Abstract
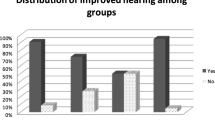
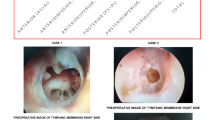
The objective of this study is to determine the subjective and objective outcomes of tympanoplasty surgery carried out in patients with otitis media and to identify factors responsible for these outcomes. The study setting is tertiary care urban referral hospital in a developing economy and the study methodology is a prospective analysis of patients with diagnosis of chronic suppurative otitis media that had tympanoplasty with or without mastoidectomy between May 2005 and September 2009 at National Hospital Abuja. Subjects were evaluated for age, sex, size and site of perforation, status of operated ear(s) (dry/discharging), status of the contralateral ear, surgical technique, subjective and objective pre-operative and post-operative hearing scores, average post-operative follow-up time, and post-operative complications, and results were statistically analyzed. A total of 45 patients (51 ears) were operated. Age distribution was 8–52 years. Type 1 tympanoplasty was done in 41 patients and Type 3 in 4 patients. Seven of the patient had concomitant mastoid surgery (cortical mastoidectomy). 3/51 of the cases had discharging ears at surgery. 16/45 of the patients (19/51 ears) had cartilage graft tympanoplasty, while 29/45 (32 ears) had temporalis fascia tympanoplasty. 15/16 of the cartilage group as well as 26/29 of the fascia group reported subjective hearing improvement, whilst the actual graft take was 12/16 of the cartilage group and 23/29 of the fascia group. Objective hearing improvement was observed in all of the cartilage as well as 26/29 of the fascia group. This study confirms success of tympanoplasty among Nigerians, and recommends that subjective hearing assessment should form part of indicators for success following tympanoplasty.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Olatoke F, Ologe FE, Nwawolo CC, Saka MJ (2008) The prevalence of hearing loss among schoolchildren with chronic suppurative otitis media in Nigeria, and its effect on academic performance. Ear Nose Throat J 87(12):E19
Olusesi AD (2008) Otitis media as a cause of significant hearing loss among Nigerians. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 72(6):787–792
Westerberg BD, Lee PK, Lukwago L, Zaramba S, Bubikere S, Stewart I (2008) Cross-sectional survey of hearing impairment and ear disease in Uganda. J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 37(6):753–758
Prescott CAJ, Robartes WJ (1991) Tympanoplasty surgery at the Red Cross War Memorial Children’s Hospital 1986–1988. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 21(3):227–234
Lasisi AO (2007) Hearing outcome after canal wall down mastoidectomy and Wullstein type III tympanoplasty. East Cent Afr J Surg 12(2):44–47
Ogisi FO, Adobamen P (2004) Type 1 tympanoplasty in Benin: a 10-year review. Niger Postgrad Med J 11(2):84–87
Olusesi AD (2009) Type 1 tympanoplasty. In: Olusesi AD (ed) A short/introduction to ear surgery. Murak Press, Abuja, pp 95–105
Zoellner F (1955) The principle of plastic surgery of the sound conducting apparatus. J Laryngol Otol 69:567–569
Wullstein HL (1952) Functional operations in the middle ear with split thickness skin graft. Arch Otorhinolaryngol 161:422–435
Uyar Y, Keles B, Koç S, Oztürk K, Arbag H (2006) Tympanoplasty in pediatric patients. Int J Pediatr Otorhinolaryngol 70(10):1805–1809
Merenda D, Koike K, Shafiei M, Ramadan H (2007) Tympanometric volume: a predictor of success of tympanoplasty in children. Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 136(2):189–192
Caye-Thomasen P, Nielsen TR, Tos M (2007) Bilateral myringoplasty in chronic otitis media. Laryngoscope 117(5):903–906
Cavalier M, Mottola G, Rondinelli M, Lemma M (2009) Tragal cartilage in tympanoplasty: anatomic and functional results in 306 cases. Acta Otolaryngol Ital 29(1):27–32
Tos M (1976) Late results in tympanoplasty. Staging the operation. Acta Otolaryngol 82(3-4):282–285
Mutoh T, Adachi O, Tsuji K, Okunaka M, Sakagami M (2007) Efficacy of mastoidectomy on MRSA-infected chronic otitis media with tympanic membrane perforation. Auris Nasus Larynx 34(1):9–13
Yuen AP, Ho WK, Hui Y, Wei WI, Au DK (2000) Correlation of pure tone audiogram results and hearing benefit of tympanoplasty for chronic suppurative otitis media. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 109(4):381–384
Conflict of Interest
None of the authors has any conflict of interest regarding subject of this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Olusesi, A.D., Opaluwah, E. & Hassan, S.B. Subjective and objective outcomes of tympanoplasty surgery at National Hospital Abuja, Nigeria 2005–2009. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol 268, 367–372 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-010-1405-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00405-010-1405-x