Abstract
Purpose
Endometriosis is a prevalent disease that affects 5–15 % of women of reproductive age. The aim of this study is to assess the effect of dienogest in the treatment of endometriosis.
Methods
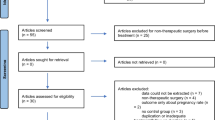
The search was applied to electronic databases PubMed, Cochrane, EMBASE and Lilacs until September 2014, in a public tertiary hospital. We performed a systematic literature search of randomized trials comparing dienogest to other medical therapies in the treatment of endometriosis, as well as their references list, using the keywords “dienogest” and “endometriosis” by two independent authors. The data extraction were performed by two authors using predefined data fields. Nine randomized trials were included. Dienogest 2 mg/day was superior to placebo in reducing pelvic pain (27.4 versus 15.1 mm, P < 0.0001), with similar results to buserelin, leuprorelin, leuprolide acetate and triptorelin, in controlling symptoms associated with endometriosis. Dienogest 2 mg/day was effective in reducing endometriotic lesions (11.4 ± 1.71–3.6 ± 0.95, P < 0.001). The extended therapy with dienogest 2 mg/day also showed an improvement in pelvic pain after 24–52 weeks (−22.5 ± 32.1 and −28.4 ± 29.9 mm, respectively) with tolerable side effects.
Conclusion
Dienogest should be considered as an alternative for controlling symptoms related to endometriosis. Nevertheless, in this systematic review, no studies were found comparing dienogest with first-line therapy, such as progestins and estrogen–progestogen combinations, which are proved to be effective in the treatment of endometriosis, are less expensive, and also can be used for contraception.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Halis G, Mechsner S, Ebert AD (2010) The diagnosis and treatment of deep infiltrating endometriosis. Dtsch Arztebl Int 107(25):446–455 (Quiz 456)
Bellelis P, Dias JA Jr, Podgaec S et al (2010) Aspectos epidemiológicos e clínicos da endometriose pélvica-uma série de casos (Epidemiological and clinical aspects of pelvic endometriosis—a case series). Rev Assoc Med Bras 56(4):467–471
Berbel BT, Podgaec S, Abrao MS (2008) Análise da associação entre o quadro clínico referido pelas pacientes portadoras de endometriose e o local de acometimento da doença (Analysis of the association between symptoms referred by patients with endometriosis and the site of the disease). Rev Med (São Paulo) 87(3):195–200
Podgaec S, Rizzo LV, Fernandes LF et al (2012) CD4(+) CD25(high) Foxp3(+) cells increased in the peritoneal fluid of patients with endometriosis. Am J Reprod Immunol 68(4):301–308
Vercellini P, Crosignani P, Somigliana E et al (2011) Waiting for Godot’: a commonsense approach to the medical treatment of endometriosis. Hum Reprod 26(1):3–13
Goncalves MO, Podgaec S, Dias JA Jr, Gonzalez M, Abrao MS (2010) Transvaginal ultrasonography with bowel preparation is able to predict the number of lesions and rectosigmoid layers affected in cases of deep endometriosis, defining surgical strategy. Hum Reprod 25(3):665–671
Vercellini P, Eskenazi B, Consonni D et al (2011) Oral contraceptives and risk of endometriosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Hum Reprod Update 17(2):159–170
Olive DL, Pritts EA (2001) Treatment of endometriosis. N Engl J Med 345(4):266–275
Petta CA, Ferriani RA, Abrao MS et al (2005) Randomized clinical trial of a levonorgestrel-releasing intrauterine system and a depot GnRH analogue for the treatment of chronic pelvic pain in women with endometriosis. Hum Reprod 20(7):1993–1998
Crosignani P, Olive D, Bergqvist A, Luciano A (2006) Advances in the management of endometriosis: an update for clinicians. Hum Reprod Update 12(2):179–189
Sitruk-Ware R, Nath A (2010) The use of newer progestins for contraception. Contraception 82(5):410–417
