Abstract
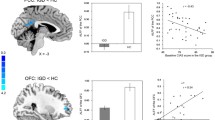
The aim of the present study was to evaluate the impulsivity and brain correlates of response inhibition and error processing among subjects with Internet gaming disorder (IGD). We evaluated the response inhibition and error processing by functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) in subjects with IGD and controls. Twenty-six men with IGD for at least 2 years and 23 controls with no history of IGD were recruited as the IGD and control groups, respectively. All subjects performed the event-related designed Go/No-go task under fMRI and completed questionnaires related to Internet addiction and impulsivity. The IGD group exhibited a higher score for impulsivity than the control group. The IGD group also exhibited higher brain activation when processing response inhibition over the left orbital frontal lobe and bilateral caudate nucleus than controls. Both the IGD and control groups exhibited activation of the insula and anterior cingulate cortex during error processing. The activation over the right insula was lower in the subjects with IGD than the control group. Our results support the fact that the fronto-striatal network involved in response inhibition, and the salience network, anchored by the anterior cingulate and insula, contributes to error processing. Further, adults with IGD have impaired insular function in error processing and greater activation of the fronto-striatal network in order to maintain their response inhibition performance.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (2013) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders, 5th edn. American Psychiatric Association, Arlington
Yen CF, Yen JY, Ko CH (2010) Internet addiction: ongoing research in Asia. World Psychiatry 9(2):97
Dong G, Devito EE, Du X, Cui Z (2012) Impaired inhibitory control in ‘Internet addiction disorder’: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. Psychiatry Res 203(2–3):153–158
Dong G, Zhou H, Zhao X (2010) Impulse inhibition in people with Internet addiction disorder: electrophysiological evidence from a Go/NoGo study. Neurosci Lett 485(2):138–142
Ko CH, Liu GC, Hsiao S, Yen JY, Yang MJ, Lin WC, Yen CF, Chen CS (2009) Brain activities associated with gaming urge of online gaming addiction. J Psychiatr Res 43(7):739–747
Ko CH, Liu GC, Yen JY, Chen CY, Yen CF, Chen CS (2011) Brain correlates of craving for online gaming under cue exposure in subjects with Internet gaming addiction and in remitted subjects. Addict Biol 18(3):559–569
Littel M, van den Berg I, Luijten M, van Rooij AJ, Keemink L, Franken IH (2012) Error processing and response inhibition in excessive computer game players: an event-related potential study. Addict Biol 17(5):934–947
Yen JY, Yen CF, Chen CS, Tang TC, Huang TH, Ko CH (2011) Cue-induced positive motivational implicit response in young adults with Internet gaming addiction. Psychiatry Res 190(2–3):282–286
Winstanley CA, Eagle DM, Robbins TW (2006) Behavioral models of impulsivity in relation to ADHD: translation between clinical and preclinical studies. Clin Psychol Rev 26(4):379–395
Lee HW, Choi JS, Shin YC, Lee JY, Jung HY, Kwon JS (2012) Impulsivity in Internet addiction: a comparison with pathological gambling. Cyberpsychol Behav Soc Netw 15(7):373–377
Gentile DA, Choo H, Liau A, Sim T, Li D, Fung D, Khoo A (2011) Pathological video game use among youths: a two-year longitudinal study. Pediatrics 127(2):e319–e329
Torregrossa MM, Quinn JJ, Taylor JR (2008) Impulsivity, compulsivity, and habit: the role of orbitofrontal cortex revisited. Biol Psychiatry 63(3):253–255
Zhou Z, Yuan G, Yao J (2012) Cognitive biases toward Internet game-related pictures and executive deficits in individuals with an Internet game addiction. PLoS ONE 7(11):e48961
Sun DL, Chen ZJ, Ma N, Zhang XC, Fu XM, Zhang DR (2009) Decision-making and prepotent response inhibition functions in excessive Internet users. CNS Spectr 14(2):75–81
Tejado Lde A, Ruiz RM, Trebbau H, Diaz-Marsa M, Perera JL (2010) Functional magnetic resonance studies in eating behavior disorders. Actas Esp Psiquiatr 38(3):183–188
Criaud M, Boulinguez P (2013) Have we been asking the right questions when assessing response inhibition in go/no-go tasks with fMRI? A meta-analysis and critical review. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 37(1):11–23
