Abstract
Aim
Hip dysplasia is one of the most common skeletal disorders. As a late consequence 20–25% of the patients are at risk to develop secondary osteoarthritis and may require total hip replacement early in life. The treatment principles of hip dislocation are (1) concentric reposition, (2) retention, i.e., plaster in human post or Pavlik harness and (3) maturation in abduction flexion orthesis. The Tübingen splint was introduced as a further development of abduction devices for the treatment of (residual) hip dysplasia with stable hips. The advantages are easy handling, adjustment according to growth and safe limitation of abduction. The aim of this study was to determine the success of treatment of unstable hips with use of the Tübingen splint from early diagnosis until final end of therapy hence normal ultrasound findings.
Methods
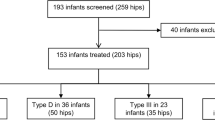
From January 2003 to August 2016 79 children with 109 sonographic unstable hips were treated with the Tübingen splint initially consequently 24 h/day. Inclusion criteria were diagnosis of type D, type III a/b or type IV hips according to Graf and beginning of treatment at an age of less or equal 6 weeks, without limitation of abduction on clinical examination.
Results
At the time of diagnosis 51 type D (46.8%), 46 type III (42.2%) and 12 type IV (11.0%) hips were noticed. In 30 patients (38.0%) bilateral hip dysplasia (type D–IV) was diagnosed. 104 of 109 hips (95.4%) treated with the Tübingen splint could be transferred in a type I hip after a mean treatment period of 88.9 days (SD ± 26.0). In 5 cases (4.6%, 1 type III and 4 type IV hips) the treatment failed.
Conclusion
Our data show, that successful treatment of unstable hips in neonates with the Tübingen splint is a comparably successful treatment modality relative to the Pavlik harness and Fettweis plaster.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schwend RM, Shaw BA (2014) Evaluation and treatment of developmental hip dysplasia in the newborn and infant. Pediatr Clin North Am 61:1095–1107
Tönnis D (1984) Die angeborene Hüftdysplasie und Hüftluxation. Springer, Berlin, pp 60–63
Edelstein J (1964) Congenital dislocation of the hip in the Bantu. J Bone Jt Surg (Br) 48:397
De Seze S, Lesquesne M, Barbannaud F (1962) La dysplasia at la subluxation congenitale de la hanche chez l’adulte; la coxarthrose secondaire a ces malformations; etude radiografique. Rev Rhum 29:293
Francillon MR, Debrunner HU (1957) Ortopädie der Coxarthrose. Doc Rheum Geigy Base 13
Günther KP, Stürmer T, Sauerland S (1998) Prevalence of generalized osteoarthritis: the Ulm Osteoarthritis Study. Ann Rheum Dis 57:717–723
Farr S, Grill F, Müller (2008) When is the optimal time for hip ultrasound screening? Orthopade 37:532, 534–536, 538–540
Graf R (2010) Sonographie der Säuglingshüfte und therapeutische Konsequenzen. Thieme, Stuttgart
Grill F, Müller D (1997) Results of hip ultrasonographic screening in Austria. Orthopade 26:25–32
Fettweis E (1968) Sitz-Hock-Stellungsgips bei Hüftgelenksdysplasien. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 63:38–51
Pavlik A (1957) Die funktionelle Behandlungs methode mittels Riemenbügel als Prinzip der konservativen Therapie bei angeborener Hüftverrenkung der Säuglinge. Z Orthop 89:341–352
Bernau A (1990) Die Tübinger Hüftbeugeschiene zur Behandlung der Hüftdysplasie. Z Orthop 128:432–435
Katthagen BD, Mittelmeier H, Becker D (1988) Incidence and start of inpatient treatment of pediatric hip dislocations in West Germany. Z Orthop Ihre Grenzgeb 126:475–483
Graf R (1997) Advantages and disadvantages of various access routes in sonographic diagnosis of dysplasia and luxation in the infant hip. J Pediatr Orthop B 6:248–252
Bensahel H, Csukonyi Z, Huguenin P (1988) Vascular disorders of the proximal femur following treatment of congenital hip dislocation. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 107:372–376
van der Sluijs JA, De Gier L, Verbeke JI et al (2009) Prolonged treatment with the Pavlik harness in infants with developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Bone Jt Surg Br 91:1090–1093
Walton MJ, Isaacson Z, McMillan D et al (2010) The success of management with the Pavlik harness for developmental dysplasia of the hip using a United Kingdom screening programme and ultrasound-guided supervision. J Bone Jt Surg Br 92:1013–1016
Zajonz D, Strobel S, Wojan M et al (2016) Pavlik harness for the treatment of congenital hip dysplasia types D III and IV. Orthopade 45(1):72–80
Seidl T, Lohmaier J, Hölker T et al (2012) Reduction of unstable and dislocated hips applying the Tübingen hip flexion splint? Orthopade 41:195–199
Pavone V, Testa G, Riccioli M, Evola FR, Avondo S, Sessa G (2015) Treatment of developmental dysplasia of hip with Tubingen hip flexion splint. J Pediatr Orthop 35(5):485–489
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Hannes Kubo, Hakan Pilge, Bettina Westhoff, Kristina Weimann–Stahlschmidt, Karoline Stefanovska and Ruediger Krauspe declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Sources of support, including pharmaceutical and industry support
No support.
Disclosure of funding received for this work
No funding.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards (Ethics committee vote of the University of Dusseldorf, study no. 4949).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kubo, H., Pilge, H., Weimann-Stahlschmidt, K. et al. Use of the Tübingen splint for the initial management of severely dysplastic and unstable hips in newborns with DDH: an alternative to Fettweis plaster and Pavlik harness. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 138, 149–153 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-017-2827-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-017-2827-3