Abstract
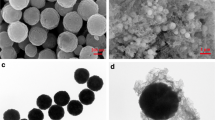
In this study, a novel mesoporous magnetic composite material (Fe3O4@SiO2/CTAB-SiO2) was prepared by a sol-gel and etching method. The morphology, composition, structure, and magnetic properties of the mesoporous Fe3O4@SiO2/CTAB-SiO2 composite material were characterized, and the feasibility of using it to remove bisphenol A (BPA) from water was studied. The results showed that under the optimal adsorption conditions, the removal efficiency of BPA by the composite material is 93.2%. Also, the adsorption isotherms and adsorption kinetic studies showed that the Freundlich isotherm model and the pseudo-second-order kinetic model could better describe the equilibrium and kinetic behaviors of the adsorption process. The maximum adsorption capacity of the composite material for the adsorption of BPA was evaluated as 208.3 mg/g, which was a remarkable amount. The thermodynamic study indicated that the adsorption process was chemical, spontaneous, and exothermic, and the main interaction mechanisms with BPA might be electrostatic and hydrophobic interactions. In addition, after 6 cycles of adsorption-desorption, the recovery efficiency was 80.5% and the FTIR, XRD, and TEM tests showed that the overall structure of the composite material was relatively stable, and the results of real sample verification show that the recovery rate of different added BPA concentration (10, 30, and 50 μg/L) was above 90%. In summary, this composite material is a promising effective magnetic adsorbent for removing bisphenols.












Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to the data also forms part of an ongoing study but are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Chen D, Kannan K, Tan H, Zheng Z, Feng YL, Wu Y, Widelka M (2016) Bisphenol analogues other than BPA: environmental occurrence, human exposure, and toxicity—a review. Environ Sci Technol 50:5438–5453. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.est.5b05387
Yan Z, Liu Y, Yan K, Wu S, Han Z, Guo R, Chen M, Yang Q, Zhang S, Chen J (2017) Bisphenol analogues in surface water and sediment from the shallow Chinese freshwater lakes: occurrence, distribution, source apportionment, and ecological and human health risk. Chemosphere 184:318–328. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.06.010
Zhao X, Qiu W, Zheng Y, Xiong J, Gao C, Hu S (2019) Occurrence, distribution, bioaccumulation, and ecological risk of bisphenol analogues, parabens and their metabolites in the Pearl River Estuary, South China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 180:43–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.04.083
Oehlmann J, Schulte-Oehlmann U, Bachmann J, Oetken M, Lutz I, Kloas W, Ternes TA (2006) Bisphenol A induces superfeminization in the ramshorn snail Marisa cornuarietis(Gastropoda: Prosobranchia) at environmentally relevant concentrations. Environ Health Perspect 114(Suppl 1):127–133. https://doi.org/10.1289/ehp.8065
Maffini MV, Rubin BS, Sonnenschein C, Soto AM (2006) Endocrine disruptors and reproductive health: the case of bisphenol-A. Mol Cell Endocrinol 254-255:179–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mce.2006.04.033
Xu J, Huang G, Guo TL (2016) Developmental bisphenol A exposure modulates immune-related diseases. Toxics 4:23. https://doi.org/10.3390/toxics4040023
Paulose T, Speroni L, Sonnenschein C, Soto AM (2015) Estrogens in the wrong place at the wrong time: fetal BPA exposure and mammary cancer. Reprod Toxicol (Elmsford NY) 54:58–65. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reprotox.2014.09.012
Staples CA, Dome PB, Klecka GM, Oblock ST, Harris LR (1998) A review of the environmental fate, effects, and exposures of bisphenol A. Chemosphere 36:2149–2173. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0045-6535(97)10133-3
Fu P, Kawamura K (2010) Ubiquity of bisphenol A in the atmosphere. Environ Pollut 158:3138–3143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2010.06.040
Michałowicz J (2014) Bisphenol A – Sources, toxicity and biotransformation. Environ Toxicol Pharmacol 37:738–758. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.etap.2014.02.003
Yamamoto T, Yasuhara A, Shiraishi H, Nakasugi O (2001) Bisphenol A in hazardous waste landfill leachates. Chemosphere 42:415–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0045-6535(00)00079-5
Dhiman P, Naushad M, Batoo KM, Kumar A, Sharma G, Ghfar AA, Kumar G, Singh M (2017) Nano Fe x Zn 1 − x O as a tuneable and efficient photocatalyst for solar powered degradation of bisphenol A from aqueous environment. J Clean Prod 165:1542–1556. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.07.245
