Abstract
Introduction
Posttraumatic craniocervical vascular injuries in pediatric traumatic brain injury (TBI) are rare, and children-specific, evidence-based standards on screening and therapy of posttraumatic carotid-cavernous fistula (CCF), craniocervical artery dissections (CCAD), traumatic aneurysms (TA), and posttraumatic sinus venous thrombosis (SVT) is lacking. The aim of this review is to summarize the data on epidemiology, clinical presentation, and treatment of these traumatic lesions in a systematic manner.
Methods
We performed a systematic PubMed search for records of CCF, CCAD, TA, and SVT related to pediatric TBI published until June 2019.
Results
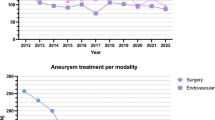
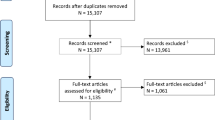
After screening 2439 records, 42 were included in the quantitative analysis. Incidences for CCAD in blunt TBI were 0.21% (range 0.02–6.82%). 11.7% (range 1.69–15.58%) of pediatric aneurysms were found to be traumatic of origin, whereas 38.2% (range 36.84–40%) of all pediatric SVT were due to blunt TBI. For all of the posttraumatic cerebrovascular pathologies, we found a clear male predominance with 68.75% in CCF, 63.4% in CCAD, 60% in TA, and 58.33% in SVT. Clinical presentation did not differ from the adult population with exception of young child. While there is only recommendation for the therapy of CCAD and SVT in the pediatric population, no such recommendation exists for the treatment of CCF’s and TA’s, and data from randomized controlled trials is lacking.
Conclusion
While these results show that posttraumatic CCF, CCAD, TA, and SVT are rarely encountered in children, misdiagnosis may have potentially drastic consequences due to a longer lifetime burden in the pediatric population. Awareness, early recognition, and prompt initiation of the appropriate therapy are essential to avoid morbidity and mortality. Further studies should focus on the development of clinical and radiological screening criteria of posttraumatic vascular lesions in children.


Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AHA:
-
American Heart Association
- AP:
-
Antiplatelet
- AC:
-
Anticoagulation
- ASA:
-
Acetylsalicylate acid
- BCVI:
-
Blunt cerebrovascular injury
- CCAD:
-
Craniocervical artery dissection
- CCF:
-
Carotid-cavernous fistula
- CT:
-
Computed tomography
- CTV:
-
CT venogram
- GCS:
-
Glasgow Coma Scale score
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- MRA:
-
Magnetic resonance angiography
- PA:
-
Pseudoaneurysm
- IA:
-
Intracranial aneurysm
- ICH:
-
Intracerebral hemorrhage
- ICA:
-
Internal carotid artery
- SVT:
-
Sinus venous thrombosis
- TA:
-
Traumatic aneurysm
References
Helmke K, Kühne D (1985) Balloon embolisation of intracranial arteriovenous fistulas in children and juveniles. Pediatr Radiol 15:85–91
Barrow DL, Fleischer AS, Hoffman JC (1982) Complications of detachable balloon catheter technique in the treatment of traumatic intracranial arteriovenous fistulas. J Neurosurg 56:396–403. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1982.56.3.0396
Debrun G, Lacour P, Vinuela F, Fox A, Drake CG, Caron JP (1981) Treatment of 54 traumatic carotid-cavernous fistulas. J Neurosurg 55:678–692. https://doi.org/10.3171/jns.1981.55.5.0678
Joshi DKC, Singh DD, Garg DD, Singh DH, Tandon DM (2016) Assessment of clinical improvement in patients undergoing endovascular coiling in traumatic carotid cavernous fistulas. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 149:46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clineuro.2016.06.008
Adepoju A, Adamo MA (2017) Posttraumatic complications in pediatric skull fracture: dural sinus thrombosis, arterial dissection, and cerebrospinal fluid leakage. J Neurosurg Pediatr 20:598–603. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.6.PEDS16702
Azarakhsh N, Grimes S, Notrica D et al (2013) Blunt cerebrovascular injury in children: underreported or underrecognized? A multicenter ATOMAC study. J Trauma Acute Care Surg 75:1006–1012. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e31829d3526
