Abstract
Introduction
Poor long-term results of total hip arthroplasty (THA) can result from femoral component misalignment. There are few reports that discuss the effectiveness of intraoperative radiographs for placing femoral components. This study is a retrospective review to find out the usefulness of intraoperative radiographs in detecting and improving the femoral component misalignment in posterior-approached primary THA.
Materials and methods
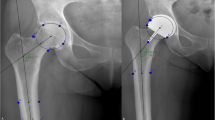
The study group included 150 primary THAs performed between September 2009 and April 2012. After the trial component insertion in lateral decubitus position, intraoperative radiography was performed. The surgeon assessed the femoral component position in three aspects: alignment, leg length, and offset. If it is not following the preoperative template, the surgeon makes the intraoperative adjustments to change the femoral component position. After the operation, postoperative radiograph was taken; the same parameters were measured and were compared to intraoperative findings. The changes in each parameter were classified into three categories: satisfactory, no change, and unsatisfactory. Among the three parameters, if one is satisfactory and the others are not unsatisfactory, we defined it as accurate positioning of the femoral component.
Results
Intraoperative adjustments were made in 122 cases (81.3 %). The adjustments included changes in the component size (35.3 %), component alignment (38.6 %), femoral offset (14.0 %), and additional femoral neck cuts (56.0 %). As a result, accurate positioning was successfully achieved in 112 cases (91.8 %) by taking intraoperative radiographs.
Conclusion
Our data suggest that intraoperative radiography is a useful method for detecting the errors of placing the femoral components, and the success of a surgeon to correct those errors after detecting them intraoperatively.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vresilovic EJ, Hozack WJ, Rothman RH (1994) Radiographic assessment of cementless femoral components: assessment of cementless femoral components: correlation with intraoperative mechanical stability. J Arthroplast 9:137–141
Mollan RA, Watters PH, Steele R, McClelland CJ (1984) Failure of the femoral component in the Howse total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat 190:142–147
Thomas J, Sledge John B, Orler Renee, Ganz Reinhold (1999) Lateral insufficiency fractures of the femur caused by osteopenia and varus angulation. J Arthroplast 8:982–987
Khanuja HS, Goytia RN, Goddard MS, Bhargava T, Jones LC (2010) Preoperative templating and intraoperative radiograph comparison for primary total hip arthroplasty. Poster presented at, AAOS Annual Meeting
Devitt A, O’Sullivan T, Quinlan W (1997) 16- to 25-Year follow-up study of cemented arthroplasty of the hip in patients aged 50 years or younger. J Arthroplast 12:479–489
Kobayashi S, Eftekhar NS, Terayama M (1994) Predisposing factors in fixation failure of femoral prostheses following primary charnley low friction arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 306:73–83
Khalily C, Lester DK (2002) Results of a tapered cementless femoral stem implanted in varus. J Arthroplast 17:463–466
de Beer J, McKenzie S, Hubmann M, Petruccelli D, Winemaker M (2006) Influence of cementless femoral seems insered in varus on functional outcome in primary total hip arthroplasty. Can J Surg 49:407–411
Cruckler JM (2005) Limb length and stability in total hip replacement. Orthopedics 28:951–953
Ishii K, Kobayashi M, Matsubara M, Okuda N, Hirasawa N, Nogi K, Sato A, Hagio S (2010) Application of the alignment rod for the adjustment of cementless stem insertion. Hip Joint 36:271–273 (in Japanese)
White CA, Carsen S, Rasuli K, Feibel RJ, Kim PR, Beaule PE (2012) High incidence of migration with poor initial fixation of the accolade stem. Clin Orthop Relat 470:410–417
Dastane M, Dorr LD, Tarwala R, Wan Z (2011) Hip offset in total hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:429–436
Murphy SB, Ecker TM (2007) Evaluation of a new leg length measurement algorithm in hip arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 463:85–89
Eggli S, Pisan M, Muller ME (1998) The value of preoperative planning for total hip arthroplasty. JBJS Br 80:382–390
Gross TP, Liu F, Webb L (2011) Intraoperative radiographs for placing acetabular components in hip resurfacing arthroplasty. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:1554–1559
Hayakawa K, Minoda Y, Aihara M, Sakawa A, Ohzono K, Tada K (2009) Acetabular component orientation in intra-and postoperative position in total hip arthroplasty. Arch Othop Trauma Surg 129:1151–1156
Park SW, Park JH, Han SB, Choi GW, Song DI, An ES (2009) Are portable imaging intraoperative radiographs helpful for assessing adequate acetabular cup position in total hip arthroplasty. J Korean Med Sci 24:315–319
Hofmann AA, Bolognesi M, Lahav A, Kurtin S (2008) Minimizing leg-length inequality in total hip arthroplasty: use preoperative templating and an intraoperative X-ray. Am J Orthop 37:18–23
Takao M, Nakamura N, Ohzono K, Sakai T, Nishii T, Sugano N (2011) The results of a press-fit-only technique for acetabular fixation in hip dysplasia. J Arthroplast 26:562–568
Sugano N, Noble PC, Kamaric E (1999) Predicting the position of the femoral head center. J Arthroplast 14:102–107
Hananouchi T, Sugano N, Nakamura N, Nishii T, Miki H, Yamamura M, Yoshikawa H (2007) Preoperative templating of femoral components on plain X-rays. Arch Othop Trauma Surg 127:381–385
Carletta J (1996) Assessing agreement on classification tasks: the kappa statistic. Comput Linguist 22:249–254
Butler JBV, Lansky D, Duwelius PJ (2005) Prospective evaluation of total hip arthroplasty with a cementless, anatomically designed, porous-coated femoral implant: mean 11-year follow-up. J Arthroplast 20:709–716
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuroda, K., Kabata, T., Maeda, T. et al. Do we need intraoperative radiographs for positioning the femoral component in total hip arthroplasty?. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134, 727–733 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-014-1962-3
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-014-1962-3