Zhai Y, Dai Y, Guo J, Zhou L, Chen M, Yang H, Peng L (2020) Novel biochar@CoFe2O4/Ag3PO4 photocatalysts for highly efficient degradation of bisphenol a under visible-light irradiation. J Colloid Interface Sci 560:111–121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2019.08.065
Wu M, He X, Jing B, Wang T, Wang C, Qin Y, Ao Z, Wang S, An T (2020) Novel carbon and defects co-modified g-C3N4 for highly efficient photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A under visible light. J Hazard Mater 384:121323. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121323
Xuan YJ, Endo Y, Fujimoto K (2002) Oxidative degradation of bisphenol A by crude enzyme prepared from potato. J Agric Food Chem 50:6575–6578. https://doi.org/10.1021/jf0205918
Wang W, Yu H, Qin H, Long Y, Ye J, Qu Y (2020) Bisphenol A degradation pathway and associated metabolic networks in Escherichia coli harboring the gene encoding CYP450. J Hazard Mater 388:121737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121737
Sarma H, Nava AR, Manriquez AME, Dominguez DC, Lee W-Y (2019) Biodegradation of bisphenol A by bacterial consortia isolated directly from river sediments. Environ Technol Innov 14:100314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2019.01.008
Bhatia D, Datta D (2019) Removal of bisphenol-a using amine-modified magnetic multiwalled carbon nanotubes: batch and column studies. J Chem Eng Data 64:2877–2887. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jced.9b00240
Gupta VK, Agarwal S, Sadegh H, Ali GAM, Bharti AK, Hamdy Makhlouf AS (2017) Facile route synthesis of novel graphene oxide-β-cyclodextrin nanocomposite and its application as adsorbent for removal of toxic bisphenol A from the aqueous phase. J Mol Liq 237:466–472. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2017.04.113
Lee JH, Kwak SY (2019) Rapid adsorption of bisphenol A from wastewater by β-cyclodextrin-functionalized mesoporous magnetic clusters. Appl Surf Sci 467-468:178–184. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.10.054
Pahigian JM, Zuo Y (2018) Occurrence, endocrine-related bioeffects and fate of bisphenol A chemical degradation intermediates and impurities: a review. Chemosphere 207:469–480. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.05.117
Reddy PVL, Kim K-H, Kavitha B, Kumar V, Raza N, Kalagara S (2018) Photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol A in aqueous media: a review. J Environ Manag 213:189–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.02.059
Husain Q, Qayyum S (2013) Biological and enzymatic treatment of bisphenol A and other endocrine disrupting compounds: a review. Crit Rev Biotechnol 33:260–292. https://doi.org/10.3109/07388551.2012.694409
Esvandi Z, Foroutan R, Mirjalili M, Sorial GA, Ramavandi B (2019) Physicochemical behavior of Penaeuse semisulcatuse chitin for Pb and Cd removal from aqueous environment. J Polym Environ 27(2):263–274. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-018-1345-x
Foroutan R, Mohammadi R, Adeleye AS, Farjadfard S, Esvandi Z, Arfaeinia H, Sorial GA, Ramavandi B, Sahebi S (2019) Efficient arsenic (V) removal from contaminated water using natural clay and clay composite adsorbents. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(29):29748–29762. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06070-5
Foroutan R, Mohammadi R, Ramavandi B (2019) Elimination performance of methylene blue, methyl violet, and Nile blue from aqueous media using AC/CoFe 2 O 4 as a recyclable magnetic composite. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26(19):19523–19539. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05282-z
Foroutan R, Mohammadi R, Ramavandi B, Bastanian M (2018) Removal characteristics of chromium by activated carbon/CoFe 2 O 4 magnetic composite and Phoenix dactylifera stone carbon. Korean J Chem Eng 35(11):2207–2219. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11814-018-0145-2
Mohammed L, Gomaa HG, Ragab D, Zhu J (2017) Magnetic nanoparticles for environmental and biomedical applications: a review. Particuology 30:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2016.06.001
Mehta D, Mazumdar S, Singh SK (2015) Magnetic adsorbents for the treatment of water/wastewater—a review. J Water Process Eng 7:244–265. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2015.07.001
