Abstract
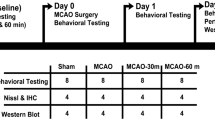
We hypothesized that exercise preconditioning strengthens brain microvascular integrity against ischemia/reperfusion injury through the tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-integrin signaling pathway. Adult male Sprague Dawley rats (n = 24) were studied in: (1) exercise (the animals run on a treadmill 30 min each day) for 3 weeks, (2) non-exercise. Six animals from each group (n = 12) were subjected to stroke, the remaining animals served as controls (n = 6 × 2). Brain infarction and edema were determined by Nissl staining. Cerebral integrin expression was detected by immunochemistry and stereological methods. In addition, we used flow cytometry to address the causal role of TNF-α in inducing the expression of integrins in the human umbilical vein endothelial cells under TNF-α or vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) pretreatment. Exercise reduces brain infarction and brain edema in stroke. Expressions of integrin subunit α1, α6, β1, and β4 were increased after exercise. Exercise preconditioning reversed stroke-reduced integrin expression. An in vitro study revealed a causal link between the gradual upregulation of TNF-α (rather than VEGF) and cellular expression of integrins. These results demonstrated an increase in cerebral expression of integrins and a decrease in brain injury from stroke after exercise preconditioning. The study suggests that upregulation of integrins during exercise enhances neurovascular integrity after stroke. The changes in integrins might be altered by TNF-α.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ang ET, Wong PT, Moochhala S, Ng YK (2003) Neuroprotection associated with running: is it a result of increased endogenous neurotrophic factors? Neuroscience 118:335–345
Belayev L, Alonso OF, Busto R, Zhao W, Ginsberg MD (1996) Middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat by intraluminal suture. Neurological and pathological evaluation of an improved model. Stroke 27:1616–1622
Black JE, Isaacs KR, Anderson BJ, Alcantara AA, Greenough WT (1990) Learning causes synaptogenesis, whereas motor activity causes angiogenesis, in cerebellar cortex of adult rats. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:5568–5572
Blair SN, Cheng Y, Holder JS (2001) Is physical activity or physical fitness more important in defining health benefits? Med Sci Sports Exerc 33:S379–S399
Botchkina GI, Meistrell ME, Botchkina IL, Tracey KJ (1997) Expression of TNF and TNF receptors (p55 and p75) in the rat brain after focal cerebral ischemia. Mol Med 3:765–781
Brett J, Gerlach H, Nawroth P, Steinberg S, Godman G, Stern D (1989) Tumor necrosis factor/cachectin increases permeability of endothelial cell monolayers by a mechanism involving regulatory G proteins. J Exp Med 169:1977–1991
Brooks PC, Clark RA, Cheresh DA (1994) Requirement of vascular integrin alpha v beta 3 for angiogenesis. Science 264:569–571
Brooks PC, Montgomery AM, Rosenfeld M, Reisfeld RA, Hu T, Klier G, Cheresh DA (1994) Integrin alpha v beta 3 antagonists promote tumor regression by inducing apoptosis of angiogenic blood vessels. Cell 79:1157–1164
Brooks PC, Stromblad S, Klemke R, Visscher D, Sarkar FH, Cheresh DA (1995) Antiintegrin alpha v beta 3 blocks human breast cancer growth and angiogenesis in human skin. J Clin Invest 96:1815–1822
Bruce AJ, Boling W, Kindy MS, Peschon J, Kraemer PJ, Carpenter MK, Holtsberg FW, Mattson MP (1996) Altered neuronal and microglial responses to excitotoxic and ischemic brain injury in mice lacking TNF receptors. Nat Med 2:788–794
Buttini M, Appel K, Sauter A, Gebicke H, Boddeke HW (1996) Expression of tumor necrosis factor alpha after focal cerebral ischaemia in the rat. Neuroscience 71:1–16