Chambers CD, Garavan H, Bellgrove MA (2009) Insights into the neural basis of response inhibition from cognitive and clinical neuroscience. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 33(5):631–646
Li CS, Yan P, Sinha R, Lee TW (2008) Subcortical processes of motor response inhibition during a stop signal task. Neuroimage 41(4):1352–1363
Isoda M, Hikosaka O (2011) Cortico-basal ganglia mechanisms for overcoming innate, habitual and motivational behaviors. Eur J Neurosci 33(11):2058–2069
Everitt BJ, Hutcheson DM, Ersche KD, Pelloux Y, Dalley JW, Robbins TW (2007) The orbital prefrontal cortex and drug addiction in laboratory animals and humans. Ann NY Acad Sci 1121:576–597
Goldstein RZ, Volkow ND (2002) Drug addiction and its underlying neurobiological basis: neuroimaging evidence for the involvement of the frontal cortex. Am J Psychiatry 159(10):1642–1652
Yeung N, Summerfield C (2012) Metacognition in human decision-making: confidence and error monitoring. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 367(1594):1310–1321
Shiels K, Hawk LW Jr (2010) Self-regulation in ADHD: the role of error processing. Clin Psychol Rev 30(8):951–961
Debener S, Ullsperger M, Siegel M, Fiehler K, von Cramon DY, Engel AK (2005) Trial-by-trial coupling of concurrent electroencephalogram and functional magnetic resonance imaging identifies the dynamics of performance monitoring. J Neurosci 25(50):11730–11737
Hester R, Fassbender C, Garavan H (2004) Individual differences in error processing: a review and reanalysis of three event-related fMRI studies using the GO/NOGO task. Cereb Cortex 14(9):986–994
Taylor SF, Stern ER, Gehring WJ (2007) Neural systems for error monitoring: recent findings and theoretical perspectives. Neuroscientist 13(2):160–172
Luijten M, van Meel CS, Franken IH (2011) Diminished error processing in smokers during smoking cue exposure. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 97(3):514–520
de Bruijn ER, Grootens KP, Verkes RJ, Buchholz V, Hummelen JW, Hulstijn W (2006) Neural correlates of impulsive responding in borderline personality disorder: ERP evidence for reduced action monitoring. J Psychiatr Res 40(5):428–437
Ruchsow M, Walter H, Buchheim A, Martius P, Spitzer M, Kachele H, Gron G, Kiefer M (2006) Electrophysiological correlates of error processing in borderline personality disorder. Biol Psychol 72(2):133–140
Hester R, Nestor L, Garavan H (2009) Impaired error awareness and anterior cingulate cortex hypoactivity in chronic cannabis users. Neuropsychopharmacology 34(11):2450–2458
Ko CH, Yen JY, Chen SH, Yang MJ, Lin HC, Yen CF (2009) Proposed diagnostic criteria and the screening and diagnosing tool of Internet addiction in college students. Compr Psychiatry 50(4):378–384
Sheehan DV, Lecrubier Y, Sheehan KH, Amorim P, Janavs J, Weiller E, Herqueta T, Baker R, Dunbar GC (1998) The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (M.I.N.I.): the development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. J Clin Psychiatry 59(Suppl 20):22–33; (quiz: 34–57)
Chen SH, Weng LC, Su YJ, Wu HM, Yang PF (2003) Development of Chinese Internet addiction scale and its psychometric study. Chin J Psychol 45(3):279–294
Li CS, Chen SH (2007) Obsessive-compulsiveness and impulsivity in a non-clinical population of adolescent males and females. Psychiatry Res 149(1–3):129–138
Patton JH, Stanford MS, Barratt ES (1995) Factor structure of the Barratt impulsiveness scale. J Clin Psychol 51(6):768–774
Dickman SJ (1990) Functional and dysfunctional impulsivity: personality and cognitive correlates. J Pers Soc Psychol 58(1):95–102
Graf H, Abler B, Freudenmann R, Beschoner P, Schaeffeler E, Spitzer M, Schwab M, Gron G (2011) Neural correlates of error monitoring modulated by atomoxetine in healthy volunteers. Biol Psychiatry 69(9):890–897
Brett M, Anton JL, Valabregue R, Poline JB (2002) Region of interest analysis using an SPM toolbox. Dissertation, 8th International conference on functional mapping of the human brain
Tzourio-Mazoyer N, Landeau B, Papathanassiou D, Crivello F, Etard O, Delcroix N, Mazoyer B, Joliot M (2002) Automated anatomical labeling of activations in SPM using a macroscopic anatomical parcellation of the MNI MRI single-subject brain. Neuroimage 15(1):273–289
Bossaerts P (2010) Risk and risk prediction error signals in anterior insula. Brain Struct Funct 214(5–6):645–653
