Abstract
Introduction
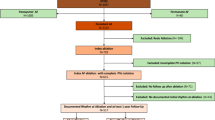
Patients with persistent atrial fibrillation (AF) may additionally suffer from a concealed sinus node disease. We sought to determine the incidence, indications and predictors of acute pacemaker [PM] implantation within 1 week after the ablation of persistent AF.
Methods and results
We performed a retrospective analysis of patients, who had had an ablation of persistent AF at our center. Between 01/2011 and 08/2016, 1234 patients (mean age 65 ± 10 years, 66.7% male) without prior PM implantation underwent an ablation of persistent AF. Pulmonary vein isolation (PVI) was performed in 1158 (93.8%), the additional ablation of complex fractionated atrial electrograms (CFAE) in 1109 (89.9%) and linear ablation in 524 (42.5%) patients. Temporary cardiac pacing was necessary in 27 (2.2%) patients. The temporary PM was removed in 15 patients (1.2%) because sinus node recovered after a median of 1.0 (minimum 0.1−maximum 2.0) day. The remaining 12 (1.0%) patients required the implantation of a permanent PM. Another 13 (1.1%) patients required permanent PM implantation without prior temporary pacing. In a multivariable regression model, age [OR 1.07 (1.02–1.12), p = 0.006], sinus pauses prior to ablation [OR 7.97 (2.36–26.88), p = 0.001] and atria with low voltage [OR 2.83 (1.31–6.11), p = 0.008] were identified as significant predictors for acute cardiac pacing.
Conclusion
Acute cardiac pacing within 1 week after the ablation of persistent AF was necessary in 40 (3.2%) patients. Age, sinus pauses in history prior to ablation and the existence of low-voltage areas in the atria were identified as relevant risk factors.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chugh SS, Roth GA, Gillum RF, Mensah GA (2014) Global burden of atrial fibrillation in developed and developing nations. Glob Heart 9:113–119
Freeman JV, Simon DN, Go AS, Spertus J, Fonarow GC, Gersh BJ, Hylek EM, Kowey PR, Mahaffey KW, Thomas LE, Chang P, Peterson ED, Piccini JP (2015) Outcomes registry for better informed treatment of atrial fibrillation (ORBIT-AF) investigators and patients. Association between atrial fibrillation symptoms, quality of life, and patient outcomes: results from the outcomes registry for better informed treatment of atrial fibrillation (ORBIT-AF). Circ Cardiovasc Qual Outcomes 8:393–402
Haim M, Hoshen M, Reges O, Rabi Y, Balicer R, Leibowitz M (2015) Prospective national study of the prevalence, incidence, management and outcome of a large contemporary cohort of patients with incident non-valvular atrial fibrillation. J Am Heart Assoc 4:e001486
Schnabel RB, Yin X, Gona P, Larson MG, Beiser AS, McManus DD, Newton-Cheh C, Lubitz SA, Magnani JW, Ellinor PT, Seshadri S, Wolf PA, Vasan RS, Benjamin EJ, Levy D (2015) 50 year trends in atrial fibrillation prevalence, incidence, risk factors, and mortality in the Framingham Heart Study: a cohort study. Lancet 386:154–162
Marrouche N, Brachmann J, Andresen D, Siebels J, Boersma L, Jordaens L, Merkely B, Pokushalov E, Sanders P, Proff J, Schunkert H, Christ H, Vogt J, Bänsch D, for the CASTLE-AF Investigators (2018) Catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation with heart failure. NEJM 378:417–427
Mohanty S, Santangeli P, Mohanty P, Di Biase L, Holcomb S, Trivedi C, Bai R, Burkhardt D, Hongo R, Hao S, Beheiry S, Santoro F, Forleo G, Gallinghouse JG, Horton R, Sanchez JE, Bailey S, Hranitzky PM, Zagrodzky J, Natale A (2014) Catheter ablation of asymptomatic longstanding persistent atrial fibrillation: impact on quality of life, exercise performance, arrhythmia perception, and arrhythmia-free survival. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 25:1057–1064
Santangeli P, Di Biase L, Burkhardt DJ, Horton R, Sanchez J, Bai R, Pump A, Perez M, Wang PJ, Natale A, Al-Ahmad A (2012) Catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: state-of-the-art techniques and future perspectives. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown) 13:108–124
Steven D, Sultan A, Schäffer B, Servatius H, Hoffmann B, Lüker J, Willems S (2013) Catheter ablation of persistent and long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation. Strategies and results. Herzschrittmacherther Elektrophysiol 24(1):15–18
Tilz RR, Lin T, Rillig A, Heeger CH, Scholz L, Wohlmuth P, Bucur T, Metzner A, Mathew S, Wissner E, Ouyang F, Kuck KH (2017) Focal Impulse and rotor modulation for the treatment of atrial fibrillation: locations and 1 year outcomes of human rotors identified using a 64-electrode basket catheter. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 28:367–374
Wang YL, Liu X, Tan HW, Zhou L, Jiang WF, Gu J, Liu YG (2013) Evaluation of linear lesions in the left and right atrium in ablation of long-standing atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 36:1202–1210
Jackson LR II, Rathakrishnan B, Campbell K, Thomas KL, Piccini JP, Bahnson T, Stiber JA, Daubert JP (2017) Sinus node dysfunction and atrial fibrillation: a reversible phenomenon? Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 40:442–450
