Abstract
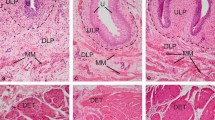
The interstitial cells of Cajal (ICC) play an important role in the control of gut motility. The recognition that the ICC cell membrane harbors the c-kit receptor (CD117) sparked rapid advancement in ICC research on the gut and certain pathologies using immunochemical and molecular methods. The question arises whether ICC exist in the upper urinary tract (UUT) and trigger motility. The present study analyzed the distribution of the c-kit receptor in the normal human UUT compared with various species. Immunohistochemistry (alkaline-phosphatase–anti-alkaline-phosphatase technique, immunofluorescence) was applied on serial sections using monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies recognizing the c-kit receptor. C-kit staining was compared with standard endothelial, epithelial, neurogenic, histiocytic, mast cell, and smooth muscle markers, as well as a negative control. Normal proximal, middle, and distal ureter segments were analyzed in rodents, carnivores, porcines, cow, and humans. In all species the c-kit receptor was detected in either round or spindle-shaped cells. Because of their antigenic profile, the round cells were identified as mast cells occurring in all layers of the ureteral wall except the urothelium and were more frequent in humans. In contrast, the population of spindle-shaped cells was marked only by anti-c-kit receptor antibodies, thus resembling ICC. These ICC-like cells were found among the inner and outer smooth muscle layers and in the lamina propria of all species. In humans, spindle-shaped cells were also found vertically oriented within the urothelium. Our morphological data present for the first time the distribution of ICC in the UUT of various species. The ubiquitous distribution in the entire pyeloureteral complex provides strong evidence that ICC generate electrical pacemaker activity within the UUT as an intrinsic system. Animal studies may help to understand the physiological importance of these ICC-like cells. The significance of these findings needs to be evaluated by functional studies and investigations of certain congenital pathologies with disturbance of the urinary outflow.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Santicioli P, Maggi CA (1998) Myogenic and neurogenic factors in the control of pyeloureteral motility and ureteral peristalsis. Pharmacol Rev 50:683
Klemm MF, Exintaris B, Lang RI (1999) Identification of the cells underlying pacemaker activity in the guineapig upper urinary tract. J Physiol 519(Pt)3:867
Gosling JA, Dixon JS (1974) Species variation in the location of upper urinary tract pacemaker cells. Invest Urol 11:418
Constantinou CE (1974) Renal pelvic pacemaker control of ureteral peristaltic rate. Am J Physiol 226:1413
Lang RJ, Exintaris B, Teele ME, et al. (1998) Electrical basis of peristalsis in the mammalian upper urinary tract. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol 25:310
Shafik A (1996) Electroureterogram human study of the electromechanical activity of the ureter. Urology 48:696
Kim YC, Koh SD, Sanders KM (2002) Voltage-dependent inward currents of interstitial cells of Cajal from murine colon and small intestine. J Physiol 541:797
Huizinga JD, Thuneberg L, Kluppel M, et al. (1995) Wildt gene required for interstitial cells of Cajal and for intestinal pacemaker activity. Nature 373:347
Torihashi S, Ward SM, Nishikawa S, et al. (1995) C-kit-dependent development of interstitial cells and electrical activity in the murine gastrointestinal tract. Cell Tissue Res 280:97
Lammie A, Drobnjak M, Gerald W, et al. (1994) Expression of c-kit and kit ligand proteins in normal human tissues. J Histochem Cytochem 42:1417
Hagger R, Gharaie S, Finlayson C, et al. (1998) Regional and transmural density of interstitial cells of Cajal in human colon and rectum. Am J Physiol 275:G1309
Hagger R, Gharaie S, Finlayson C, et al. (1998) Distribution of the interstitial cells of Cajal in the human anorectum. J Auton Nerv Syst 73:75
Kenny SE, Connell G, Woodward MN, et al. (1999) Ontogeny of interstitial cells of Cajal in the human intestine. J Pediatr Surg 34:1241
Streutker CJ, Huizinga JD, Campbell F, et al. (2003) Loss of CDl17 (c-kit)- and CD34-positive ICC and associated CD34-positive fibroblasts defines a subpopulation of chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Am J Surg Pathol 27:228
Rolle U, Piotrowska AP, Nemeth L, et al. (2002) Altered distribution of interstitial cells of Cajal in Hirschsprung disease. Arch Pathol Lab Med 126:928
Rolle U, Yoneda A, Solari V, et al. (2002) Abnormalities of c-kit-positive cellular network in isolated hypoganglionosis. J Pediatr Surg 37:709
Yamataka A, Kato Y, Tibboel D, et al. (1995) A lack of intestinal pacemaker (c-kit) in aganglionic bowel of patients with Hirschsprung’s disease. J Pediatr Surg 30:441
Isozaki K, Hirota S, Miyagawa I, et al. (1997) Deficiency of c-kit+ cells in patients with a myopathic form of chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. Am J Gastroenterol 92:332
Vanderwinden IM, Liu H, De Laet MH, et al. (1996) Study of the interstitial cells of Cajal in infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis. Gastroenterology 111:279
