Abstract
Objectives
Both aquaporin (AQP) 1 and the stem-cell factor/C-kit system seem to have a definite role in testis function, but very few studies have been reported in humans, especially in the paediatric age group. With the present study we wanted to investigate the expression of these proteins to better delineate their role in normal and pathologic testes.
Methods
Immunohistology using AQP 1 and C-kit antibodies was performed on paraffin sections of open-testicular biopsies from 32 undescended testes. The testes of cryptorchid patients, with ages ranging from 2 to 15 years, were biopsied during an orchidopexy operation, after obtaining informed consent. Control biopsies, from 8 patients of matched age, were obtained during operations for inguinal hernia or hydrocele, always after obtaining informed consent. Positive results were recorded as diffuse or focal patterns and scored as weak, moderate or strong immunostaining.
Results
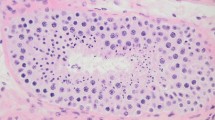
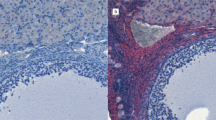
AQP 1 antibody strongly depicted microvessel endothelial cells, but was unlabeled in endotubular and interstitial cell lines, in both control and undescended testes. The C-kit immunostaining in normal testes revealed a diffuse, strong staining in the cytoplasm of spermatogonia and primary spermatocytes. However, in the undescended testes a focal C-kit immunolabelling was weakly recognized in both spermatogonial and immature Sertoli cells.
Conclusions
These results indicate a direct involvement of AQP 1 in the regulation of fluid transport across the endothelial cell membranes of testicular microvessels. A role of the C-kit receptor protein is also substantiated by its strong expression in the maturing spermatogonia of the normal testes, but was minimally or not recognizable in undescended prepubertal testes.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Badran HH, Hermo LS (2002) Expression and regulation of aquaporins 1, 8, and 9 in the testis, efferent ducts, and epididymis of adult rats and during postnatal development. J Androl 23:358–373
Fisher JS, Turner KJ, Fraser HM, Saunders PT, Brown D, Sharpe RM (1998) Immunoexpression of aquaporin-1 in the efferent ducts of the rat and marmoset monkey during development, its modulation by estrogens, and its possible role in fluid resorption. Endocrinology 139:3935–3945
Shanahan CM, Connolly DL, Tyson KL, Cary NR, Osbourn JK, Agre P, Weissberg PL (1999) Aquaporin-1 is expressed by vascular smooth muscle cells and mediates rapid water transport across vascular cell membranes. J Vasc Res 36:353–362
Vigodner M, Lewin LM, Shochat L, Golan R (2001) Spermatogenesis in the golden hamster: the role of c-kit. Mol Reprod Dev 60:562–568
Sandlow JI, Feng HL, Sandra A (1997) Localization and expression of the c-kit receptor protein in human and rodent testis and sperm. Urology 49:494–500
Feng H, Sandlow JI, Sandra A (1998) The c-kit receptor and its possible signaling transduction pathway in mouse spermatozoa. Mol Reprod Dev 49:317–326
Feng HL, Sandlow JI, Sparks AE, Sandra A, Zheng LJ (1999) Decreased expression of the c-kit receptor is associated with increased apoptosis in subfertile human testes. Fertil Steril 71:85–89
Tsuchida J, Dohmae K, Kitamura Y, Nishimune Y (2003) The role of the c-kit receptor in the regenerative differentiation of rat Leydig cells. Int J Androl 26:121–125
Sandlow JI, Feng HL, Cohen MB, Sandra A (1996) Expression of c-Kit and its ligand, stem cell factor, in normal and subfertile human testicular tissue. J Androl 17:403–408
Mauduit C, Hamamah S, Benahmed M (1999) Stem cell factor/c-kit system in spermatogenesis. Hum Reprod Update 5:535–545
Yoshinaga K, Nishikawa S, Ogawa M, Hayashi S, Kunisada T, Fujimoto T, Nishikawa S (1991) Role of c-kit in mouse spermatogenesis: identification of spermatogonia as a specific site of c-kit expression and function. Development 113:689–699
Ohta H, Yomogida K, Dohmae K, Nishimune Y (2000) Regulation of proliferation and differentiation in spermatogonial stem cells: the role of c-kit and its ligand SCF. Development 127:2125–2131
Yan W, Suominen J, Toppari J (2000) Stem cell factor protects germ cells from apoptosis in vitro. J Cell Sci 113:161–168
Pinart E, Bonet S, Briz MD, Pastor LM, Sancho S, Garcia N, Badia E (2001) Morphologic and histochemical study of blood capillaries in boar testes: effects of abdominal cryptorchidism. Teratology 63:42–45
Nistal M, Paniagua R, Diez-Pardo JA (1980) Histologic classification of undescended testes. Hum Pathol 11:666–674
Nicòtina PA (1986) Grading del danno testicolare nel criptorchidismo. Valore predittivo nei disordini testicolari dell’infanzia. Riv Anat Pat Oncol 45:175–186
Nicòtina PA, Arena F, Romeo C, Ferlazzo G, Arena S, Gentile C, Romeo G (2001) Il danno testicolare nel criptorchidismo. Grading isto-prognostico in età pediatrica. Pediatr Oggi Med Chir 1:11–17
Nicòtina PA, Arena F, Romeo C, Ferlazzo G, Arena S, Basile G, Romeo G (2001) Inibin B-unit immunocytochemistry for a prognostic assessment of the changes in undescended testes of pediatric patients. Pediatr Med Chir 23:51–55
Verkman AS (2002) Aquaporin water channels and endothelial cell function. J Anat 200:617–627
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nicòtina, P.A., Romeo, C., Arena, S. et al. Immunohistology of aquaporin-1 and stem cell factor-receptor in human undescended testes. Ped Surgery Int 20, 271–275 (2004). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-003-1125-z
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00383-003-1125-z