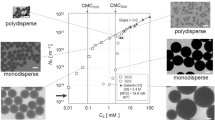
Abstract
Soap-free emulsion polymerization of styrene using oil-soluble initiators and electrolytes was investigated to synthesize micron-sized polystyrene particles. It was clear that an oil-soluble initiator, such as AIBN, worked like a water-soluble initiator in soap-free emulsion polymerization of styrene to prepare monodispersed particles with negative charges, probably because of the polarization of the electron-attractive functional groups decomposed from the initiators and the pi electron cloud of benzene in a styrene monomer. The addition of an electrolyte enabled secondary particles to effectively promote hetero-coagulation for particle growth by reduction of an electrical double layer and prevention of self-growth. Changing the concentration and type of electrolyte enabled us to control the size up to 12 μm in soap-free emulsion polymerization of styrene using AIBN. Conventionally, organic solvents and surfactants have been used to prepare micron-sized polymeric particles, but this method enabled the synthesis of micron-sized polymeric particles in water using electrolytes without surfactants.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Svec F, Frechet JMJ (1996) Science 273:205
Ugelstad J, Berge A, Ellingsen T, Schmid R, Nilsen TN, Mork PC et al (1992) Prog Polym Sci 17:87
Kawaguchi H (2000) Prog Polym Sci 25:1171
Tseng CM, Lu YY, Elaasser MS, Vanderhoff JW (1986) J Polym Sci Pol Chem 24:2995
Lok KP, Ober CK (1985) Can J Chem 63:209
Goodall AR, Wilkinson MC, Hearn J (1977) J Polym Sci Pol Chem 15:2193
Gu SC, Inukai S, Konno M (2002) J Chem Eng Jpn 35:977
Gu S, Akama H, Nagao D, Kobayashi Y, Konno M (2004) Langmuir 20:7948
Yamada Y, Sakamoto T, Gu S, Konno M (2005) J Colloid Interface Sci 281:249
Yamamoto T, Kanda Y, Higashitani K (2004) Langmuir 20:4400
Yamamoto T, Nakayama M, Kanda Y, Higashitani K (2006) J Colloid Interface Sci 297:112
Yamamoto T, Kanda Y, Higashitani K (2006) J Colloid Interface Sci 299:493
Yamamoto T, Kanda Y, Higashitani K (2006) J Chem Eng Jpn 39:596
Yoshida E (2010) Colloid Polym Sci 288:341
Yoshida E (2010) Colloid Polym Sci 288:901
Qiu J, Gaynor SG, Matyjaszewski K (1999) Macromolecules 32:2872
Anon., Product Bulletin V-50,. Wako Chemicals, USA. 1985.
Talaterben M, Bywater S (1955) J Am Chem Soci 77:3712
Overberger CG, Oshaughnessy MT, Shalit H (1949) J Am Chem Soc 71:2661
Verwey EJW, Overbeek JTG. Theory of the stability of lyophobic colloids. Dover Publications, Mineola, USA. 1948.
Nakabayashi H, Yamada A, Noba M, Kobayashi Y, Konno M, Nagao D (2010) Langmuir 26:7512
Yamamoto T, Fukushima T, Kanda Y, Higashitani K (2005) J Colloid Interface Sci 292:392
Acknowledgement
This study was financially supported in part by Grants-in-Aid for Young Scientists (B) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (No. 23760721). FE- SEM in cryogenics and instrumental analysis Division Natural Science Center for Basic Research and Development (N-BARD) Hiroshima University was used.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, T. Synthesis of micron-sized polymeric particles in soap-free emulsion polymerization using oil-soluble initiators and electrolytes. Colloid Polym Sci 290, 1023–1031 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-012-2618-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00396-012-2618-x