Abstract
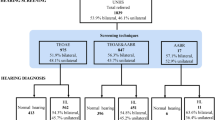
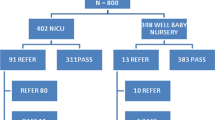
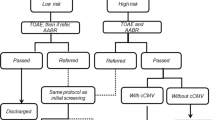
The objective of this work was to evaluate the prevalence of sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) and distribution of the main risk factors associated to it focusing on their role in the development of deafness and their interaction. We performed a global audiological assessment (through TEOAE, tympanometry and ABR) in 508 infants at risk studying the main risk factors reported by Joint Committee on Infant Hearing (2007). Fifty-one infants (10.03 %) were diagnosed with SNHL (45 bilateral and 6 unilateral) with a mean hearing threshold of 87.39 ± 28.25 dB HL; family history of hearing impairment (HI) and TORCH infections indicated independent significant risk factors (P < 0.00001 and P = 0.024, respectively). High SNHL percentages were evidenced also in NICU babies, due to the various pathologies and risk factors presented by these infants, and among newborns who suffered from hyperbilirubinemia (11.97 and 9.52 %, respectively). The mean degree of hearing loss for children with family history of HI (>100 dB HL) emphasizes the necessity of an early diagnosis to avoid the consequences of auditory deprivation. Craniofacial abnormalities and syndromes associated to HI showed an important relationship (P < 0.00001) with conductive hearing loss. A progressive increase was evidenced in SNHL incidence as the number of risk factors rises (from 5.12 for 2 risk factors to 28.5 % for 5 or more) with a significant difference among the groups (P = 0.049); multiple risk factors showed an additional cofactor for HL (r 2 = 0.93). Considering the high SNHL prevalence (10.03 %) in infants at risk, this study highlights the necessity to implement a neonatal hearing screening program in Western Sicily.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fortnum HM (2003) Epidemiology of permanent childhood hearing impairment: implication for neonatal hearing screening. Audiol Med 1:155–164
Declau F, Boudewyns A, Van den Ende J, Peeters A, van den Heyning P (2008) Etiologic and audiologic evaluations after universal neonatal hearing screening: analysis of 170 referred neonates. Pediatrics 121:1119–1126
Yoshinaga-Itano C, Coulter D, Thomson V (2000) The Colorado Newborn Hearing Screening Project: effects on speech and language development for children with hearing loss. J Perinatol 20:S132–S137
Moeller MP (2000) Early intervention and language development in children who are deaf and hard of hearing. Pediatrics 106:E43
American Academy of Pediatrics (2007) Joint Committee on Infant Hearing. Year 2007 position statement: principles and guidelines for early hearing detection and intervention programs. Pediatrics 120:898–921
American academy of Pediatrics (1982) Joint Committee on Infant Hearing. Position Statement 1982. Pediatrics 70:496–497
Nield TA, Schreir S, Ramos AD, Platzker D, Warburton ACG (1986) Unexpected hearing loss in high-risk infants. Pediatrics 78:417–422
Salamy A, Eldredge L, Tooley WH (1989) Neonatal status and hearing loss in high-risk infants. J Pediatr 114:847–852
Borradori C, Fawer CL, Baclin T, Calame A (1997) Risk factors of sensorineural hearing loss in preterm infants. Biol Neonate 71:1–10
Borg E (1997) Perinatal asphyxia, hypoxia, ischemia, and hearing loss: an overview. Scand Audiol 26:77–91
American Academy of Pediatrics, Committee on Environmental Health (1997) Noise: a hazard for the fetus and newborn. Pediatrics 100:724–727
Marlow ES, Hunt LP, Marlow N (2000) Sensorineural hearing loss and prematurity. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal 82:F141–F144
Fanaroff JM, Wilson-Costell DE, Newman NS, Montpetite MM, Fanaroff AA (2006) Treated hypotension is associated with neonatal morbidity and hearing loss in extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics 117:1131–1135
Hille ETM, van Straaten HLM, Verlerk PH (2007) Dutch NICU Neonatal Hearing Screening Working Group. Prevalence and independent risk factors for hearing loss in NICU infants. Acta Paediatr 96:1155–1158
Vander Werff KR, Prieve BA, Georgantas LM (2009) Infant air and bone conduction tone burst auditory brain stem responses for classification of hearing loss and the relationship to behavioral thresholds. Ear Hear 30:350–368
Martines F, Porrello M, Ferrara M, Martines M, Martines E (2007) Newborn hearing screening project using transient evoked otoacoustic emissions: Western Sicily experience. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 71:107–112
Martines F, Bentivegna D, Ciprì S, Costantino C, Marchese D, Martines E (2012) On the threshold of effective well infant nursery hearing screening in Western Sicily. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 76:423–427
Martines F, Salvago P, Bentivegna D, Bartolone A, Dispenza F, Martines E (2012) Audiologic profile of infants at risk: experience of a Western Sicily tertiary care centre. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 76:1285–1291