Chabrier S, Lasjaunias P, Husson B et al (2003) Ischaemic stroke from dissection of the craniocervical arteries in childhood: report of 12 patients. Eur J Paediatr Neurol 7:39–42
Dewan MC, Ravindra VM, Gannon S, Prather CT, Yang GL, Jordan LC, Limbrick D, Jea A, Riva-Cambrin J, Naftel RP (2016) Treatment practices and outcomes after blunt cerebrovascular injury in children. Neurosurgery 79:872–878. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0000000000001352
Dlamini N, Freeman JL, Mackay MT, Hawkins C, Shroff M, Fullerton HJ, Deveber GA (2011) Intracranial dissection mimicking transient cerebral arteriopathy in childhood arterial ischemic stroke. J Child Neurol 26:1203–1206. https://doi.org/10.1177/0883073811408904
Duke BJ, Partington MD (1996) Blunt carotid injury in children. Pediatr Neurosurg 25:188–193. https://doi.org/10.1159/000121122
Frantzen E, Jacobsen HH, Therkelsen J (1961) Cerebral artery occlusions in children due to trauma to the head and neck. A report of 6 cases verified by cerebral angiography. Neurology 11:695–700. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.11.8.695
Fullerton HJ, Johnston SC, Smith WS (2001) Arterial dissection and stroke in children. Neurology 57:1155–1160. https://doi.org/10.1212/wnl.57.7.1155
James CA, Glasier CM, Angtuaco EE (1995) Altered vertebrobasilar flow in children: angiographic, MR, and MR angiographic findings. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 16:1689–1695
Jones TS, Burlew CC, Kornblith LZ, Biffl WL, Partrick DA, Johnson JL, Barnett CC, Bensard DD, Moore EE (2012) Blunt cerebrovascular injuries in the child. Am J Surg 204:7–10. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2011.07.015
Kopelman TR, Berardoni NE, O’Neill PJ et al (2011) Risk factors for blunt cerebrovascular injury in children: do they mimic those seen in adults? J Trauma 71:559–564; discussion 564. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e318226eadd
Lew SM, Frumiento C, Wald SL (1999) Pediatric blunt carotid injury: a review of the National Pediatric Trauma Registry. Pediatr Neurosurg 30:239–244. https://doi.org/10.1159/000028804
Maillard AAJ, Urso RG, Jarolimek AM (2010) Trauma to the intracranial internal carotid artery. J Trauma 68:545–547. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e3181a70a25
Orman G, Tekes A, Poretti A, Robertson C, Huisman TA (2014) Posttraumatic carotid artery dissection in children: not to be missed! J Neuroimaging 24:467–472. https://doi.org/10.1111/jon.12071
Pozzati E, Giuliani G, Poppi M, Faenza A (1989) Blunt traumatic carotid dissection with delayed symptoms. Stroke 20:412–416
Rafay MF, Armstrong D, Deveber G et al (2006) Craniocervical arterial dissection in children: clinical and radiographic presentation and outcome. J Child Neurol 21:8–16. https://doi.org/10.1177/08830738060210010101
Ravindra VM, Riva-Cambrin J, Sivakumar W et al (2015) Risk factors for traumatic blunt cerebrovascular injury diagnosed by computed tomography angiography in the pediatric population: a retrospective cohort study. J Neurosurg Pediatr 15:599–606. https://doi.org/10.3171/2014.11.PEDS14397
Rossidis AC, Tharakan SJ, Bose SK et al (2018) Predictors of pediatric blunt cerebrovascular injury. J Pediatr Surg 53:141–145. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2017.10.037
Ugalde IT, Claiborne MK, Cardenas-Turanzas M, Shah MN, Langabeer JR 2nd, Patel R (2018) Risk factors in pediatric blunt cervical vascular injury and significance of seatbelt sign. West J Emerg Med 19:961–969. https://doi.org/10.5811/westjem.2018.9.39429
Weber CD, Lefering R, Weber MS et al (2019) Predictors for pediatric blunt cerebrovascular injury (BCVI): an international multicenter analysis. World J Surg. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00268-019-05041-8
Hills NK, Johnston SC, Sidney S, Zielinski BA, Fullerton HJ (2012) Recent trauma and acute infection as risk factors for childhood arterial ischemic stroke. Ann Neurol 72:850–858. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.23688
