Abstract
Purpose
To investigate whether a maternal high-fat diet (HF) during pregnancy and/or suckling periods predisposes adult C57BL/6 mice offspring to morphological pancreatic modifications.
Methods
Male pups were divided into 5 groups: SC (standard chow)—from dams fed SC during gestation and lactation, maintaining an SC diet from postweaning to adulthood; G—from dams fed HF diets during gestation; L—from dams fed HF diets during lactation; GL—from dams fed HF diets during gestation and lactation; and GL/HF—from dams fed HF diets during gestation and lactation, maintaining an HF diet from postweaning to adulthood. We analysed body mass (BM), plasma insulin, pancreas and adipose tissue structures.
Results
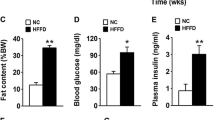
During the entire experiment, the SC group had the lowest BM. However, GL/HF offspring were heavier than the other groups. This weight gain was also accompanied by adipocyte hypertrophy. At 3 months, G offspring showed an increased insulin levels and impairment in carbohydrates metabolism. Furthermore, pancreatic islets were hypertrophied in G, GL and GL/HF offspring in comparison with SC offspring.
Conclusion
HF diet administration during the gestation period is more harmful than during the lactation period, exerting deleterious effects on pancreatic morphology in addition to larger fat deposits in adult mice offspring.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Katulanda P, Jayawardena MA, Sheriff MH, Constantine GR, Matthews DR (2010) Prevalence of overweight and obesity in Sri Lankan adults. Obes Rev 11:751–756
Duvnjak L, Duvnjak M (2009) The metabolic syndrome—an ongoing story. J Physiol Pharmacol 60(Suppl 7):19–24
Tierney AC, McMonagle J, Shaw DI, Gulseth HL, Helal O, Saris WH, Paniagua JA, Golabek-Leszczynska I, Defoort C, Williams CM, Karsltrom B, Vessby B, Dembinska-Kiec A, Lopez-Miranda J, Blaak EE, Drevon CA, Gibney MJ, Lovegrove JA, Roche HM (2011) Effects of dietary fat modification on insulin sensitivity and on other risk factors of the metabolic syndrome—LIPGENE: a European randomized dietary intervention study. Int J Obes (Lond) 35:800–809
Cerf ME (2010) High fat programming of beta-cell failure. Adv Exp Med Biol 654:77–89
Drake AJ, Reynolds RM (2010) Impact of maternal obesity on offspring obesity and cardiometabolic disease risk. Reproduction 140:387–398
Fraulob JC, Ogg-Diamantino R, Fernandes-Santos C, Aguila MB, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA (2010) A mouse model of metabolic syndrome: insulin resistance, fatty liver and non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease (NAFPD) in C57BL/6 mice fed a high fat diet. J Clin Biochem Nutr 46:212–223
Charlton M (2009) Fetal obesity syndrome: maternal nutrition as a cause of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 50:1696–1698
White CL, Purpera MN, Morrison CD (2009) Maternal obesity is necessary for programming effect of high-fat diet on offspring. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 296:R1464–1472
Souza-Mello V, Gregorio BM, Cardoso-de-Lemos FS, de Carvalho L, Aguila MB, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA (2010) Comparative effects of telmisartan, sitagliptin and metformin alone or in combination on obesity, insulin resistance, and liver and pancreas remodelling in C57BL/6 mice fed on a very high-fat diet. Clin Sci (Lond) 119:239–250
Pelleymounter MA, Cullen MJ, Baker MB, Hecht R, Winters D, Boone T, Collins F (1995) Effects of the obese gene product on body weight regulation in ob/ob mice. Science 269:540–543
Campfield LA, Smith FJ, Guisez Y, Devos R, Burn P (1995) Recombinant mouse OB protein: evidence for a peripheral signal linking adiposity and central neural networks. Science 269:546–549
Lee Y, Wang MY, Kakuma T, Wang ZW, Babcock E, McCorkle K, Higa M, Zhou YT, Unger RH (2001) Liporegulation in diet-induced obesity. The antisteatotic role of hyperleptinemia. J Biol Chem 276:5629–5635
Lee Y, Lingvay I, Szczepaniak LS, Ravazzola M, Orci L, Unger RH (2010) Pancreatic steatosis: harbinger of type 2 diabetes in obese rodents. Int J Obes (Lond) 34:396–400
Gregorio BM, Souza-Mello V, Carvalho JJ, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA, Aguila MB (2010) Maternal high-fat intake predisposes nonalcoholic fatty liver disease in C57BL/6 offspring. Am J Obstet Gynecol 203(495):e491–498
Reeves PG, Nielsen FH, Fahey GC Jr (1993) AIN-93 purified diets for laboratory rodents: final report of the American Institute of Nutrition ad hoc writing committee on the reformulation of the AIN-76A rodent diet. J Nutr 123:1939–1951
Langley-Evans SC, Gardner DS, Jackson AA (1996) Maternal protein restriction influences the programming of the rat hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal axis. J Nutr 126:1578–1585
Wainwright PE (1998) Issues of design and analysis relating to the use of multiparous species in developmental nutritional studies. J Nutr 128:661–663
Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA, Fernandes-Santos C, Aguila MB (2010) Image analysis and quantitative morphology. Methods Mol Biol 611:211–225
Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA (2003) Stereological tools in biomedical research. An Acad Brasil Cienc 75:469–486
Srinivasan M, Katewa SD, Palaniyappan A, Pandya JD, Patel MS (2006) Maternal high-fat diet consumption results in fetal malprogramming predisposing to the onset of metabolic syndrome-like phenotype in adulthood. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 291:E792–799
Ashino NG, Saito KN, Souza FD, Nakutz FS, Roman EA, Velloso LA, Torsoni AS, Torsoni MA (2012) Maternal high-fat feeding through pregnancy and lactation predisposes mouse offspring to molecular insulin resistance and fatty liver. J Nutr Biochem 23:341–348
