Abstract
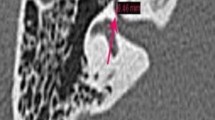
Facial nerve edema is an important finding in Bell’s palsy patients. Inflammation may cause facial nerve edema, and mechanical compression and ischemic change of the facial nerve may occur in the facial nerve canal. A few studies have reported the dimensions of the facial nerve canal using conventional computed tomography or human temporal bone sections. However, the cross-sectional area of the facial nerve canal has not been fully understood. Therefore, the cross-sectional area of the facial nerve canal was measured in patients with unilateral Bell’s palsy by computer tomography with multiplanar reconstruction. Sixteen patients with unilateral Bell’s palsy were enrolled. Computed tomography of the temporal bone was performed, and perpendicular images to the facial nerve canal were reconstructed by the multiplanar reconstruction technique. The cross-sectional area of the facial nerve canal on the affected and unaffected sides was measured at the labyrinthine segment, the horizontal segment, and the mastoid segment. Both in the labyrinthine and horizontal segments, the mean cross-sectional area of the facial nerve canal was significantly smaller on the affected side than on the unaffected side. There was no significant difference between the affected and unaffected sides in the cross-sectional area of the facial nerve canal in the mastoid segment. The labyrinthine segment was the narrowest segment in the facial nerve canal. These findings suggest that the facial nerve is vulnerable, especially in the labyrinthine segment of the facial nerve canal, and a narrow facial nerve canal may be one of the risk factors for Bell’s palsy.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yanagihara N, Honda N, Hato N, Murakami S (2000) Edematous swelling of the facial nerve in Bell’s palsy. Acta Otolaryngol 120:667–671
Kefalidis G, Riga M, Argyropoulou P, Katotomichelakis M, Gouveris C, Prassopoulos P, Danielides V (2010) Is the width of the labyrinthine portion of the fallopian tube implicated in the pathophysiology of Bell’s palsy? A prospective clinical study using computed tomography. Laryngoscope 120:1203–1207
Wadin K, Thomander L, Wilbrand H (1987) The labyrinthine portion of the facial canal in patients with Bell’s palsy investigated by computed tomography. Acta Radiol 28:25–30
Eicher SA, Coker NJ, Alford BR, Igarashi M, Smith RJ (1990) A comparative study of the fallopian canal at the meatal foramen and labyrinthine segment in young children and adults. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 116:1030–1035
Watanabe Y, Sugai Y, Hosoya T, Yamaguchi K, Aoyagi M (2000) High-resolution computed tomography using multiplanar reconstruction for the facial nerve canal. Acta Otolaryngol Suppl 542:44–48
May M, Schaitkin B (2000) The facial nerve, 2nd edn. Thieme Medical, New York
Sugita T, Murakami S, Yanagihara N, Fujiwara Y, Hirata Y, Kurata T (1995) Facial nerve paralysis induced by herpes simplex virus in mice: an animal model of acute and transient facial paralysis. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 104:574–581
Honda N, Hato N, Takahashi H, Wakisaka H, Kisaki H, Murakami S, Gyo K (2002) Pathophysiology of facial nerve paralysis induced by herpes simplex virus type 1 infection. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 111(7 Pt 1):616–622
Takahashi H, Hitsumoto Y, Honda N, Hato N, Mizobuchi M, Murakami S, Kisaki H, Wakisaka H, Gyo K (2001) Mouse model of Bell’s palsy induced by reactivation of herpes simplex virus type 1. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 60:621–627
Nakashima S, Sando I, Takahashi H, Fujita S (1993) Computer-aided 3-D reconstruction and measurement of the facial canal and facial nerve. I. Cross-sectional area and diameter: preliminary report. Laryngoscope 103:1150–1156
Ogawa A, Sando I (1982) Spatial occupancy of vessels and facial nerve in the facial canal. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 91(1 Pt 1):14–19
Ni Y, Sha Y, Dai P, Li H (2008) Quantitative morphology of facial nerve based on three-dimensional reconstruction of temporal bone. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 138:23–29
Fatterpekar GM, Doshi AH, Dugar M, Delman BN, Naidich TP, Som PM (2006) Role of 3D CT in the evaluation of the temporal bone. Radiographics 26(Suppl 1):S117–S132
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by Grants-in-Aid for Scientific Research from The Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest, and have no financial relationship to other organizations.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Murai, A., Kariya, S., Tamura, K. et al. The facial nerve canal in patients with Bell’s palsy: an investigation by high-resolution computed tomography with multiplanar reconstruction. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 270, 2035–2038 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2253-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-012-2253-7