Aron AR, Poldrack RA (2005) The cognitive neuroscience of response inhibition: relevance for genetic research in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Biol Psychiatry 57(11):1285–1292
Kadota H, Sekiguchi H, Takeuchi S, Miyazaki M, Kohno Y, Nakajima Y (2010) The role of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in the inhibition of stereotyped responses. Exp Brain Res 203(3):593–600
Asahi S, Okamoto Y, Okada G, Yamawaki S, Yokota N (2004) Negative correlation between right prefrontal activity during response inhibition and impulsiveness: a fMRI study. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 254(4):245–251
Boehler CN, Appelbaum LG, Krebs RM, Hopf JM, Woldorff MG (2010) Pinning down response inhibition in the brain–conjunction analyses of the stop-signal task. Neuroimage 52(4):1621–1632
Blasi G, Goldberg TE, Weickert T, Das S, Kohn P, Zoltick B, Bertolino A, Callicott JH, Weinberger DR, Mattay VS (2006) Brain regions underlying response inhibition and interference monitoring and suppression. Eur J Neurosci 23(6):1658–1664
Wolf RC, Thomann PA, Sambataro F, Vasic N, Schmid M, Wolf ND (2012) Orbitofrontal cortex and impulsivity in borderline personality disorder: an MRI study of baseline brain perfusion. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 262(8):677–685
Sheinkopf SJ, Lester BM, Sanes JN, Eliassen JC, Hutchison ER, Seifer R, Lagasse LL, Durston S, Casey BJ (2009) Functional MRI and response inhibition in children exposed to cocaine in utero. Preliminary findings. Dev Neurosci 31(1–2):159–166
Fryer SL, Tapert SF, Mattson SN, Paulus MP, Spadoni AD, Riley EP (2007) Prenatal alcohol exposure affects frontal-striatal BOLD response during inhibitory control. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 31(8):1415–1424
Menon V, Uddin LQ (2010) Saliency, switching, attention and control: a network model of insula function. Brain Struct Funct 214(5–6):655–667
Klein TA, Endrass T, Kathmann N, Neumann J, von Cramon DY, Ullsperger M (2007) Neural correlates of error awareness. Neuroimage 34(4):1774–1781
Botvinick MM (2007) Conflict monitoring and decision making: reconciling two perspectives on anterior cingulate function. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 7(4):356–366
Agam Y, Joseph RM, Barton JJ, Manoach DS (2010) Reduced cognitive control of response inhibition by the anterior cingulate cortex in autism spectrum disorders. Neuroimage 52(1):336–347
Seeley WW, Menon V, Schatzberg AF, Keller J, Glover GH, Kenna H, Reiss AL, Greicius MD (2007) Dissociable intrinsic connectivity networks for salience processing and executive control. J Neurosci 27(9):2349–2356
Anderson BM, Stevens MC, Meda SA, Jordan K, Calhoun VD, Pearlson GD (2011) Functional imaging of cognitive control during acute alcohol intoxication. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 35(1):156–165
Klein TA, Ullsperger M, Danielmeier C (2013) Error awareness and the insula: links to neurological and psychiatric diseases. Front Hum Neurosci 7:14
Li CS, Luo X, Yan P, Bergquist K, Sinha R (2009) Altered impulse control in alcohol dependence: neural measures of stop signal performance. Alcohol Clin Exp Res 33(4):740–750
Zhou Y, Lin FC, Du YS, Qin LD, Zhao ZM, Xu JR, Lei H (2011) Gray matter abnormalities in Internet addiction: a voxel-based morphometry study. Eur J Radiol 79(1):92–95
Katsyri J, Hari R, Ravaja N, Nummenmaa L (2013) The opponent matters: elevated fMRI reward responses to winning against a human versus a computer opponent during interactive video game playing. Cereb Cortex 23(12):2829–2839
Acknowledgments
The present study was supported by Grants from the National Science Council, Taiwan (NSC 98-2410-H-037-007), and the Kaohsiung Municipal Hsiao-Kang Hospital (KMHK-98-001).
Conflict of interest
Dr. Chih-Hung Ko received research grants from the National Science Council, Kaohsiung Medical University, and Kaohsiung Municipal Hsiao-Kang Hospital. These institutions had no role in the design, process, analyses, and production of the present study. The other authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ko, CH., Hsieh, TJ., Chen, CY. et al. Altered brain activation during response inhibition and error processing in subjects with Internet gaming disorder: a functional magnetic imaging study. Eur Arch Psychiatry Clin Neurosci 264, 661–672 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-013-0483-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00406-013-0483-3