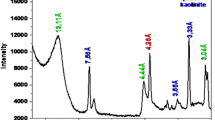
Abstract
The adsorption of promethazine chloride [10-(2-dimethylammonium propyl) fenothiazine chloride] and buformin hydrochloride (1-butylbiguanidine chloride) on montmorillonite was studied in previous work. The present article focuses on the desorption of these molecules from their organocomplexes in a medium of artificial intestinal juice (pH 7.0 ± 0.1) at the temperature of the human body (37 ± 0.5 °C). The desorption was investigated by kinetic studies, basal spacing measurements and Fourier transform IR studies. Important quantitative differences were observed: buformin, which adsorbed in a monolayer coverage, exhibited a very high desorption rate, whereas promethazine formed a pseudotrilayer arrangement and showed a lower dissolution rate.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 20 January 2001 Accepted: 8 March 2001
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fejér, I., Kata, M., Erös, I. et al. Release of cationic drugs from loaded clay minerals. Colloid Polym Sci 279, 1177–1182 (2001). https://doi.org/10.1007/s003960100527
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003960100527