Kirkham FJ, Hogan AM (2004) Risk factors for arterial ischemic stroke in childhood. CNS Spectr 9:451–464
Fox CK, Hills NK, Vinson DR, Numis AL, Dicker RA, Sidney S, Fullerton HJ (2017) Population-based study of ischemic stroke risk after trauma in children and young adults. Neurology 89:2310–2316. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000004708
Pandey AS, Hill E, Al-Holou WN et al (2015) Management of pediatric craniocervical arterial dissections. Childs Nerv Syst 31:101–107. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-014-2547-8
Steinborn M, Schäffeler C, Kabs C, Kraus V, Rüdisser K, Hahn H (2010) CT and MR imaging of primary cerebrovascular complications in pediatric head trauma. Emerg Radiol 17:309–315. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10140-010-0860-4
Fleck SK, Langner S, Baldauf J et al (2011) Incidence of blunt craniocervical artery injuries: use of whole-body computed tomography trauma imaging with adapted computed tomography angiography. Neurosurgery 69:615–623; discussion 623-624. https://doi.org/10.1227/NEU.0b013e31821a8701
Stence NV, Fenton LZ, Goldenberg NA, Armstrong-Wells J, Bernard TJ (2011) Craniocervical arterial dissection in children: diagnosis and treatment. Curr Treat Options Neurol 13:636–648. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11940-011-0149-2
Roach ES, Golomb MR, Adams R, Biller J, Daniels S, Deveber G, Ferriero D, Jones BV, Kirkham FJ, Scott RM, Smith ER, American Heart Association Stroke Council, Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young (2008) Management of stroke in infants and children: a scientific statement from a Special Writing Group of the American Heart Association Stroke Council and the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Young. Stroke 39:2644–2691. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.108.189696
Monagle P, Chalmers E, Chan A et al (2008) Antithrombotic therapy in neonates and children: American College of Chest Physicians Evidence-Based Clinical Practice Guidelines (8th edition). Chest 133:887S–968S. https://doi.org/10.1378/chest.08-0762
Lyrer P, Engelter S (2003) Antithrombotic drugs for carotid artery dissection. Cochrane Database Syst Rev
Burlew CC, Biffl WL, Moore EE, Pieracci FM, Beauchamp KM, Stovall R, Wagenaar AE, Jurkovich GJ (2014) Endovascular stenting is rarely necessary for the management of blunt cerebrovascular injuries. J Am Coll Surg 218:1012–1017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jamcollsurg.2014.01.042
Buis DR, van Ouwerkerk WJR, Takahata H, Vandertop WP (2006) Intracranial aneurysms in children under 1 year of age: a systematic review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst 22:1395–1409. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-006-0142-3
Chen R, Zhang S, Guo R, Ma L, You C (2018) Pediatric intracranial distal arterial aneurysms: report of 35 cases. Acta Neurochir 160:1633–1642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00701-018-3574-0
Chen R, Zhang S, Guo R et al (2018) Pediatric intracranial pseudoaneurysms: a report of 15 cases and review of the literature. World Neurosurg 116:e951–e959. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2018.05.140
Fulkerson DH, Voorhies JM, McCanna SP, Payner TD, Leipzig TJ, Scott JA, DeNardo A, Redelman K, Horner TG (2010) Endovascular treatment and radiographic follow-up of proximal traumatic intracranial aneurysms in adolescents: case series and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst 26:613–620. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-010-1104-3
Hetts SW, Narvid J, Sanai N, Lawton MT, Gupta N, Fullerton HJ, Dowd CF, Higashida RT, Halbach VV (2009) Intracranial aneurysms in childhood: 27-year single-institution experience. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30:1315–1324. https://doi.org/10.3174/ajnr.A1587
Kim M, Lee HS, Lee S et al (2019) Pediatric intracranial aneurysms: favorable outcomes despite rareness and complexity. World Neurosurg. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wneu.2019.01.280