Yamaura M, Camilo RL, Sampaio LC, Macêdo MA, Nakamura M, Toma HE (2004) Preparation and characterization of (3-aminopropyl)triethoxysilane-coated magnetite nanoparticles. J Magn Magn Mater 279:210–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmmm.2004.01.094
Dong A, Lan S, Huang J, Wang T, Zhao T, Xiao L, Wang W, Zheng X, Liu F, Gao G, Chen Y (2011) Modifying Fe3O4-functionalized nanoparticles with N-halamine and their magnetic/antibacterial properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces 3:4228–4235. https://doi.org/10.1021/am200864p
Zhang F, Braun GB, Pallaoro A, Zhang Y, Shi Y, Cui D, Moskovits M, Zhao D, Stucky GD (2011a) Mesoporous multifunctional upconversion luminescent and magnetic “nanorattle” materials for targeted chemotherapy. Nano Lett 12:61–67. https://doi.org/10.1021/nl202949y
Zhang K, Chen H-L, Albela B, Jiang J-G, Wang Y-M, He M-Y, Bonneviot L (2011b) High-temperature synthesis and formation mechanism of stable, ordered MCM-41 silicas by using surfactant cetyltrimethylammonium tosylate as template. Eur J Inorg Chem 2011:59–67. https://doi.org/10.1002/ejic.201000754
Cao D, Jin X, Gan L, Wang T, Chen Z (2016) Removal of phosphate using iron oxide nanoparticles synthesized by eucalyptus leaf extract in the presence of CTAB surfactant. Chemosphere 159:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2016.05.080
Guo J, Chen S, Liu L, Li B, Yang P, Zhang L, Feng Y (2012) Adsorption of dye from wastewater using chitosan–CTAB modified bentonites. J Colloid Interface Sci 382:61–66. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2012.05.044
Wang S, Zhao Q, Wei H, Wang J-Q, Cho M, Cho HS, Terasaki O, Wan Y (2013) Aggregation-free gold nanoparticles in ordered mesoporous carbons: toward highly active and stable heterogeneous catalysts. J Am Chem Soc 135:11849–11860. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja403822d
Fang X, Chen C, Liu Z, Liu P, Zheng N (2011) A cationic surfactant assisted selective etching strategy to hollow mesoporous silica spheres. Nanoscale 3:1632–1639. https://doi.org/10.1039/c0nr00893a
Mardani HR (2017) (Cu/Ni)–Al layered double hydroxides@Fe3O4 as efficient magnetic nanocomposite photocatalyst for visible-light degradation of methylene blue. Res Chem Intermed 43:5795–5810. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11164-017-2963-y
Samarghandi MR, Al-Musawi TJ, Mohseni-Bandpi A, Zarrabi M (2015) Adsorption of cephalexin from aqueous solution using natural zeolite and zeolite coated with manganese oxide nanoparticles. J Mol Liq 211:431–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.06.067
Dehghani MH, Sanaei D, Ali I, Bhatnagar A (2016) Removal of chromium(VI) from aqueous solution using treated waste newspaper as a low-cost adsorbent: kinetic modeling and isotherm studies. J Mol Liq 215:671–679. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.12.057
Zhang K, Li H, Xu X, Yu H (2018) Synthesis of reduced graphene oxide/NiO nanocomposites for the removal of Cr(VI) from aqueous water by adsorption. Microporous Mesoporous Mater 255:7–14. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.micromeso.2017.07.037
Li K, Zeng Z, Xiong J, Yan L, Guo H, Liu S, Dai Y, Chen T (2015) Fabrication of mesoporous Fe3O4@SiO2@CTAB–SiO2 magnetic microspheres with a core/shell structure and their efficient adsorption performance for the removal of trace PFOS from water. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 465:113–123. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.10.044
Zandipak R, Sobhanardakani S (2018) Novel mesoporous Fe3O4/SiO2/CTAB–SiO2 as an effective adsorbent for the removal of amoxicillin and tetracycline from water. Clean Techn Environ Policy 20:871–885. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10098-018-1507-5
Tsai WT, Lai CW, Su TY (2006) Adsorption of bisphenol-a from aqueous solution onto minerals and carbon adsorbents. J Hazard Mater 134:169–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.10.055
Guo S, Huang L, Li W, Wang Q, Wang W, Yang Y (2019) Willow tree-like functional groups modified magnetic nanoparticles for ultra-high capacity adsorption of dye. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 101:99–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2019.04.041
Najafi F, Moradi O, Rajabi M, Asif M, Tyagi I, Agarwal S, Gupta VK (2015) Thermodynamics of the adsorption of nickel ions from aqueous phase using graphene oxide and glycine functionalized graphene oxide. J Mol Liq 208:106–113. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.04.033