Curtis TM, McKeown L, Vincent PA, Homan SM, Wheatley EM, Saba TM (1995) Fibronectin attenuates increased endothelial monolayer permeability after RGD peptide, anti-alpha 5 beta 1, or TNF-alpha exposure. Am J Physiol 269:L248–L260
Dans MJ, Giancotti FG (1999) Guidebook to the extracellular matrix, anchor, and adhesion proteins. Sambrook and Tooze Publication at Osford University Press, Oxford
del Zoppo GJ, Hallenbeck JM (2000) Advances in the vascular pathophysiology of ischemic stroke. Thromb Res 98:73–81
del Zoppo GJ, Mabuchi T (2003) Cerebral microvessel responses to focal ischemia. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 23:879–894
Ding Y, Casagrande VA (1998) Synaptic and neurochemical characterization of parallel pathways to the cytochrome oxidase blobs of primate visual cortex. J Comp Neurol 391:429–443
Ding Y, Ding YH, Li J, Rafols JA (2005) Exercise induces integrin overexpression and improves neurovascular integrity in ischemic stroke. Stroke 36(2):470
Ding Y, Ding YH, Luan X, Phillis JW, Diaz FG (2004) Neuroprotective effect of exercise-induced angiogenic factors on ischemia/reperfusion injury in stroke. Stroke 35:273
Ding Y, Li J, Rafols JA, Phillis JW, Diaz FG (2002) Pre-reperfusion flushing of ischemic territory reduces inflammatory injury following transient middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Stroke 33:2492–2498
Ding Y, Li J, Luan X, Ding YH, Lai Q, Rafols JA, Phillis JW, Clark J, Diaz FG (2004) Exercise pre-conditioning reduces brain damage in ischemic rats that may be associated with regional angiogenesis and cellular overexpression of neurotrophin. Neuroscience 124:583–591
Ding Y, Li J, Rafols JA, Clark J, Phillis JW, Diaz FG (2003) Pre-ischemic motor exercise reduces ischemia/reperfusion injury in rats that correlates with regional angiogenesis and cellular expression of neurotrophin. Stroke 34:240–241
Ding YH, Li J, Rafols JA, Ding Y (2004) Reduced brain edema and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP) expression by pre-reperfusion infusion into ischemic territory in rat. Neurosci Lett 372:35–39
Ding YH, Luan X, Li J, Rafols JA, Guthikonda M, Diaz FG, Ding Y (2004) Exercise-induced overexpression of angiogenic factors and reduction of ischemia/reperfusion injury in stroke. Curr Neurovasc Res 1:411–420
Ding YH, Young CN, Luan X, Li J, Rafols JA, Clark JC, McAllister JP, Ding Y (2005) Exercise preconditioning ameliorates inflammatory injury in ischemic rats during reperfusion. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 109:237–246
Dulabon L, Olson EC, Taglienti MG, Eisenhuth S, McGrath B, Walsh CA, Kreidberg JA, Anton ES (2000) Reelin binds alpha3beta1 integrin and inhibits neuronal migration. Neuron 27:33–44
Ellekjaer H, Holmen J, Ellekjaer E, Vatten L (2000) Physical activity and stroke mortality in women. Ten-year follow-up of the Nord-Trondelag health survey, 1984–1986. Stroke 31:14–18
Endres M, Gertz K, Lindauer U, Katchanov J, Schultze J, Schrock H, Nickenig G, Kuschinsky W, Dirnagl U, Laufs U (2003) Mechanisms of stroke protection by physical activity. Ann Neurol 54:582–590
Evenson KR, Rosamond WD, Cai J, Toole JF, Hutchinson RG, Shahar E, Folsom AR (1999) Physical activity and ischemic stroke risk. The atherosclerosis risk in communities study. Stroke 30:1333–1339
Ferrero E, Zocchi MR, Magni E, Panzeri MC, Curnis F, Rugarli C, Ferrero ME, Corti A (2001) Roles of tumor necrosis factor p55 and p75 receptors in TNF-alpha-induced vascular permeability. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 281:C1173–C1179
Feuerstein GZ, Wang X (2001) Inflammation and stroke: benefits without harm? Arch Neurol 58:672–674