Jackson LR II, Kim SH, Piccini JP Sr, Gersh BJ, Naccarelli GV, Reiffel JA, Freeman J, Thomas L, Chang P, Fonarow GC, Go AS, Mahaffey KW, Peterson ED, Kowey PR (2016) Sinus node dysfunction is associated with higher symptom burden and increased comorbid illness: results from the ORBIT-AF registry. Clin Cardiol 39:119–125
John RM, Kumar S (2016) Sinus node and atrial arrhythmias. Circulation 133:1892–1900
Killu AM, Fender EA, Deshmukh AJ, Munger TM, Araoz P, Brady PA, Cha YM, Packer DL, Friedman PA, Asirvatham SJ, Noseworthy PA, Mulpuru SK (2016) Acute sinus node dysfunction after atrial ablation: incidence, risk factors, and management. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 39:1116–1125
Sohns C, Staab W, O´Neill M, Vollmann D (2016) Reversible sinus node injury during circumferential pulmonary vein ablation. Clin Res Cardiol 105:968–970
Camm AJ, Kirchhof P, Lip GY, Schotten U, Savelieva I, Ernst S, Van Gelder IC, Al-Attar N, Hindricks G, Prendergast B, Heidbuchel H, Alfieri O, Angelini A, Atar D, Colonna P, De Caterina R, De Sutter J, Goette A, Gorenek B, Heldal M, Hohloser SH, Kolh H, Le Heuzey JY, Ponikowski P, Rutten FH (2010) Guidelines for the management of atrial fibrillation. Eur Heart J 31:2369–2429
Deshmukh AJ, Yao X, Schilz S, Van Houten H, Sangaralingham LR, Asirvatham SJ, Friedman PA, Packer DL, Noseworthy PA (2016) Pacemaker implantation after catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation. J Interv Card Electrophysiol 45:99–105
Masuda M, Inoue K, Iwakura K, Okamura A, Koyama Y, Kimura R, Toyoshima Y, Doi A, Sotomi Y, Komuro I, Fujii K (2012) Preprocedural ventricular rate predicts subsequent sick sinus syndrome after ablation for long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 35:1074–1080
Bao Z, Chen H, Yang B, Shehata M, Ju W, Zhang F, Yang G, Gu K, Li M, Cao K, Wang X, Chen M (2017) Prolonged sinus pauses upon termination of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation: abnormal right atrial electrophysiologic and electroanatomic findings. Tex Heart Inst J 44:107–114
De Sisti A, Leclercq JF, Fiorello P, Manot S, Halimi F, Attuel P (2000) Electrophysiologic characteristics of the atrium in sinus node dysfunction: atrial refractoriness and conduction. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 11:30–33
Weirich J (2017) Remodeling of the aging heart: sinus node dysfunction and atrial fibrillation. Herzschrittmacherther Elektrophysiol 28:29–38
Schumacher K, Dagres N, Hindricks G, Husser D, Bollmann A, Kornej J (2017) Characteristics of PR interval as predictor for atrial fibrillation: association with biomarkers and outcomes. Clin Res Cardiol 106:767–775
Chen G, Dong JZ, Liu XP, Zhang XY, Long DY, Sang CH, Ning M, Tang RB, Jiang CX, Ma CS (2011) Sinus node injury as a result of superior vena cava isolation during catheter ablation for atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter. Pacing Clin Electrophysiol 34:163–170
Inada K, Yamane T, Tokutake K, Yokoyama K, Mishima T, Hioki M, Narui R, Ito K, Tanigawa S, Yamashita S, Tokuda M, Matsuo S, Shibayama K, Miyanaga S, Date T, Sugimoto K, Yoshimura M (2014) The role of successful catheter ablation in patients with paroxysmal atrial fibrillation and prolonged sinus pauses: outcome during a 5-year follow-up. Europace 16:208–213
Hocini M, Sanders P, Deisenhofer I, Jaïs P, Hsu LF, Scavée C, Weerasoriya R, Raybaud F, Macle L, Shah DC, Garrigue S, Le Metayer P, Clémenty J, Haïssaguerre M (2003) Reverse remodeling of sinus node function after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation in patients with prolonged sinus pauses. Circulation 108:1172–1175
Khaykin Y, Marrouche NF, Martin DO, Saliba W, Schweikert R, Wexman M, Strunk B, Beheiry S, Saad E, Bhargava M, Burkhardt JD, Joseph G, Tchou P, Natale A (2004) Pulmonary vein isolation for atrial fibrillation in patients with symptomatic sinus bradycardia or pauses. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol 15:784–789
Rosen KM, Loeb HS, Sinno Z, Rahimtoola SH, Gunnar R (1971) Cardiac conduction in patients with symptomatic sinus node disease. Circulation 43:836–844
Sairaku A, Nakano Y, Oda N, Makita Y, Kajihara K, Tokuyama T, Motoda C, Fujiwara M, Kihara Y (2012) Prediction of sinus node dysfunction in patients with long-standing persistent atrial fibrillation using the atrial fibrillatory cycle length. J Electrocardiol 45:141–147
Chung H, Uhm JS, Sung JH, Kim JY, Pak HN, Lee MH, Joung B (2014) The type of sinus node dysfunction might predict the severity of atrial remodeling and clinical outcome after catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation. Int J Cardiol 172:487–489
Funding
No financial support of the study
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest concerning this study.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Semmler, V., von Krogh, F., Haller, B. et al. The incidence, indications and predictors of acute pacemaker implantation after ablation of persistent atrial fibrillation. Clin Res Cardiol 108, 651–659 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-018-1393-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00392-018-1393-1