Lasjaunias P, Wuppalapati S, Alvarez H, Rodesch G, Ozanne A (2005) Intracranial aneurysms in children aged under 15 years: review of 59 consecutive children with 75 aneurysms. Childs Nerv Syst 21:437–450. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-004-1125-x
Yang T-C, Lo Y-L, Huang Y-C, Yang S-T (2007) Traumatic anterior cerebral artery aneurysm following blunt craniofacial trauma. Eur Neurol 58:239–245. https://doi.org/10.1159/000107970
Yazbak PA, McComb JG, Raffel C (1995) Pediatric traumatic intracranial aneurysms. Pediatr Neurosurg 22:15–19. https://doi.org/10.1159/000121294
Ventureyra EC, Higgins MJ (1994) Traumatic intracranial aneurysms in childhood and adolescence. Case reports and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst 10:361–379
Aeron G, Abruzzo TA, Jones BV (2012) Clinical and imaging features of intracranial arterial aneurysms in the pediatric population. Radiographics 32:667–681. https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.323105224
Blount JP, Oakes WJ, Tubbs RS, Humphreys RP (2006) History of surgery for cerebrovascular disease in children. Part I. Intracranial arterial aneurysms. Neurosurg Focus 20:E9
Krings T, Geibprasert S, terBrugge KG (2010) Pathomechanisms and treatment of pediatric aneurysms. Childs Nerv Syst 26:1309–1318. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-009-1054-9
Larson PS, Reisner A, Morassutti DJ et al (2000) Traumatic intracranial aneurysms. Neurosurg Focus 8:e4
O’Brien K, Leach J, Jones B et al (2013) Calcifications associated with pediatric intracranial arterial aneurysms: incidence and correlation with pathogenetic subtypes. Childs Nerv Syst 29:643–649. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-012-1985-4
Buckingham MJ, Crone KR, Ball WS, Tomsick TA, Berger TS, Tew JM Jr (1988) Traumatic intracranial aneurysms in childhood: two cases and a review of the literature. Neurosurgery 22:398–408. https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-198802000-00022
Huisman TA, Holzmann D, Martin E, Willi UV (2001) Cerebral venous thrombosis in childhood. Eur Radiol 11:1760–1765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300100822
Holzmann D, Huisman TA, Linder TE (1999) Lateral dural sinus thrombosis in childhood. Laryngoscope 109:645–651. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005537-199904000-00024
Hersh DS, Shimony N, Groves ML, Tuite GF, Jallo GI, Liu A, Garzon-Muvdi T, Huisman TAGM, Felling RJ, Kufera JA, Ahn ES (2018) Pediatric cerebral venous sinus thrombosis or compression in the setting of skull fractures from blunt head trauma. J Neurosurg Pediatr 21:258–269. https://doi.org/10.3171/2017.9.PEDS17311
Matsushige T, Nakaoka M, Kiya K, Takeda T, Kurisu K (2009) Cerebral sinovenous thrombosis after closed head injury. J Trauma 66:1599–1604. https://doi.org/10.1097/TA.0b013e3181a3a8e6
Stiefel D, Eich G, Sacher P (2000) Posttraumatic dural sinus thrombosis in children. Eur J Pediatr Surg 10:41–44. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2008-1072321
Taha JM, Crone KR, Berger TS et al (1993) Sigmoid sinus thrombosis after closed head injury in children. Neurosurgery 32:541–545; discussion 545-546. https://doi.org/10.1227/00006123-199304000-00008
Xavier F, Komvilaisak P, Williams S et al (2014) Anticoagulant therapy in head injury-associated cerebral sinovenous thrombosis in children. Pediatr Blood Cancer 61:2037–2042. https://doi.org/10.1002/pbc.25168
Benifla M, Yoel U, Melamed I, Merkin V, Cohen A, Shelef I (2016) Dural sinus obstruction following head injury: a diagnostic and clinical study. J Neurosurg Pediatr 18:253–262. https://doi.org/10.3171/2016.3.PEDS15690
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hejrati, N., Ebel, F., Guzman, R. et al. Posttraumatic cerebrovascular injuries in children. A systematic review. Childs Nerv Syst 36, 251–262 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-019-04482-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-019-04482-9