Dunn GA, Bale TL (2009) Maternal high-fat diet promotes body length increases and insulin insensitivity in second-generation mice. Endocrinology 150:4999–5009
Guo F, Jen KL (1995) High-fat feeding during pregnancy and lactation affects offspring metabolism in rats. Physiol Behav 57:681–686
Parente LB, Aguila MB, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA (2008) Deleterious effects of high-fat diet on perinatal and postweaning periods in adult rat offspring. Clin Nutr 27:623–634
Gniuli D, Calcagno A, Caristo ME, Mancuso A, Macchi V, Mingrone G, Vettor R (2008) Effects of high-fat diet exposure during fetal life on type 2 diabetes development in the progeny. J Lipid Res 49:1936–1945
Lucas A (1998) Programming by early nutrition: an experimental approach. J Nutr 128:401S–406S
Rooney K, Ozanne SE (2011) Maternal over-nutrition and offspring obesity predisposition: targets for preventative interventions. Int Journal of obesity 35:883–890
Fraulob JC, Souza-Mello V, Aguila MB, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA (2012) Beneficial effects of rosuvastatin on insulin resistance, adiposity, inflammatory markers and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in mice fed on a high-fat diet. Clin Sci (Lond) 123:259–270
Jarrar MH, Baranova A, Collantes R, Ranard B, Stepanova M, Bennett C, Fang Y, Elariny H, Goodman Z, Chandhoke V, Younossi ZM (2008) Adipokines and cytokines in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 27:412–421
Nivoit P, Morens C, Van Assche FA, Jansen E, Poston L, Remacle C, Reusens B (2009) Established diet-induced obesity in female rats leads to offspring hyperphagia, adiposity and insulin resistance. Diabetologia 52:1133–1142
Portha B, Chavey A, Movassat J (2011) Early-life origins of type 2 diabetes: fetal programming of the beta-cell mass. Exp Diabetes Res 2011:105076
Ackermann AM, Gannon M (2007) Molecular regulation of pancreatic beta-cell mass development, maintenance, and expansion. J Mol Endocrinol 38:193–206
Fex M, Nitert MD, Wierup N, Sundler F, Ling C, Mulder H (2007) Enhanced mitochondrial metabolism may account for the adaptation to insulin resistance in islets from C57BL/6 J mice fed a high-fat diet. Diabetologia 50:74–83
Flier SN, Kulkarni RN, Kahn CR (2001) Evidence for a circulating islet cell growth factor in insulin-resistant states. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98:7475–7480
Kahn SE (2001) Clinical review 135: the importance of beta-cell failure in the development and progression of type 2 diabetes. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 86:4047–4058
Sesti G (2006) Pathophysiology of insulin resistance. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab 20:665–679
Theys N, Ahn MT, Bouckenooghe T, Reusens B, Remacle C (2011) Maternal malnutrition programs pancreatic islet mitochondrial dysfunction in the adult offspring. J Nutr Biochem 22:985–994
Rasmussen KM, Catalano PM, Yaktine AL (2009) New guidelines for weight gain during pregnancy: what obstetrician/gynecologists should know. Curr Opin Obstet Gynecol 21:521–526
Symonds ME, Sebert SP, Budge H (2009) The impact of diet during early life and its contribution to later disease: critical checkpoints in development and their long-term consequences for metabolic health. Proc Nutr Soc 68:416–421
Cerf ME, Williams K, Chapman CS, Louw J (2007) Compromised beta-cell development and beta-cell dysfunction in weanling offspring from dams maintained on a high-fat diet during gestation. Pancreas 34:347–353
Cerf ME, Williams K, Nkomo XI, Muller CJ, Du Toit DF, Louw J, Wolfe-Coote SA (2005) Islet cell response in the neonatal rat after exposure to a high-fat diet during pregnancy. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol 288:R1122–1128
Cerf ME, Chapman CS, Muller CJ, Louw J (2009) Gestational high-fat programming impairs insulin release and reduces Pdx-1 and glucokinase immunoreactivity in neonatal Wistar rats. Metabolism 58:1787–1792
Cerf ME (2011) Parental high-fat programming of offspring development, health and beta-cells. Islets 3:118–120
Catta-Preta M, Martins MA, Brunini TMC, Mendes-Ribeiro AC, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA, Aguila MB (2012) Modulation of cytokines, resistin, and distribution of adipose tissue in C57BL/6 mice by different high-fat diets. Nutrition 28:212–219
Ellingsgaard H, Ehses JA, Hammar EB, Van Lommel L, Quintens R, Martens G, Kerr-Conte J, Pattou F, Berney T, Pipeleers D, Halban PA, Schuit FC, Donath MY (2008) Interleukin-6 regulates pancreatic alpha-cell mass expansion. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 105:13163–13168
Gluckman PD, Hanson MA (2004) Developmental origins of disease paradigm: a mechanistic and evolutionary perspective. Pediatr Res 56:311–317
Gluckman PD, Hanson MA (2004) The developmental origins of the metabolic syndrome. Trends Endocrinol Metab 15:183–187
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by grants from the Brazilian agencies CNPq (Conselho Nacional de Ciencia e Tecnologia) and FAPERJ (Fundaçao para o Amparo a Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro). The authors would like to thank Thatiany Marinho and Angelica Figueiredo for their technical assistance.
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gregorio, B.M., Souza-Mello, V., Mandarim-de-Lacerda, C.A. et al. Maternal high-fat diet is associated with altered pancreatic remodelling in mice offspring. Eur J Nutr 52, 759–769 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-012-0382-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00394-012-0382-9