Abstract
Purpose
Arterial stiffness, represented by estimated pulse wave velocity (ePWV), is the independent surrogate marker for cardiovascular event. The aim of the study was to investigate the significance of ePWV in the treatment outcome of idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss (SSNHL).
Methods
One hundred and ten patients with idiopathic SSNHL who hospitalized between April 2019 and March 2022 were evaluated. Arterial stiffness was calculated with formula for ePWV and other cardiovascular parameters of body mass index (BMI), and serum lipid level was determined. All patients received systemic high-dose steroid therapy and intratympanic steroid injections as a salvage management. Treatment outcome was assessed at 6 months after treatment, and classified as recovery and nonrecovery groups according to hearing recovery.
Results
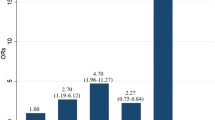
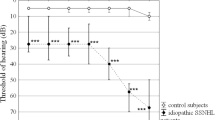
The initial pure-tone hearing threshold was 72.6 ± 23.8 dB and final hearing threshold was 52.63 ± 31.10 dB. After treatment, 60 (54.5%) patients included in recovery group and other 50 (45.5%) were classified as nonrecovery group. Age, days of onset to treatment, BMI, waist circumference, and ePWV were higher in the nonrecovery group compared to recovery group in univariate analysis (p = 0.039, p = 0.049, p = 0.003, p = 0.004, p = 0.007, respectively). In multivariate analysis, days of onset to treatment, BMI, and ePWV were associated with recovery (p = 0.030, p = 0.007, p = 0.022).
Conclusion
Higher ePWV, a measure of arterial stiffness, was associated with a poor hearing recovery of SSNHL.



Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The data supporting the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Kuhn M, Heman-Ackah SE, Shaikh JA, Roehm PC (2011) Sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a review of diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis. Trends Amplif 15:91–105
Chung JH, Cho SH, Jeong JH, Park CW, Lee SH (2015) Multivariate analysis of prognostic factors for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss in children. Laryngoscope 125:2209–2215
Jeong JY, Byun H, Lee SH, Chung JH (2023) Sudden hearing loss and vertigo with silent pontine infarction: a case report. J Audiol Otol. 27(4):240–245
Crowson MG, Mulder H, Cyr DD, Langman AW, Lee WT, Parham K, Pynnonen MA, Schulz K, Shin JJ, Witsell D (2018) Idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss is not a sentinel event for acute myocardial infarction. Otol Neurotol 39:e518
Byun H, Chung JH, Lee SH, Park CW, Park DW, Kim TY (2018) Clinical value of 4-hour delayed gadolinium-enhanced 3D FLAIR MR images in acute vestibular neuritis. Laryngoscope 128:1946–1951
Chung JH, Lee SH, Park CW, Kim C, Park JK, Shin JH (2016) Clinical significance of arterial stiffness in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 126:1918–1922
Capaccio P, Ottaviani F, Cuccarini V, Bottero A, Schindler A, Cesana BM, Censuales S, Pignataro L (2007) Genetic and acquired prothrombotic risk factors and sudden hearing loss. Laryngoscope 117:547–551
Lin RJ, Krall R, Westerberg BD, Chadha NK, Chau JK (2012) Systematic review and meta-analysis of the risk factors for sudden sensorineural hearing loss in adults. Laryngoscope 122:624–635
Byun H, Chung JH, Lee SH (2020) Clinical implications of posterior semicircular canal function in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Sci Rep 10:1–8
Vlachopoulos C, Aznaouridis K, Stefanadis C (2010) Prediction of cardiovascular events and all-cause mortality with arterial stiffness: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J Am Coll Cardiol 55:1318–1327
Collaboration RVfAS, (2010) Determinants of pulse wave velocity in healthy people and in the presence of cardiovascular risk factors:‘establishing normal and reference values.’ Eur Heart J 31:2338–2350
Jadhav UM, Kadam N (2005) Non-invasive assessment of arterial stiffness by pulse-wave velocity correlates with endothelial dysfunction. Indian Heart J 57:226–232
Greve SV, Blicher MK, Kruger R, Sehestedt T, Gram-Kampmann E, Rasmussen S, Vishram JK, Boutouyrie P, Laurent S, Olsen MH (2016) Estimated carotid–femoral pulse wave velocity has similar predictive value as measured carotid–femoral pulse wave velocity. J Hypertens 34:1279–1289
Suh MJ et al (2023) Improving accuracy and reliability of hearing tests: an exploration of international standards. J Audiol Otol 27(4):169–180
Chau JK, Lin JR, Atashband S, Irvine RA, Westerberg BD (2010) Systematic review of the evidence for the etiology of adult sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Laryngoscope 120:1011–1021
