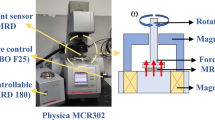
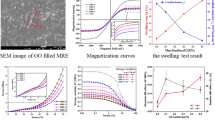
Abstract
This study focuses on the magnetorheology of graphite-based magnetorheological elastomers (Gr MREs). By introducing graphite to conventional MREs, the Gr MREs with various graphite weight fractions are fabricated. Both steady-state and dynamic tests were conducted to study rheological properties of the samples. For dynamic tests, the effects of magnetic field, strain amplitude and frequency on both storage modulus and loss modulus were measured. The influence of graphite weight fraction on mechanical performances of these samples was summarized. Also, the microstructures of isotropic and anisotropic Gr MREs were observed. In anisotropic MREs, the graphite powders disperse in matrix randomly. The graphite particles lead to an increment of initial mechanical properties and a decrement of the MR effect.






















Similar content being viewed by others
Explore related subjects
Discover the latest articles and news from researchers in related subjects, suggested using machine learning.References
Bica I (2009) Influence of the transverse magnetic field intensity upon the electric resistance of the magnetorheological elastomer containing graphite microparticles. Mater Lett 63(26):2230–2232
Bica I (2010) Influence of the magnetic field on the electric conductivity of magnetorheological elastomers. J Ind Eng Chem 16(3):359–363
Chen L, Gong XL, Li WH (2007) Microstructure and viscoelastic properties of anisotropic magnetorheological elastomers. Smart Mater Struc 16(6):2645–2650
Davis LC (1999) Model of magnetorheological elastomers. J Appl Phys 85(6):3348–3351
De Buyl F (2001) Silicone sealants and structural adhesives. Int J Adhes Adhes 21:411–422
Demchuk SA, Kuzmin VA (2002) Viscoelastic properties of magnetorheological elastomers in the regime of dynamic deformation. J Eng Phys Thermophys 75(2):396–400
Deng HX, Gong XL, Wang LH (2006) Development of an adaptive tuned vibration absorber with magnetorheological elastomer. Smart Mater Struc 15(5):N111-N116
Fang FF, Choi HJ, Jhon MS (2009) Magnetorheology of soft magnetic carbonyl iron suspension with single-walled carbon nanotube additive and its yield stress scaling function. Colloids Surf A 351:46–51
Ginder JM, Clark SM, Schlotter WF, Nichols ME (2002) Magnetostrictive phenomena in magnetorheological elastomers. Int J Mod Phys B 16(17&18):2412–2418
Gong XL, Zhang XZ, Zhang PQ (2005) Fabrication and characterization of isotropic magnetorheological elastomers. Polym Test 24(5):669–676
Kim YK, Koo JH, Kim KS, Kim SH (2011) Suppressing harmonic vibrations of a miniature cryogenic cooler using an adaptive tunable vibration absorber based on MR elastomers. Rev Sci Instrum 82:035103
Leblanc JL (2002) Rubber-filler interactions and rheological properties in filled compounds. Prog Polym Sci 27(4):627–687
Li WH, Zhang XZ (2010) A study of the magnetorheological effect of bimodal particle based magnetorheological elastomers. Smart Mater Struct 19(3):035002
Li WH, Du H, Chen G, Yeso SH, Guo NQ (2002) Nonlinear rheological behavior of MR fluids: step strain experiments. Smart Mater Struct 11:209–217
Li WH, Du H, Chen G, Yeo SH, Guo NQ (2003) Nonlinear viscoelastic properties of MR fluids under large-amplitude oscillatory shear. Rheol Acta 42:280–286
Li WH, Kostidis K, Zhang XZ, Zhou Y (2009) Development of a force sensor working with MR Elastomers. In: 2009 Ieee/Asme International Conference on Advanced Intelligent Mechatronics, vols 1-3. ISBN: 978-1-4244-2853-3, pp 233–238
Li WH, Zhou Y, Tian TF (2010) Viscoelastic properties of MR elastomers under harmonic loading. Rheol Acta 49:733–740
Lokander M, Stenberg B (2003) Performance of isotropic magnetorheological rubber materials. Polym Test 22(3):245–251
Ni ZC, Gong XL, Li JF, Chen L (2009) Study on a dynamic stiffness-tuning absorber with squeeze-strain enhanced magnetorheological elastomer. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 20(10):1195–1202
Park BJ, Song KH, Choi HJ (2009) Magnetic carbonyl iron naaoparticle based magnetorheological suspension and its characteristics. Mater Lett 63:1350–1352
Shiga T, Okada A, Kurauchi T (1995) Magnetroviscoelastic behaviour of composite gels. J Appl Polym Sci 58:787–792
Xu ZB, Gong XL, Liao GJ, Chen XM (2010) An active-damping-compensated magnetorheological elastomer adaptive tuned vibration absorber. J Intell Mater Syst Struct 21(10):1039–1047
Zhang XZ, Li WH (2009) Adaptive tuned dynamic vibration absorbers working with MR elastomers. Smart Struct Syst 5(5):517–529
Zhang XZ, Peng SL, Wen WJ, Li WH (2008) Analysis and fabrication of patterned magnetorheological elastomers. Smart Mater Struct 17(4):045001
Zhang W, Gong XL, Jiang WQ, Fan YC (2010) Investigation of the durability of anisotropic magnetorheological elastomers based on mixed rubber. Smart Mater Struct 19:085008
Zou H, Zhang LQ, Tian M, Wu SZ, Zhao SH (2009) Study on the structure and properties of conductive silicone rubber filled with nickel-coated graphite. J Appl Polym Sci 115(5):2710–2717
Acknowledgements
This project is supported by University of Wollongong through a UIC grant.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tian, T.F., Li, W.H., Alici, G. et al. Microstructure and magnetorheology of graphite-based MR elastomers. Rheol Acta 50, 825–836 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-011-0567-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-011-0567-9