Abstract
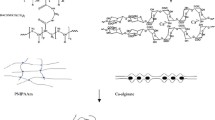
We report the preparation and rheological characterization of interpenetrating polymer network (IPN) hydrogels made from alginate and hydrophobically modified ethyl hydroxyl ethyl cellulose (HMEHEC). To our knowledge, there have been no studies of the gelation behavior of IPNs. We found that the rheology of these systems can be easily tuned, with the elastic modulus of the IPN strongly dependent on the relative ratio of HMEHEC to alginate. The sol–gel transition of these systems was found to satisfy the Winter–Chambon criterion for gelation at various crosslinker densities. From the power law relationship of the dynamic moduli (G ′ ~G ″ ~ω n), the exponent n appears to be dependent on both the crosslinker density and relative amount of two polymers. The value of n was found to be ~0.5 for all samples for stoichiometric amounts of crosslinker. The effect of molecular weight of HMEHEC on the gel point and viscoelastic exponent has also been reported. Alginate seems to dominate the kinetics of the process but the effect of high molecular weight HMEHEC on the gel point, especially at lower proportion was also evident.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aamer KA, Sardinha H, Bhatia SR, Tew GN (2004) Rheological studies of PLLA-PEO-PLLA triblock copolymer hydrogels. Biomaterials 25:1087–1093
Agrawal SK, Sanabria-DeLong N, Coburn JM, Tew GN, Bhatia SR (2006) Novel drug release profiles from micellar solutions of PLA-PEO-PLA triblock copolymers. J Control Release 112:64–71
Augst AD, Kong HJ, Mooney DJ (2006) Alginate hydrogels as biomaterials. Macromol Biosci 6:623–633
Banerjee A, Arha M, Choudhary S, Ashton RS, Bhatia SR, Schaffer DV, Kane RS (2009) The influence of hydrogel modulus on the proliferation and differentiation of encapsulated neural stem cells. Biomaterials 30:4695–4699
Bhatia SR, Khattak SF, Roberts SC (2005) Polyelectrolytes for cell encapsulation. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 10:45–51
Bhattarai N, Li ZS, Edmondson D, Zhang MQ (2006) Alginate-based nanofibrous scaffolds: structural, mechanical, and biological properties. Adv Mater 18:1463–1467
Caron G, Gaillard P, Carrupt PA, Testa B (1997) Lipophililicity behavior of model and medicinal compounds containing a sulfide, sulfoxide or sulfone moiety. Helv Chim Acta 80:449–462
Chambon F, Winter HH (1987) Linear viscoelasticity at the gel point of a cross-linking PDMS with imbalanced stoichiometry. J Rheol 31:683–697
Daoud M (2000) Viscoelasticity near the sol-gel transition. Macromolecules 33:3019–3022
De Gennes PG (1979) Scaling concepts in polymer physics. Cornell University Press, Ithaca
de Moura MR, Aouada FA, Guilherme MR, Radovanovic E, Rubira AF, Muniz EC (2006) Thermo-sensitive IPN hydrogels composed of PNIPAAm gels supported on alginate-Ca2+ with LCST tailored close to human body temperature. Polym Test 25:961–969
De Vos P, De Haan B, Van Schilfgaarde R (1997) Effect of the alginate composition on the biocompatibility of alginate-polylysine microcapsules. Biomaterials 18:273
Discher DE, Janmey P, Wang YL (2005) Tissue cells feel and respond to the stiffness of their substrate. Science 310:1139–1143
Draget KI, Ostgaard K, Smidsrod O (1990) Homogeneous alginate gels—a technical approach. Carbohydr Polym 14:159–178
Draget KI, Simensen MK, Onsoyen E, Smidsrod O (1993) Gel strength of ca-limited alginate gels made in situ. Hydrobiogia 260–261:563–569
Erkamp RQ, Wiggins P, Skovoroda AR, Emelianov SY, O’Donnell M (1998) Measuring the elastic modulus of small tissue samples. Ultrason Imag 20:17–28
Ju HK, Kim SY, Lee YM (2001) pH/temperature-responsive behaviors of semi-IPN and comb-type graft hydrogels composed of alginate and poly (N-isopropylacrylamide). Polymer 42:6851–6857
Karlberg M, Thuresson K, Piculell L, Lindman B (2004) Mixed solutions of hydrophobically modified graft and block copolymers. Colloids Surf, A Physicochem Eng Asp 236:159–164
Karlson L, Joabsson F, Thuresson K (2000) Phase behavior and rheology in water and in model paint formulations thickened with HM-EHEC: influence of the chemical structure and the distribution of hydrophobic tails. Carbohydr Polym 41:25–35
Karlson L, Thuresson K, Lindman B (2002) A rheological investigation of the complex formation between hydrophobically modified ethyl (hydroxy ethyl) cellulose and cyclodextrin. Carbohydr Polym 50:219–226
Klock G, Pfeffermann A, Ryser C, Grohn P, Kuttler B, Hahn HJ, Zimmermann U (1997) Biocompatibility of mannuronic acid-rich alginates. Biomaterials 18:707–713
Kuo CK, Ma PX (2001) Ionically crosslinked alginate hydrogels as scaffolds for tissue engineering: part 1. Structure, gelation rate and mechanical properties. Biomaterials 22:511–521
