Abstract
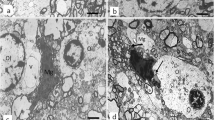
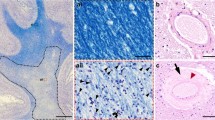
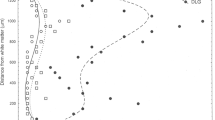
The purpose of the present study was to document the topographical and cytopathological lesions in the white matter (WM) of Binswanger’s disease (BD) brains. Subcortical WM lesions in each lobe and fiber bundle lesions related to the medial thalamic and hippocampal structures in clinicopathologically proven BD brains were evaluated by Klüver-Barrera staining using a grading score. Lesions in the frontal subcortical WM of BD brains, brains from non-neurological patients, and brains with cerebral hemorrhage or large cortical infarcts were also examined immunohistochemically using molecular markers for axonal flow damage: amyloid precursor protein (APP); and for demyelinating axonopathy: encephalitogenic peptide (EP). Our results indicated that the WM lesions in BD were significantly more prominent in the frontal periventricular and subcortical regions as compared with other subcortical WM lesions, in the order of the parietal, occipital and temporal lobes. Fiber bundle lesions in the capsular genu, including the anterior thalamic peduncle, were also significantly more prominent in BD brains as compared with the other bundle lesions. Furthermore, the frequency of damaged nerve fibers labeled by the EP antiserum and APP immunoreactive fibers was significantly higher in BD brains as compared with the control brains. The grading scores for the WM damage correlated significantly with those for the APP and EP immunoreactive fibers in all brains, including the control brains. The axonal damage in the frontal WM lesions of the BD brains was clearly revealed in our study using immunohistochemistry for APP and EP.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akiguchi I, Ino T, Nabatame H, Udaka F, Matsubayashi K, Fukuyama H, Kameyama M (1987) Acute-onset amnestic syndrome with localized infarct on the dominant side: comparison between anteromedial thalamic lesion and posterior cerebral artery territory lesion. Jpn J Med (Intern Med) 26:15–20
Akiguchi I, Ino T, Hara T, Anegawa T, Kimura J (1990) Acute-onset lethargia and prolonged abulia: a syndrome of the genu of internal capsule [Abstract]. Stroke 21: 1–149
Akiguchi I, Tomimoto H, Suenaga T, Wakita H, Budka H (1997) Alterations in glia and axons in the brains of Binswanger’s disease patients. Stroke 28:1423–1429
Akiguchi I, Tomimoto H, Suenaga T, Wakita H, Budka H (1998) Blood-brain barrier dysfunction in Binswanger’s disease: an immunohistochemical study. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 95:78–84
Akiguchi I, Tomimoto H, Wakita H, Yamamoto Y, Suenaga T, Ueno M, Budka H (1999) Cytopathological alterations and therapeutic approaches in Binswanger’s disease. Neuropathology 19:119–128
Binswanger O (1894) Die Abgrenzung der allgemeinen progressiven Paralyse. Berl Klin Wochenschr 31:1103–1105, 1137–1139, 1180–1186
Bjartmar C, Battistuta J, Teruda N, Dupree E, Trapp BD (2002) N-acetylaspartate is an axon-specific marker of mature white matter in vivo: a biochemical and immunohistochemical study on the rat optic nerve. Ann Neurol 51:51–58
Bogousslavsky J (1992) Binswanger’s disease. In: Barnett HJM, Mohr JP, Stein BM (eds) Stroke: pathophysiology, diagnosis, and management, 2nd edn. Churchill Livingstone, New York, pp 805–819
Caplan LR (1995) Binswanger’s disease: revisited. Neurology 45:626–633
Castaigne P, Lhermitte F, Buge A, Escourolle R, Hauw JJ, Lyon-Caen O (1981) Paramedian thalamic and midbrain infarcts: clinical and neuropathological study. Ann Neurol 10:127–148
Englund E, Brun A (1990) White matter changes in dementia of Alzheimer’s type: the difference in vulnerability between cell compartments. Histopathology 16:433–439
Erkinjuntti T (2002) Diagnosis and management of vascular cognitive impairment and dementia. J Neural Transm 63 (Suppl):91–109
Furuta A, Ishii N, Nishihara Y, Horie A (1991) Medullary arteries in aging and dementia. Stroke 22:442–446
Goto K, Ishii N, Fukasawa H (1981) Diffuse white-matter disease in the geriatric population: a clinical, neuropathological, and CT study. Radiology 141:687–695
Ishii N, Nishihara Y, Imamura T (1986) Why do frontal lobe symptoms predominate in vascular dementia with lacunes? Neurology 36:340–345
Jellinger K, Neumayer E (1964) Progressive subcorticale vasculare Encephalopathie Binswanger: Eine klinische-neuropathologische Studie. Arch Psychiatr Nervenkr Zietschr Ges Neurol 205:523–554
Kenny RA, Kalaria R, Ballard C (2002) Neurocardiovascular instability in cognitive impairment and dementia. Ann NY Acad Sci 977:183–195
