Abstract
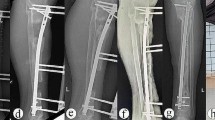
Rigid intramdullary nailing with cancellous bone grafting provided by intramedullary reaming was prospectively used to treat femoral shaft aseptic nonunions after plating. Indications for this technique were a femoral shaft nonunion with an inserted plate, no previous infection sign in the treatment course, less than 1.5 cm shortening, and no segmental bony defects. After the plate was removed, a flexible guidewire was inserted antegradely. The local wound was closed, and intramedullary reaming was done as widely as possible until some resistance to it occurred. Finally, a rigid intramedullary nail was inserted. Twenty-four consecutive patients were treated with this regimen, and 21 were followed-up for at least 1 year (range 1–5 years). All 21 nonunions healed with a union rate of 100% (21/21). The time to union was 4.5 ± 1.0 months. There were no significant complications. We conclude that for indicated cases, reaming bone grafting is a very effective technique and avoided donor site morbidity. Therefore, whenever possible, this technique could be considered first.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 2 October 1998
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wu, C., Shih, C., Chen, W. et al. Effect of reaming bone grafting on treating femoral shaft aseptic nonunion after plating. Arch Orth Traum Surg 119, 303–307 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004020050415
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004020050415