Vanderwinden IM, Rumessen II, Liu H, et al. (1996) Interstitial cells of Cajal in human colon and in Hirschsprung’s disease. Gastroenterology 111:901
Isozaki K, Hirota S, Nakama A, et al. (1995) Disturbed intestinal movement, bile reflux to the stomach, and deficiency of c-kit-expressing cells in WsIWs mutant rats. Gastroenterology 109:456
Ward SM, Burns AI, Torihashi S, et al. (1994) Mutation of the proto-oncogene c-kit blocks development of interstitial cells and electrical rhythmicity in murine intestine. J Physiol 480 (Part 1):91
Pezzone MA, Watkins SC, Alber SM, et al. (2003) Identification of c-kit-positive cells in the mouse ureter: the interstitial cells of Cajal of the urinary tract. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol 284:F925–F929
Der-Silaphet T, Malysz J, Hagel S, et al. (1998) Interstitial cells of Cajal direct normal propulsive contractile activity in the mouse small intestine. Gastroenterology 114:724
Metzger R, Schuster T, Till H, et al. (2004) Cajal-like cells in the human upper urinary tract. J Urol 172:769
Cordell JL, Falini B, Erber WN, et al. (1984) Immunoenzymatic labeling of monoclonal antibodies using immune complexes of alkaline phosphatase and monoclonal anti-alkaline phosphatase (AP AAP complexes). J Histochem Cytochem 32:219
Aldenborg F, Peeker R, Fall M, et al. (1998) Metaplastic transformation of urinary bladder epithelium: effect on mast cell recruitment, distribution, and phenotype expression. Am J Pathol 153:149
Drew E, Merkens H, Chelliah S, et al. (2002) CD34 is a specific marker of mature murine mast cells. Exp Hematol 30:1211
Jerde TJ, Saban R, Bjorling DE, et al. (2000) Distribution of neuropeptides, histamine content, and inflammatory cells in the ureter. Urology 56:173
Metzger R, Bohle RM, Chumachenko P, et al. (2000) CD143 in the development of atherosclerosis. Atherosclerosis 150:21
Mikkelsen HB, Malysz J, Huizinga JD, et al. (1998) Action potential generation, kit receptor immunohistochemistry and morphology of steel-Dickie (Sl/Sld) mutant mouse small intestine. Neurogastroenterol Motil 10:11
Huizinga JD, Robinson TL, Thomsen L (2000) The search for the origin of rhythmicity in intestinal contraction; from tissue to single cells. Neurogastroenterol Motil 12:3
Notley RG (1968) Electron microscopy of the upper ureter and the pelvi-ureteric junction. Br J Urol 40:37
Hoyes AD, Barber P, Martin BG (1975) Comparative ultrastructure of ureteric innervation. Cell Tissue Res 160:515
Gosling JA, Dixon JS (1971) Morphologic evidence that rhe renal calyx and pelvis control ureteric activity in the rabbit. Am J Anat 130:393
Rolle U, Brylla E, Tillig B (1999) Immunohistochemical detection of neuronal plexuses and nerve cells within the upper urinary tract of pigs. BJU Int 83:1045
Edyvane KA, Trussell DC, Jonavicius J, et al. (1992) Presence and regional variation in peptide-containing nerves in the human ureter. J Auton Nerv Syst 39:127
Maeda H, Yamagata A, Nishikawa S, et al. (1992) Requirement of c-kit for development of intestinal pacemaker system. Development 116:369
Kenny SE, Connell MG, Rintala RJ, et al. (1998) Abnormal colonic interstitial cells of Cajal in children with anorectal malformations. J Pediatr Surg 33:130
Masumoto K, Suita S, Nada O, et al. (1999) Abnormalities of enteric neurons, intestinal pacemaker cells, and smooth muscle in human intestinal atresia. J Pediatr Surg 34:1463
Masumoto K, Suita S, Nada O, et al. (1999) Alterations of the intramural nervous distributions in a chick intestinal atresia model. Pediatr Res 45:30
Yamataka A, Ohshiro K, Kobayashi H, et al. (1998) Abnormal distribution of intestinal pacemaker (C-KIT positive) cells in an infant with chronic idiopathic intestinal pseudoobstruction. J Pediatr Surg 33:859
Kenny SE, Vanderwinden IM, Rintala RJ, et al. (1998) Delayed maturation of the interstitial cells of Cajal: a new diagnosis for transient neonatal pseudoobstruction. Report of two cases. J Pediatr Surg 33:94
Wang ZQ, Watanabe Y, Toki A, et al. (2000) Involvement of endogenous nitric oxide and c-kit-expressing cells in chronic intestinal pseudo-obstruction. J Pediatr Surg 35:539
He CL, Burgart L, Wang L, et al. (2000) Decreased interstitial cell of Cajal volume in patients with slow-transit constipation. Gastroenterology 118:14
Altdorfer K, Bagameri G, Donath T, et al. (2002) Nitric oxide synthase immunoreactivity of interstitial cells of Cajal in experimental colitis. Inflamm Res 51:569
Hagger R, Finlayson C, Kahn F, et al. (2000) A deficiency of interstitial cells of Cajal in Chagasic megacolon. J Auton Nerv Syst 80:108
Der T, Bercik P, Donnelly G, et al. (2000) Interstitial cells of Cajal and inflammation-induced motor dysfunction in the mouse small intestine. Gastroenterology 119:1590
Yamataka A, Yamataka T, Lane GI, et al. (1998) Necrotizing enterocolitis and C-KIT. J Pediatr Surg 33:1682
Wang XY, Berezin I, Mikkelsen HB, et al. (2002) Pathology of interstitial cells of Cajal in relation to inflammation revealed by ultrastructure but not immunohistochemistry. Am J Pathol 160:1529
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Metzger, R., Schuster, T., Till, H. et al. Cajal-like cells in the upper urinary tract: comparative study in various species. Ped Surgery Int 21, 169–174 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-004-1314-4
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-004-1314-4