Kitani M, Tomonaga M, Yoshimura M, Mori H (1986 ) A clinicopathological study on progressive subcortical vascular encephalopathy (Binswanger type) observed in the elderly persons: classification of PSVE according to white-matter degeneration. Jpn J Geriatr 23:155–162 [in Japanese with English abstract]
Kiyohara Y (1999) Prevalence, incidence, and risk factors of vascular dementia; the Hisayama study. Clinical Neurol 39:47–49 [in Japanese with English abstract]
Matsuo A, Akiguchi I, Lee GC, McGeer EG, McGeer PL, Kimura J (1998) Myelin degeneration in multiple system atrophy detected by unique antibodies. Am J Pathol 153:735–744
Nakamura Y, Okudera T, Hashimoto T (1994) Vascular architecture in white matter of neonates: its relationship to periventricular leukomalacia. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 53:582–589
Nieuwenhuys R, Voogd J, van Huijzen C (1988) In: The Human central nervous system: a synopsis and atlas, 3rd edn. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York
Ohtani R, Tomimoto H, Kawasaki T, Yagi H, Akiguchi I, Shibasaki H (2003) Cerebral vasomotor reactivity to postural change is impaired in patients with cerebrovascular white matter lesions. J Neurol 250:412–417
Olszewski J (1962) Subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy: review of the literature on the so-called Binswanger’s disease and presentation of two cases. World Neurol 3:359–375
Pellissier J-F, Poncet M (1989) Binswanger’s encephalopathy. In: Toole JF (ed) Handbook of clinical neurology, vol 10. Vascular diseases, part II. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 221–233
Press GA, Amaral DG, Squire LR (1989) Hippocampal abnormalities in amnesic patients revealed by high-resolution magnetic resonance imaging. Nature 341:54–57
Román GC (1987) Senile dementia of the Binswanger type. J Am Med Assoc 258:1782–1788
Román GC, Tatemichi TK, Erkinjuntti T, Cummings JL, Masdeu JC, Garcia JH, Amaducci L, Orgogozo JM, Brun A, Hofman A (1993) Vascular dementia: diagnostic criteria for research studies. Report of the NINDS-AIREN International Workshop. Neurology 43:250–260
Révész T, Hawkins CP, du Boulay EPGH, Barnard RO, McDonald WI (1989) Pathological findings correlated with magnetic resonance imaging in subcortical arteriosclerotic encephalopathy (Binswanger’s disease). J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 52:1337–1344
Suenaga T, Ohnishi K, Nishimura M, Nakamura S, Akiguchi I, Kimura J (1994) Bundles of amyloid precursor protein: immunoreactive axons in human cerebrovascular white matter lesions. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 87:450–455
Tatemichi TK, Desmond DW, Prohovnic I, Cross DT, Gropen TI, Mohr JP, Stern Y (1992) Confusion and memory loss from capsular genu infarction: a thalamocortical disconnection syndrome? Neurology 42:1966–1979
Tomimoto H, Akiguchi I, Matsuo A, Terai K, Wakita H, Kimura J, McGeer PL, Budka H (1997) Encephalitogenic peptide (EP) in human cerebrovascular white matter lesions. NeuroReport 8:3727–3730
Tomimoto H, Ihara M, Wakita H, Ohtani R, Lin JX, Akiguchi I, Kinoshita M, Shibasaki H (2003) Chronic cerebral hypoperfusion induces white matter lesions and loss of oligodendroglia with DNA fragmentation in the rat. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 106:527–534
Watanabe T, Akiguchi I, Yagi H, Onishi K, Kawasaki T, Shiino A, Inubushi T (2002) Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy and white matter hyperintensities on magnetic resonance imaging in patients with Alzheimer’s diseases. Ann NY Acad Sci 977:423–429
Yamamoto Y, Akiguchi I, Oiwa K, Hayashi M, Kasai T, Ozasa K (2002) Twenty-four-hour blood pressure and MRI as predictive factors for different outcome in patients with lacunar infarct. Stroke 33:297–305
Yamanouchi H, Sugiura S, Tomonaga M (1989) Decrease in nerve fibers in cerebral white matter in progressive subcortical vascular encephalopathy of Binswanger type: an electron microscopic study. J Neurol 236:382–387
Yamanouchi H, Nagura H (1997) Neurological signs and frontal white matter lesions in vascular parkinsonism. Stroke 28:965–969
Yoshitake T, Kiyohara Y, Kato I, Ohmura T, Iwamoto H, Nakayama K, Ohmori M, Nomiyama K, Kawano H, Ueda K (1995) Incidence and risk factors of vascular dementia and Alzheimer’s disease in defined elderly Japanese population; the Hisayama Study. Neurology 45:1161–1168
Acknowledgements
The authors thank M. Fukuda, H. Nakabayashi, and Y. Sasaki for their excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Akiguchi, I., Tomimoto, H., Wakita, H. et al. Topographical and cytopathological lesion analysis of the white matter in Binswanger’s disease brains. Acta Neuropathol 107, 563–570 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-004-0850-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-004-0850-2