Jung SY, Shim HS, Hah YM, Kim SH, Yeo SG (2018) Association of metabolic syndrome with sudden sensorineural hearing loss. JAMA Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surg 144:308–314
Haynes DS, O’Malley M, Cohen S, Watford K, Labadie RF (2007) Intratympanic dexamethasone for sudden sensorineural hearing loss after failure of systemic therapy. Laryngoscope 117:3–15
Marcucci R, Alessandrello Liotta A, Cellai A, Rogolino A, Berloco P, Leprini E, Pagnini P, Abbate R, Prisco D (2005) Cardiovascular and thrombophilic risk factors for idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. J Thromb Haemost 3:929–934
Ciccone MM, Cortese F, Pinto M, Di Teo C, Fornarelli F, Gesualdo M, Mezzina A, Sabatelli E, Scicchitano P, Quaranta N (2012) Endothelial function and cardiovascular risk in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Atherosclerosis 225:511–516
Aimoni C, Bianchini C, Borin M, Ciorba A, Fellin R, Martini A, Scanelli G, Volpato S (2010) Diabetes, cardiovascular risk factors and idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a case-control study. Audiol Neurotol 15:111–115
Cruickshank K, Riste L, Anderson SG, Wright JS, Dunn G, Gosling RG (2002) Aortic pulse-wave velocity and its relationship to mortality in diabetes and glucose intolerance: an integrated index of vascular function? Circulation 106:2085–2090
Laurent S, Boutouyrie P, Asmar R, Gautier I, Laloux B, Guize L, Ducimetiere P, Benetos A (2001) Aortic stiffness is an independent predictor of all-cause and cardiovascular mortality in hypertensive patients. Hypertension 37:1236–1241
Vlachopoulos C, Terentes-Printzios D, Laurent S, Nilsson PM, Protogerou AD, Aznaouridis K, Xaplanteris P, Koutagiar I, Tomiyama H, Yamashina A (2019) Association of estimated pulse wave velocity with survival: a secondary analysis of SPRINT. JAMA Netw Open 2:e1912831–e1912831
Greve SV, Laurent S, Olsen MH (2016) Estimated pulse wave velocity calculated from age and mean arterial blood pressure. Pulse 4:175–179
Lawrence M (1982) Structure and function of the ear and auditory nervous system. Environ Health Perspect 44:9–13. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.82449
Tinazli R, Tinazli M (2022) Detection and grading of early-stage cochlear damage in land hunters by comparison of extended high-frequency audiograms with conventional high-frequency audiograms. J Audiol Otol 26:83–89. https://doi.org/10.7874/jao.2021.00605
Rudack C, Langer C, Stoll W, Rust S, Walter M (2006) Vascular risk factors in sudden hearing loss. Thromb Haemost 95:454–461
Keller JJ, Wu C-S, Kang J-H, Lin H-C (2013) Association of acute myocardial infarction with sudden sensorineural hearing loss: a population-based case-control study. Audiol Neurotol 18:3–8
Lin C, Lin SW, Lin YS, Weng SF, Lee TM (2013) Sudden sensorineural hearing loss is correlated with an increased risk of acute myocardial infarction: a population-based cohort study. Laryngoscope 123:2254–2258
Kim J-Y, Hong JY, Kim D-K (2018) Association of sudden sensorineural hearing loss with risk of cardiocerebrovascular disease: a study using data from the Korea National Health Insurance Service. JAMA Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surgery 144:129–135
Chang Y, Park S, Lee M, Rah Y, Choi J (2020) Framingham risk score is associated with hearing outcomes in patients with idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. J Laryngol Otol 134:419–423
Hwang JH, Wu CC, Hsu CJ, Liu TC, Yang WS (2009) Association of central obesity with the severity and audiometric configurations of age-related hearing impairment. Obesity 17:1796–1801
Hwang J-H (2015) Role of obesity on the prognosis of sudden sensorineural hearing loss in adults. Otolaryngol-Head Neck Surgy 153:251–256
Lalwani AK, Katz K, Liu YH, Kim S, Weitzman M (2013) Obesity is associated with sensorineural hearing loss in adolescents. Laryngoscope 123:3178–3184
Funding
This work was supported by a grant from the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare, Republic of Korea (Grant number: HI21C1574).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
None reported.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Hanyang University Guri Hospital (IRB FILE No: 2022-06-036.)
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, H.W., Ko, S.H., Chung, J.H. et al. A prognostic value of estimated pulse wave velocity in idiopathic sudden sensorineural hearing loss. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 281, 1745–1751 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-08289-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-023-08289-y