Fathi MR, Asfaram A, Farhangi A (2015) Removal of Direct Red 23 from aqueous solution using corn stalks: Isotherms, kinetics and thermodynamic studies. Spectrochim Acta A Mol Biomol Spectrosc 135:364–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.saa.2014.07.008
Foroutan R, Mohammadi R, MousaKhanloo F, Sahebi S, Ramavandi B, Kumar PS, Vardhan KH (2020) Performance of montmorillonite/graphene oxide/CoFe2O4 as a magnetic and recyclable nanocomposite for cleaning methyl violet dye-laden wastewater. Adv Powder Technol 31(9):3993–4004. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2020.08.001
Foroutan R, Peighambardoust SJ, Mohammadi R, Omidvar M, Sorial GA, Ramavandi B (2020) Influence of chitosan and magnetic iron nanoparticles on chromium adsorption behavior of natural clay: adaptive neuro-fuzzy inference modeling. Int J Biol Macromol 151:355–365. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.02.202
Peighambardoust SJ, Bavil OA, Foroutan R, Arsalani N (2020) Removal of malachite green using carboxymethyl cellulose-g-polyacrylamide/montmorillonite nanocomposite hydrogel. Int J Biol Macromol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.05.093
Ding Y, Xu Y, Ding B, Li Z, Xie F, Zhang F, Wang H, Liu J, Wang X (2017) Structure induced selective adsorption performance of ZIF-8 nanocrystals in water. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 520:661–667. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2017.02.012
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0032-9592(98)00112-5
Foroutan R, Mohammadi R, Peighambardoust SJ, Jalali S, Ramavandi B (2020) Application of nano-silica particles generated from offshore white sandstone for cadmium ions elimination from aqueous media. Environ Technol Innov 19:101031. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101031
Savari A, Hashemi S, Arfaeinia H, Dobaradaran S, Foroutan R, Mahvi AH, Fouladvand M, Sorial GA, Farjadfard S, Ramavandi B (2020) Physicochemical characteristics and mechanism of fluoride removal using powdered zeolite-zirconium in modes of pulsed & continuous sonication and stirring. Adv Powder Technol 31(8):3521–3532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apt.2020.06.039
Foroutan R, Peighambardoust SJ, Aghdasinia H, Mohammadi R, Ramavandi B (2020) Modification of bio-hydroxyapatite generated from waste poultry bone with MgO for purifying methyl violet-laden liquids. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-10330-0
Ahmadi A, Foroutan R, Esmaeili H, Tamjidi S (2020) The role of bentonite clay and bentonite clay@ MnFe2O4 composite and their physico-chemical properties on the removal of Cr (III) and Cr (VI) from aqueous media. Environ Sci Pollut Res:1–14. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-07756-x
Dehghani MH, Mahvi AH, Rastkari N, Saeedi R, Nazmara S, Iravani E (2015) Adsorption of bisphenol A (BPA) from aqueous solutions by carbon nanotubes: kinetic and equilibrium studies. Desalin Water Treat 54:84–92. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.876671
Mphahlele K, Onyango MS, Mhlanga SD (2015) Adsorption of aspirin and paracetamol from aqueous solution using Fe/N-CNT/β-cyclodextrin nanocomopsites synthesized via a benign microwave assisted method. J Environ Chem Eng 3:2619–2630. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2015.02.018
Xu J, Wang L, Zhu Y (2012) Decontamination of bisphenol A from aqueous solution by graphene adsorption. Langmuir 28:8418–8425. https://doi.org/10.1021/la301476p
Acknowledgments
We thank American Journal Experts (AJE) for English language editing.
Funding
This study was funded by the Post-graduate’s Innovation Fund Project of Hebei Province (CXZZBS2019022); the National Natural Science Foundation of China (grant numbers 21377033, NSFC); the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province (B2018201224); and the Natural Science Foundation of Hebei Province, General Program (E2020201036).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Yichao Gong designed the study, performed the experiments, analyzed the data, and wrote the manuscript; Guisui Liu, Qianqian Wang, Aixue Zhu, and Qiuhua Wu provided the resources; Pengyan Liu provided funding acquisition, project administration, supervision, and writing—review and editing.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gong, Y., Liu, G., Wang, Q. et al. Synthesis of a novel mesoporous Fe3O4@SiO2/CTAB-SiO2 composite material and its application in the efficient removal of bisphenol A from water. Colloid Polym Sci 299, 807–822 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04801-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-020-04801-6