Friedlander M, Brooks PC, Shaffer RW, Kincaid CM, Varner JA, Cheresh DA (1995) Definition of two angiogenic pathways by distinct alpha v integrins. Science 270:1500–1502
Gillum RF, Mussolino ME, Ingram DD (1996) Physical activity and stroke incidence in women and men. The NHANES I epidemiologic follow-up study. Am J Epidemiol 143:860–869
Ginis I, Schweizer U, Brenner M, Liu J, Azzam N, Spatz M, Hallenbeck JM (1999) TNF-alpha pretreatment prevents subsequent activation of cultured brain cells with TNF-alpha and hypoxia via ceramide. Am J Physiol 276:C1171–C1183
Greenlund KJ, Giles WH, Keenan NL, Croft JB, Mensah GA (2002) Physician advice, patient actions, and health-related quality of life in secondary prevention of stroke through diet and exercise. Stroke 33:565–571
Gundersen HJ, Bendtsen TF, Korbo L, Marcussen N, Moller A, Nielsen K, Nyengaard JR, Pakkenberg B, Sorensen FB, Vesterby A (1988) Some new, simple and efficient stereological methods and their use in pathological research and diagnosis. APMIS 96:379–394
Hamann GF, Liebetrau M, Martens H, Burggraf D, Kloss CU, Bultemeier G, Wunderlich N, Jager G, Pfefferkorn T (2002) Microvascular basal lamina injury after experimental focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion in the rat. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 22:526–533
Hogervorst F, Admiraal LG, Niessen C, Kuikman I, Janssen H, Daams H, Sonnenberg A (1993) Biochemical characterization and tissue distribution of the A and B variants of the integrin alpha 6 subunit. J Cell Biol 121:179–191
Hu FB, Stampfer MJ, Colditz GA, Ascherio A, Rexrode KM, Willett WC, Manson JE (2000) Physical activity and risk of stroke in women. JAMA 283:2961–2967
Hynes RO (1992) Integrins: versatility, modulation, and signaling in cell adhesion. Cell 69:11–25
Igarashi Y, Utsumi H, Chiba H, Yamada S, Tobioka H, Kamimura Y, Furuuchi K, Kokai Y, Nakagawa T, Mori M, Sawada N (1999) Glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor induces barrier function of endothelial cells forming the blood–brain barrier. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 261:108–112
Isaacs KR, Anderson BJ, Alcantara AA, Black JE, Greenough WT (1992) Exercise and the brain: angiogenesis in the adult rat cerebellum after vigorous physical activity and motor skill learning. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 12:110–119
Janzer RC, Raff MC (1987) Astrocytes induce blood–brain barrier properties in endothelial cells. Nature 325:253–257
Kleim JA, Cooper NR, VandenBerg PM (2002) Exercise induces angiogenesis but does not alter movement representations within rat motor cortex. Brain Res 934:1–6
Kondo T, Kinouchi H, Kawase M, Yoshimoto T (1996) Astroglial cells inhibit the increasing permeability of brain endothelial cell monolayer following hypoxia/reoxygenation. Neurosci Lett 208:101–104
Lecour S, Smith RM, Woodward B, Opie LH, Rochette L, Sack MN (2002) Identification of a novel role for sphingolipid signaling in TNF alpha and ischemic preconditioning mediated cardioprotection. J Mol Cell Cardiol 34:509–518
Lee CD, Folsom AR, Blair SN (2003) Physical activity and stroke risk: a meta-analysis. Stroke 34:2475–2481
Lee IM, Hennekens CH, Berger K, Buring JE, Manson JE (1999) Exercise and risk of stroke in male physicians. Stroke 30:1–6
Lee SW, Kim WJ, Choi YK, Song HS, Son MJ, Gelman IH, Kim YJ, Kim KW (2003) SSeCKS regulates angiogenesis and tight junction formation in blood–brain barrier. Nat Med 9:900–906
Li J, Ding YH, Rafols JA, Lai Q, McAllister JP II, Ding Y (2005) Increased astrocyte proliferation in rats after running exercise. Neurosci Lett 386:160–164
Li J, Luan X, Clark J, Rafols JA, Ding Y (2004) Neuroprotection against transient cerebral ischemia by exercise pre-conditioning in rats. Neurol Res 26:404–408