Köhler G, Faustmann TA, Gerlinger C, Seitz C, Mueck AO (2010) A dose-ranging study to determine the efficacy and safety of 1, 2, and 4 mg of dienogest daily for endometriosis. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 108(1):21–25
Harada T, Momoeda M, Taketani Y et al (2009) Dienogest is as effective as intranasal buserelin acetate for the relief of pain symptoms associated with endometriosis–a randomized, double-blind, multicenter, controlled trial. Fertil Steril 91(3):675–681
Liberati A, Altman DG, Tetzlaff J, Mulrow C, Gøtzsche PC, Ioannidis JP et al (2009) The PRISMA statement for reporting systematic reviews and meta-analyses of studies that evaluate healthcare interventions: explanation and elaboration. BMJ 339:b2700
Revised American Society for Reproductive Medicine classification of endometriosis. Fertil Steril. 1997;67(5):817–21
Kamiński K, Fiegler P, Marr J, Moore C (2001) Treatment of endometriosis with dienogest: preliminary report. Ginekol Pol 72(5):299–304
Seitz C, Gerlinger C, Faustmann T et al (2009) Safety of dienogest in the long-term treatment of endometriosis: a one-year, open-label, follow-up study. Fertil Steril 92(3):107
Strowitzki T, Faustmann T, Gerlinger C, Seitz C (2010) Dienogest in the treatment of endometriosis-associated pelvic pain: a 12-week, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 151(2):193–198
Momoeda M, Taketani Y (2007) A randomized, double-blind, multicenter, parallel, dose-response study of dienogest in patients with endometriosis (in Japanese). J Pharmacol Ther 35:769–783
Cosson M, Querleu D, Donnez J et al (2002) Dienogest is as effective as triptorelin in the treatment of endometriosis after laparoscopic surgery: results of a prospective, multicenter, randomized study. Fertil Steril 77(4):684–692
Strowitzki T, Marr J, Gerlinger C, Faustmann T, Seitz C (2010) Dienogest is as effective as leuprolide acetate in treating the painful symptoms of endometriosis: a 24-week, randomized, multicentre, open-label trial. Hum Reprod 25(3):633–641
Strowitzki T, Marr J, Gerlinger C, Faustmann T, Seitz C (2012) Detailed analysis of a randomized, multicenter, comparative trial of dienogest versus leuprolide acetate in endometriosis. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 117(3):228–233
Petraglia F, Hornung D, Seitz C et al (2012) Reduced pelvic pain in women with endometriosis: efficacy of long-term dienogest treatment. Arch Gynecol Obstet 285(1):167–173
Momoeda M, Harada T, Terakawa N et al (2009) Long-term use of dienogest for the treatment of endometriosis. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 35(6):1069–1076
Johnson NP (2013) Hummelshoj L; World Endometriosis Society Montpellier Consortium. Consensus on current management of endometriosis. Hum Reprod 28(6):1552–1568
Vercellini P, Crosignani P, Somigliana E, Viganò P, Frattaruolo MP, Fedele L (2011) Waiting for Godot: a commonsense approach to the medical treatment of endometriosis. Hum Reprod 26:3–13
Crosignani PG, Luciano A, Ray A, Bergqvist A (2006) Subcutaneous depot medroxyprogesterone acetate versus leuprolide acetate in the treatment of endometriosis-associated pain. Hum Reprod 21:248–256
Taylor RN, Hummelshoj L, Stratton P (2012) Vercellini P Pain and endometriosis: etiology, impact, and therapeutics. Middle East Fertil Soc J 17(4):221–225
Brown J, Pan A, Hart RJ (2010) Gonadotrophin-releasing hormone analogues for pain associated with endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 12:CD008475
Brown J, Kives S, Akhtar M (2012) Progestagens and anti-progestagens for pain associated with endometriosis. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 3:CD002122
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Andres, M.d., Lopes, L.A., Baracat, E.C. et al. Dienogest in the treatment of endometriosis: systematic review. Arch Gynecol Obstet 292, 523–529 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-015-3681-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-015-3681-6