43–48
Quade D (1967) Rank analysis of covariance. J Am Stat Assoc 62:1187–1200
Resendez SL, Dome M, Gormley G, Franco D, Nevarez N, Hamid AA, Aragona BJ (2013) Mu-opioid receptors within subregions of the striatum mediate pair bond formation through parallel yet distinct reward mechanisms. J Neurosci 33:9140–9149
Robinson TE, Kolb B (1999) Morphine alters the structure of neurons in the nucleus accumbens and neocortex of rats. Synapse 33:160–162
Russo SJ, Nestler EJ (2013) The brain reward circuitry in mood disorders. Nat Rev Neurosci 14:609–625
Schmidt A, Borgwardt S, Gerber H, Wiesbeck GA, Schmid O, Riecher-Rossler A, Smieskova R, Lang UE, Walter M (2014) Acute effects of heroin on negative emotional processing: relation of amygdala activity and stress-related responses. Biol Psychiatry 76:289–296
Shen Y, Wang E, Wang X, Lou M (2012) Disrupted integrity of white matter in heroin-addicted subjects at different abstinent time. J Addict Med 6:172–176
Smith SM, Jenkinson M, Woolrich MW, Beckmann CF, Behrens TE, Johansen-Berg H, Bannister PR, De Luca M, Drobnjak I, Flitney DE, Niazy RK, Saunders J, Vickers J, Zhang Y, De Stefano N, Brady JM, Matthews PM (2004) Advances in functional and structural MR image analysis and implementation as FSL. Neuroimage 23(Suppl 1):S208–S219
Spielberger CD (1983) Manual for the State-Trait Anxiety Inventory (STAI). Santa Clara, PaloAlto
Sun J, Bi J, Chan G, Oslin D, Farrer L, Gelernter J, Kranzler HR (2012) Improved methods to identify stable, highly heritable subtypes of opioid use and related behaviors. Addict Behav 37:1138–1144
Szczytkowski JL, Fuchs RA, Lysle DT (2011) Ventral tegmental area-basolateral amygdala-nucleus accumbens shell neurocircuitry controls the expression of heroin-conditioned immunomodulation. J Neuroimmunol 237:47–56
Tiffany ST (1999) Cognitive concepts of craving. Alcohol Res Health 23:215–224
Upadhyay J, Maleki N, Potter J, Elman I, Rudrauf D, Knudsen J, Wallin D, Pendse G, McDonald L, Griffin M, Anderson J, Nutile L, Renshaw P, Weiss R, Becerra L, Borsook D (2010) Alterations in brain structure and functional connectivity in prescription opioid-dependent patients. Brain 133:2098–2114
Vogel M, Knopfli B, Schmid O, Prica M, Strasser J, Prieto L, Wiesbeck GA, Dursteler-Macfarland KM (2013) Treatment or “high”: benzodiazepine use in patients on injectable heroin or oral opioids. Addict Behav 38:2477–2484
Volkow ND, Wang GJ, Fowler JS, Tomasi D, Telang F (2011) Addiction: beyond dopamine reward circuitry. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108:15037–15042
Wacker J, Dillon DG, Pizzagalli DA (2009) The role of the nucleus accumbens and rostral anterior cingulate cortex in anhedonia: integration of resting EEG, fMRI, and volumetric techniques. Neuroimage 46:327–337
Walter M, Denier N, Gerber H, Schmid O, Lanz C, Brenneisen R, Riecher-Rossler A, Wiesbeck GA, Scheffler K, Seifritz E, McGuire P, Fusar-Poli P, Borgwardt S (2014) Orbitofrontal response to drug-related stimuli after heroin administration. Addict Biol. doi:10.1111/adb.12145
Walter M, Gerber H, Kuhl HC, Schmid O, Joechle W, Lanz C, Brenneisen R, Schachinger H, Riecher-Rossler A, Wiesbeck GA, Borgwardt SJ (2013) Acute effects of intravenous heroin on the hypothalamic–pituitary–adrenal axis response: a controlled trial. J Clin Psychopharmacol 33:193–198
Walter M, Wiesbeck GA, Degen B, Albrich J, Oppel M, Schulz A, Schachinger H, Dursteler-MacFarland KM (2011) Heroin reduces startle and cortisol response in opioid-maintained heroin-dependent patients. Addict Biol 16:145–151
Wang X, Li B, Zhou X, Liao Y, Tang J, Liu T, Hu D, Hao W (2012) Changes in brain gray matter in abstinent heroin addicts. Drug Alcohol Depend 126:304–308
Wheeler AL, Lerch JP, Chakravarty MM, Friedel M, Sled JG, Fletcher PJ, Josselyn SA, Frankland PW (2013) Adolescent cocaine exposure causes enduring macroscale changes in mouse brain structure. J Neurosci 33:1797–1803
Woolrich MW, Jbabdi S, Patenaude B, Chappell M, Makni S, Behrens T, Beckmann C, Jenkinson M, Smith SM (2009) Bayesian analysis of neuroimaging data in fsl. Neuroimage 45:S173–S186
Yuan K, Qin W, Dong M, Liu J, Liu P, Zhang Y, Sun J, Wang W, Wang Y, Li Q, Yang W, Tian J (2010) Combining spatial and temporal information to explore resting-state networks changes in abstinent heroin-dependent individuals. Neurosci Lett 475:20–24
Yuan K, Qin W, Dong M, Liu J, Sun J, Liu P, Zhang Y, Wang W, Wang Y, Li Q, Zhao L, von Deneen KM, Liu Y, Gold MS, Tian J (2010) Gray matter deficits and resting-state abnormalities in abstinent heroin-dependent individuals. Neurosci Lett 482:101–105
Yuan Y, Zhu Z, Shi J, Zou Z, Yuan F, Liu Y, Lee TM, Weng X (2009) Gray matter density negatively correlates with duration of heroin use in young lifetime heroin-dependent individuals. Brain Cogn 71:223–228
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the Swiss National Science Foundation (SNSF) (32003B-127544). We would like to acknowledge the infrastructural support of the Medical Image Analysis Centre, University Hospital Basel.
Conflict of interest
Till Sprenger served on advisory boards for Mitsubishi Pharma, Eli Lilly, Genzyme, Novartis, Biogen and Allergan. The other authors declare no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seifert, C.L., Magon, S., Sprenger, T. et al. Reduced volume of the nucleus accumbens in heroin addiction. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 265, 637–645 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-014-0564-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-014-0564-y
Keywords
Profiles
- Stefan Borgwardt View author profile