Ohl C, Dornier L, Czajka C, Chobaut JC, Tavernier L (2009) Newborn hearing screening on infants at risk. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 73:1691–1695
Meyer C, Witte J, Hildmann A, Hennecke KH, Schunck KU, Maul K, Franke U, Fahnenstich H, Rabe H, Rossi R, Hartmann S, Gortner L (1999) Neonatal screening for hearing disorders in infants at risk: incidence, risk factors, and follow-up. Pediatrics 104:900–904
Robertson CM, Howarth TM, Bork DL, Dinu IA (2009) Permanent bilateral sensory and neural hearing loss of children after neonatal intensive care because of extreme prematurity: a thirty-year study. Pediatrics 123:e797–e807
Elahi MM, Elahi F, Elahi A, Elahi SB (1998) Paediatric hearing loss in rural Pakistan. J Otolaryngol 27:348–353
Martines E, Amodeo AM, Grisanti S, Martines F (2000) Sordità ereditaria recessiva nella Sicilia occidentale: studio epidemiologico su tre coorti. Acta Medica Mediterranea 16:19–22
Picciotti PM, Pietrobono R, Neri G, Paludetti G, Fetoni AR, Cianfrone F, Pomponi MG (2009) Correlation between GJB2 mutations and audiological deficits: personal experience. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 266:489–494
Jakubíková J, Kabátová Z, Pavlovcinová G, Profant M (2009) Newborn hearing screening and strategy for early detection of hearing loss in infants. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 73:607–612
Grosse SD, Ross DS, Dollard SC (2008) Congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) infection as a cause of permanent bilateral hearing loss: a quantitative assessment. J Clin Virol 41:57–62
Barbi M, Binda S, Caroppo S, Primache V (2006) Neonatal screening for congenital cytomegalovirus infection and hearing loss. J Clin Virol 35:206–209
Madden C, Wiley S, Schleiss M, Benton C, Meinzen-Derr J, Greinwald J, Choo D (2005) Audiometric, clinical and educational outcomes in a pediatric symptomatic congenital cytomegalovirus (CMV) population with sensorineural hearing loss. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 69:1191–1198
Mussi-Pinhata MM, Yamamoto AY, Moura Brito RM, de Lima Isaac M, de Carvalho e Oliveira PF, Boppana S, Britt WJ (2009) Birth prevalence and natural history of congenital cytomegalovirus infection in a highly seroimmune population. Clin Infect Dis 49:522–528
Van Naarden K, Decouflé P, Caldwell K (1999) Prevalence and characteristics of children with serious hearing impairment in metropolitan Atlanta, 1991–1993. Pediatrics 103:570–575
Davis AC, Parving A (1993) Towards appropriate epidemiological data on childhood hearing disability: a comparative European study of birth cohorts. J Audiol Med 3:35–47
Sutton GJ, Rowe SJ (1997) Risk factors for childhood sensorineural hearing loss in the Oxford region. Br J Audiol 31:39–54
Shiu J, Purvis M, Sutton G (1996) Detection of childhood hearing impairment in the Oxford Region. Report of the Regional audit project. Oxfordshire RHA, Oxford
Fortnum H, Davis A (1997) Epidemiology of permanent childhood hearing impairment in Trent Region, 1985–1993. Br J Audiol 31:409–446
Pitt T (1995) Management and outcome: children fitted with hearing aids in Ireland. Br J Audiol 29:199–207
Coenraad S, Goedegebure A, Hoeve LJ (2011) An initial overestimation of sensorineural hearing loss in NICU infants after failure on neonatal hearing screening. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 75:159–162
Dauman R, Roussey M, Belot V, Denoyelle F, Roman S, Gavilan-Cellié I (2009) Screening to detect permanent childhood hearing impairment in neonates transferred from the newborn nursery. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 73:457–465
Leslie GI, Kalaw MB, Bowen JR, Arnold JD (1995) Risk factors for sensorineural hearing loss in extremely premature infants. J Paediatr Child Health 31:312–316
Bielecki I, Horbulewicz A, Wolan T (2011) Risk factors associated with hearing loss in infants: an analysis of 5282 referred neonates. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 75:925–930
Kwan WM, Abdullah VJ, Liu K, van Hasselt CA, Tong MC (2011) Otitis media with effusion and hearing loss in chinese children with cleft lip and palate. Cleft Palate Craniofac J 48:684–689
Sheahan P, Miller I, Sheahan JN, Earley MJ, Blayney AW (2003) Incidence and outcome of middle ear disease in cleft lip and/or cleft palate. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 67:785–793
Park AH, Wilson MA, Stevens PT, Harward R, Hohler N (2012) Identification of hearing loss in pediatric patients with Down syndrome. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 146:135–140
McPherson B, Lai SP, Leung KK, Ng IH (2007) Hearing loss in Chinese school children with Down syndrome. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 71:1905–1915
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salvago, P., Martines, E. & Martines, F. Prevalence and risk factors for sensorineural hearing loss: Western Sicily overview. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270, 3049–3056 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2379-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-013-2379-2