Abstract
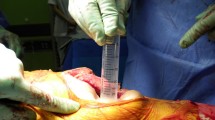
Earlier studies have found varying contamination rates using separate skin and deep knives in total hip (THA) and total knee (TKA) arthroplasty surgery. Previous studies were primarily conducted in the setting of concomitant use of laminar airflow and/or plastic adhesive draping. This has lead to conflicting conclusions regarding discarding the skin knife or not. This study evaluates the prevalence of contamination of a separate skin knife using modern antiseptic technique in primary THA and TKA without laminar airflow. Three knives from each primary THA and TKA surgery in non-laminar airflow operating rooms were collected: one used for the skin, one used for deeper tissues and one control knife. A total of 831 knife blades from 277 patients were cultured 12 days. Contamination of the skin knife was found in eight patients (2.8 %), contamination of the “deep” knife in five patients (1.8 %) and contamination of the control knife in five patients (1.8 %). No patient developed an infection with 1-year follow-up. Our findings suggest a very low rate of contamination of the skin knife using modern antiseptic technique without laminar airflow and/or plastic adhesive draping and do not support the use of a separate skin knife in arthroplasty surgery.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Pulido Luis, Ghanem Elie, Joshi Ashish, Purtill James J, Parvizi Javad (2008) FRCS, periprosthetic joint infection: the incidence, timing, and predisposing factors. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466:1710–1715
Grabe N, Falstie-Jensen S, Fredberg U, Schrøder H, Sørensen I (1985) The contaminated skin-knife: fact or fiction. J Hosp Infect 6:252–256
Jacobs HB (1974) Skin knife-deep knife: the ritual and practice of skin incisions. An Surg 179(1):102–104
Hooper GJ, Rothwell AG, Frampton C, Wyatt MC (2011) Does the use of laminar flow and space suits reduce early deep infection after total hip and knee replacement? The ten-year results of the New Zealand Joint Registry. J Bone Joint Surg Br 93(1):85–90
Webster J, Alghamdi A (2007) Use of plastic adhesive drapes during surgery for preventing surgical site infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 4:CD006353. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD006353.pub2
AlBuhairan B, Hind D, Hutchinson A (2008) Antibiotic prophylaxis for wound infections in total joint arthroplasty: a systematic review. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90(7):915–919
Lidwell OM, Lowbury EJ, Whyte W, Blowers R, Stanley SJ, Lowe D (1982) Effect of ultraclean air in operating rooms on deep sepsis in the joint after total hip or knee replacement: a randomised study. Br Med J 285:10–14 (Clin Res Ed)
Fairclough JA, Mackie IG, Mintowt-czyz W, Phillips GE (1983) The contaminated skin-knife: a surgical myth. J Bone Joint Surg Br 65(2):210
Ramón R, García S, Combalia A, Puig de la Bellacasa J, Segur JM (1994) Bacteriological study of surgical knives: is the use of two blades necessary? Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 113:157–158
Ritter MA, French ML, Eitzen HE (1975) Bacterial contamination of the surgical knife. Clin Orth 108:158–160
Hill R, Blair S, Neely J, Ramanathan M (1985) Changing knives a wasteful and unnecessary ritual. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 67(3):149–151
Schindler OS, Spencer RF, Smith MD (2006) Should we use a separate knife for the skin? J Bone Joint Surg Br 88(3):382–385
Davis N, Curry A, Gambhir AK et al (1999) Intraoperative bacterial contamination in operations for joint replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 81(5):886–889
Tanner J, Norrie P, Melen K (2011) Preoperative hair removal to reduce surgical site infection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 11:CD004122. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD004122.pub4
Van Kasteren ME, Manniën J, Ott A, Kullberg BJ, de Boer AS, Gyssens IC (2007) Antibiotic prophylaxis and the risk of surgical site infections following total hip artroplasty timely administration is the most important factor. Clin Infect Dis 44(7):921–927
Dumville JC, McFarlane E, Edwards P, Lipp A, Holmes A (2013) Preoperative skin antiseptics for preventing surgical wound infections after clean surgery. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 3:CD003949. doi:10.1002/14651858.CD003949.pub3
Tejwani NC, Immerman Igor (2008) Myths and legends in orthopaedic practice—are we all guilty? Clin Orthop Relat Res 466(11):2861–2872
Conflict of interest
No benefits in any form have been received or will be received from a commercial party related directly or indirectly to the subject of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ottesen, C., Skovby, A., Troelsen, A. et al. No need to change the skin knife in modern arthroplasty surgery. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134, 1163–1166 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-014-1974-z
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-014-1974-z