Larson RG (1999) The structure and rheology of complex fluids. Oxford University Press, New York
Lee KY, Mooney DJ (2001) Hydrogels for tissue engineering. Chem Rev 101:1869–1879
Lee SB, Park EK, Lim YM, Cho SK, Kim SY, Lee YM, Nho YC (2006) Preparation of alginate/poly(N-isopropylacrylamide) semi-interpenetrating and fully interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels with gamma-ray irradiation and their swelling behaviors. J Appl Polym Sci 100:4439–4446
Liu XX, Qian LY, Shu T, Tong Z (2003) Rheology characterization of sol-gel transition in aqueous alginate solutions induced by calcium cations through in situ release. Polymer 44:407–412
Martin JE, Adolf D, Wilcoxon JP (1988) Viscoelasticity of near-Critical Gels. Phys Rev Lett 61:2620–2623
Mason TG, Lacasse MD, Grest GS, Levine D, Bibette J, Weitz DA (1997) Osmotic pressure and viscoelastic shear moduli of concentrated emulsions. Phys Rev E 56:3150–3166
Mason TG, Weitz DA (1995) Linear viscoelasticity of colloidal hard-sphere suspensions near the glass-transition. Phys Rev Lett 75:2770–2773
McNaught AD, Wilkinson A (1997) IUPAC: compendium of chemical technology, 2nd edn. Blackwell, Oxford
Moresi M, Bruno M, Parente E (2004) Viscoelastic properties of microbial alginate gels by oscillatory dynamic tests. J Food Eng 64:179–186
Mu C, Sakai S, Ijima H, Kawakami K (2010) Preparation of cell-enclosing microcapsules through photopolymerization of methacrylated alginate solution triggered by irradiation with visible light. J Biosci Bioeng 109:618–621
Muthukumar M (1989) Screening effect on viscoelasticity near the gel point. Macromolecules 22:4656–4658
Norisuye T, Shibayama M, Nomura S (1998) Time-resolved light scattering study on the gelation process of poly(N-isopropyl acrylamide). Polymer 39:2769–2775
Nystrom B, Kjoniksen AL, Lindman B (1996) Effects of temperature, surfactant, and salt on the rheological behavior in semidilute aqueous systems of a nonionic cellulose ether. Langmuir 12:3233–3240
Park HG, Chae MY (2004) Novel type of alginate gel-based adsorbents for heavy metal removal. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 79:1080–1083
Park TG, Choi HK (1998) Thermally induced core-shell type hydrogel beads having interpenetrating polymer network (IPN) structure. Macromol Rapid Commun 19:167–172
Rowley JA, Madlambayan G, Mooney DJ (1999) Alginate hydrogels as synthetic extracellular matrix materials. Biomaterials 20:45–53
Rubinstein M, Colby R (2006) Polymer physics. Oxford University Press, Oxford
Saha K, Keung AJ, Irwin EF, Li Y, Little L, Schaffer DV, Healy KE (2008) Substrate modulus directs neural stem cell behavior. Biophys J 95:4426–4438
Scanlan JC, Winter HH (1991a) Composition dependence of the viscoelasticity of end-linked Poly(Dimethylsiloxane) at the gel point. Macromolecules 24:47–54
Scanlan JC, Winter HH (1991b) The evolution of viscoelasticity near the gel point of end-linking Poly(Dimethylsiloxane)S. Makromol Chem Macromol Symp 45:11–21
Schiessel H, Blumen A (1995) Mesoscopic pictures of the sol–gel transition—ladder models and fractal networks. Macromolecules 28:4013–4019
Silioc C, Maleki A, Zhu KZ, Kjoniksen AL, Nystrom B (2007) Effect of hydrophobic modification on rheological and swelling features during chemical gelation of aqueous polysaccharides. Biomacromolecules 8:719–728
Sollich P (1998) Rheological constitutive equation for a model of soft glassy materials. Phys Rev E 58(1):738–759
Tsianou M, Thuresson K, Piculell L (2001) Phase separation in aqueous mixtures of hydrophobically modified cellulose derivatives with their nonmodified analogues. Colloid Polym Sci 279:340–347
Winter HH, Chambon F (1986) Analysis of linear viscoelasticity of a cross-linking polymer at the gel point. J Rheol 30:367–382
Yu QL, Zhou JB, Fung YC (1993) Neutral axis location in bending and youngs modulus of different layers of arterial-wall. Am J Physiol 265:H52–H60
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge support from the NSF-funded Center for Hierarchical Manufacturing (CMMI-0531171), use of central facilities of the NSF-funded MRSEC on Polymers (DMR-0213695), a NSF IGERT Fellowship for JCW (DGE-0654128) and an NIH Chemistry-Biology Interface Traineeship for WLS (National Research Service Award T32 GM08515).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhary, S., White, J.C., Stoppel, W.L. et al. Gelation behavior of polysaccharide-based interpenetrating polymer network (IPN) hydrogels. Rheol Acta 50, 39–52 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-010-0499-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00397-010-0499-9