Lin TN, He YY, Wu G, Khan M, Hsu CY (1993) Effect of brain edema on infarct volume in a focal cerebral ischemia model in rats. Stroke 24:117–121
Liu J, Ginis I, Spatz M, Hallenbeck JM (2000) Hypoxic preconditioning protects cultured neurons against hypoxic stress via TNF-alpha and ceramide. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 278:C144–C153
Liu T, Clark RK, McDonnell PC, Young PR, White RF, Barone FC, Feuerstein GZ (1994) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha expression in ischemic neurons. Stroke 25:1481–1488
Lo EH, Dalkara T, Moskowitz MA (2003) Mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in stroke. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:399–415
Nawashiro H, Tasaki K, Ruetzler CA, Hallenbeck JM (1997) TNF-alpha pretreatment induces protective effects against focal cerebral ischemia in mice. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 17:483–490
Nielsen HG, Lyberg T (2004) Long-distance running modulates the expression of leucocyte and endothelial adhesion molecules. Scand J Immunol 60:356–362
Ohtsuki T, Ruetzler CA, Tasaki K, Hallenbeck JM (1996) Interleukin-1 mediates induction of tolerance to global ischemia in gerbil hippocampal CA1 neurons. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 16:1137–1142
Okada Y, Copeland BR, Hamann GF, Koziol JA, Cheresh DA, del Zoppo GJ (1996) Integrin alphavbeta3 is expressed in selected microvessels after focal cerebral ischemia. Am J Pathol 149:37–44
Park JA, Choi KS, Kim SY, Kim KW (2003) Coordinated interaction of the vascular and nervous systems: from molecule- to cell-based approaches. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 311:247–253
Petty MA, Lo EH (2002) Junctional complexes of the blood–brain barrier: permeability changes in neuroinflammation. Prog Neurobiol 68:311–323
Plantefaber LC, Hynes RO (1989) Changes in integrin receptors on oncogenically transformed cells. Cell 56:281–290
Rothwell NJ, Hopkins SJ (1995) Cytokines and the nervous system II: actions and mechanisms of action. Trends Neurosci 18:130–136
Rotundo RF, Curtis TM, Shah MD, Gao B, Mastrangelo A, LaFlamme SE, Saba TM (2002) TNF-alpha disruption of lung endothelial integrity: reduced integrin mediated adhesion to fibronectin. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol 282:L316–L329
Sairanen TR, Lindsberg PJ, Brenner M, Carpen O, Siren A (2001) Differential cellular expression of tumor necrosis factor-alpha and Type I tumor necrosis factor receptor after transient global forebrain ischemia. J Neurol Sci 186:87–99
Stummer W, Baethmann A, Murr R, Schurer L, Kempski OS (1995) Cerebral protection against ischemia by locomotor activity in gerbils. Underlying mechanisms. Stroke 26:1423–1429
Stummer W, Weber K, Tranmer B, Baethmann A, Kempski O (1994) Reduced mortality and brain damage after locomotor activity in gerbil forebrain ischemia. Stroke 25:1862–1869
Swain RA, Harris AB, Wiener EC, Dutka MV, Morris HD, Theien BE, Konda S, Engberg K, Lauterbur PC, Greenough WT (2003) Prolonged exercise induces angiogenesis and increases cerebral blood volume in primary motor cortex of the rat. Neuroscience 117:1037–1046
Swanson RA, Morton MT, Tsao-Wu G, Savalos RA, Davidson C, Sharp FR (1990) A semiautomated method for measuring brain infarct volume [see comments]. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 10:290–293
Tagaya M, Haring HP, Stuiver I, Wagner S, Abumiya T, Lucero J, Lee P, Copeland BR, Seiffert D, del Zoppo GJ (2001) Rapid loss of microvascular integrin expression during focal brain ischemia reflects neuron injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 21:835–846
