Abstract
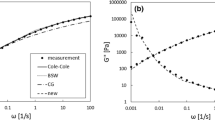
For the numerical determination of a continuous relaxation time spectrum from rheological data so-called regularization methods are necessary. The regularization method based on Tikhonov regularization and commonly used in rheology assumes the relaxation time spectrum to be smooth. Accordingly, this method is not able to properly resolve spectra containing edges or at least large curvatures as proposed in the literature. In order to reconstruct such spectra a novel edge preserving regularization (EPR) method was developed which extends the properties of the commonly used method. In order to demonstrate the efficiency of EPR it is compared with the commonly used regularization method by means of simulated and experimental data. This reveals that EPR is able to prove whether or not the theoretically predicted edge containing spectra for high-molecular-weight, monodisperse polymers are compatible with experimental data.
Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 11 June 1999/Accepted: 1 September 1999
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Roths, T., Maier, D., Friedrich, C. et al. Determination of the relaxation time spectrum from dynamic moduli using an edge preserving regularization method. Rheol. Acta 39, 163–173 (2000). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003970050016
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003970050016