Tamura RN, Rozzo C, Starr L, Chambers J, Reichardt LF, Cooper HM, Quaranta V (1990) Epithelial integrin alpha 6 beta 4: complete primary structure of alpha 6 and variant forms of beta 4. J Cell Biol 111:1593–1604
Tasaki K, Ruetzler CA, Ohtsuki T, Martin D, Nawashiro H, Hallenbeck JM (1997) Lipopolysaccharide pre-treatment induces resistance against subsequent focal cerebral ischemic damage in spontaneously hypertensive rats. Brain Res 748:267–270
Tawil N, Wilson P, Carbonetto S (1993) Integrins in point contacts mediate cell spreading: factors that regulate integrin accumulation in point contacts vs. focal contacts. J Cell Biol 120:261–271
Tawil NJ, Wilson P, Carbonetto S (1994) Expression and distribution of functional integrins in rat CNS glia. J Neurosci Res 39:436–447
van der Flier A, Sonnenberg A (2001) Function and interactions of integrins. Cell Tissue Res 305:285–298
Varner JA (1997) The role of vascular cell integrins alpha v beta 3 and alpha v beta 5 in angiogenesis. EXS 79:361–390
Wagner S, Tagaya M, Koziol JA, Quaranta V, del Zoppo GJ (1997) Rapid disruption of an astrocyte interaction with the extracellular matrix mediated by integrin alpha 6 beta 4 during focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion. Stroke 28:858–865
Wang RY, Yang YR, Yu SM (2001) Protective effects of treadmill training on infarction in rats. Brain Res 922:140–143
Wang X, Li X, Currie RW, Willette RN, Barone FC, Feuerstein GZ (2000) Application of real-time polymerase chain reaction to quantitate induced expression of interleukin-1beta mRNA in ischemic brain tolerance. J Neurosci Res 59:238–246
Wang X, Li X, Erhardt JA, Barone FC, Feuerstein GZ (2000) Detection of tumor necrosis factor-alpha mRNA induction in ischemic brain tolerance by means of real-time polymerase chain reaction. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 20:15–20
Wang X, Lo EH (2003) Triggers and mediators of hemorrhagic transformation in cerebral ischemia. Mol Neurobiol 28:229–244
Wendel-Vos GC, Schuit AJ, Feskens EJ, Boshuizen HC, Verschuren WM, Saris WH, Kromhout D (2004) Physical activity and stroke. A meta-analysis of observational data. Int J Epidemiol 33:787–798
Wheatley EM, Vincent PA, McKeown L, Saba TM (1993) Effect of fibronectin on permeability of normal and TNF-treated lung endothelial cell monolayers. Am J Physiol 264:R90–R96
Willis CL, Nolan CC, Reith SN, Lister T, Prior MJ, Guerin CJ, Mavroudis G, Ray DE (2004) Focal astrocyte loss is followed by microvascular damage, with subsequent repair of the blood–brain barrier in the apparent absence of direct astrocytic contact. Glia 45:325–337
Yamashita N, Hoshida S, Otsu K, Taniguchi N, Kuzuya T, Hori M (1999) Monophosphoryl lipid A provides biphasic cardioprotection against ischaemia-reperfusion injury in rat hearts. Br J Pharmacol 128:412–418
Yeh CH, Peng HC, Huang TF (1999) Cytokines modulate integrin alpha(v)beta(3)-mediated human endothelial cell adhesion and calcium signaling. Exp Cell Res 251:57–66
Zea Longa Z, Weinstein PR, Carlson S, Cummins R (1989) Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without craniectomy in rats. Stroke 20:84–91
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Yandong Zhou, MS and Lisa D. NeSmith, MA for their help in the preparation of this manuscript. This work was supported partially by American Heart Association Midwest Affiliate Grant in aid to Yuchuan Ding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ding, Y.H., Li, J., Yao, W.X. et al. Exercise preconditioning upregulates cerebral integrins and enhances cerebrovascular integrity in ischemic rats. Acta Neuropathol 112, 74–84 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0076-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-006-0076-6