Abstract
Purpose
Gamma knife radiosurgery (GKRS) is an established treatment modality for brain arteriovenous malformation (AVM), but there have been few published studies examining the relationship between clinical features of AVM and successful obliteration with GKRS in pediatric patients. In the current study, we investigate the outcomes of GKRS for pediatric patients with brain AVM and analyze the variables that influence obliteration.
Methods
We analyzed 68 pediatric patients (≤ 18 years) with a mean follow-up period of 61.9 months (range 6–215 months). The following parameters were analyzed to determine their influence on obliteration of AVM treated by GKRS: age, sex, target volume, irradiation dose, prior treatment, location of AVM, nidus structure, velocity of AVM, location of venous drainage, number of feeding arteries, and initial presenting symptoms. Also, we estimated clinical factors which should be considered during the follow-up period.
Results
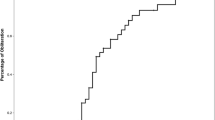
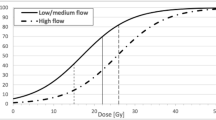
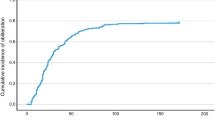
Of the 68 patients, complete obliteration was confirmed in 26 (38.2%) by cerebral angiography. The response rate of AVM for GKRS was 92.6%. No significant association was observed between any of the parameters investigated and the obliteration of AVM, with the exception of number of feeding arteries, which exhibited a statistically significant difference by univariate analysis (p = 0.003). However, on multivariate analysis, nidus structure (p = 0.007), velocity of the main arterial phase (p = 0.013), velocity of the feeding artery phase (p = 0.004), and the number of feeding arteries (p = 0.018) showed statistical significance.
Conclusion
GKRS yielded good long-term clinical outcomes in most pediatric patients. Multiple arterial feeding vessels, diffuse nidus structure, and fast flow of AVM were specific factors associated with a low rate of obliteration in pediatric AVMs.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ali MJ, Bendok BR, Rosenblatt S, Rose JE, Getch CC, Batjer HH (2003) Recurrence of pediatric cerebral arteriovenous malformations after angiographically documented resection. Pediatr Neurosurg 39:32–38
Baumann GS, Wara WM, Larson DA, Sneed PK, Gutin PH, Ciricillo SF, McDermott MW, Park E, Stalpers LJ, Verhey LJ, Smith V, Petti PL, Edwards MS (1996) Gamma knife radiosurgery in children. Pediatr Neurosurg 24:193–201
Bernier-Chastagner V, Supiot S, Carrie C, Helfre S (2012) Stereotactic radiotherapy in pediatric indications. Cancer Radiother : Journal de la Societe francaise de radiotherapie oncologique 16(Suppl):S111–S115
Bir SC, Ambekar S, Maiti TK, Nanda A (2015) Clinical outcome and complications of gamma knife radiosurgery for intracranial arteriovenous malformations. J Clin Neurosci : Off J Neurosurg Soc Australasia 22:1117–1122
Blauwblomme T, Bourgeois M, Meyer P, Puget S, Di Rocco F, Boddaert N, Zerah M, Brunelle F, Rose CS, Naggara O (2014) Long-term outcome of 106 consecutive pediatric ruptured brain arteriovenous malformations after combined treatment. Stroke 45:1664–1671
Borcek AO, Emmez H, Akkan KM, Ocal O, Kurt G, Aykol S, Karahaciogli E, Baykaner KM (2014) Gamma knife radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations in pediatric patients. Childs Nerv Syst : ChNS : Off J Int Socs Pediatr Neurosurg 30:1485–1492
Buis DR, Dirven CM, Lagerwaard FJ, Mandl ES, Lycklama ANGJ, Eshghi DS, van den Berg R, Baayen JC, Meijer OW, Slotman BJ, Vandertop WP (2008) Radiosurgery of brain arteriovenous malformations in children. J Neurol 255:551–560
Chin LS, Raffel C, Gonzalez-Gomez I, Giannotta SL, McComb JG (1992) Diffuse arteriovenous malformations: a clinical, radiological, and pathological description. Neurosurgery 31:863–868 discussion 868-869
Cohen-Gadol AA, Pollock BE (2006) Radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations in children. J Neurosurg 104:388–391
Dinca EB, de Lacy P, Yianni J, Rowe J, Radatz MW, Preotiuc-Pietro D, Kemeny AA (2012) Gamma knife surgery for pediatric arteriovenous malformations: a 25-year retrospective study. J Neurosurg Pediatr 10:445–450
Ellis MJ, Armstrong D, Vachhrajani S, Kulkarni AV, Dirks PB, Drake JM, Smith ER, Scott RM, Orbach DB (2013) Angioarchitectural features associated with hemorrhagic presentation in pediatric cerebral arteriovenous malformations. J Neurointerventional Surg 5:191–195
Fukuoka S, Takanashi M, Seo Y, Suematsu K, Nakamura J (1998) Radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations with gamma-knife: a multivariate analysis of factors influencing the complete obliteration rate. J Clin Neurosci : Off J Neurosurg Soc Australasia 5(Suppl):68–71
Galvan De la Cruz OO, Ballesteros-Zebadua P, Moreno-Jimenez S, Celis MA, Garcia-Garduno OA (2015) Stereotactic radiosurgery for pediatric patients with intracranial arteriovenous malformations: variables that may affect obliteration time and probability. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 129:62–66
Hanakita S, Koga T, Shin M, Igaki H, Saito N (2015) The long-term outcomes of radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations in pediatric and adolescent populations. J Neurosurg Pediatr 16:222–231
Hladky JP, Lejeune JP, Blond S, Pruvo JP, Dhellemmes P (1994) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations in children: report on 62 cases. Childs Nerv Syst : ChNS : Off J Int Soc Pediatr Neurosurg 10:328–333
Jung H, Shah A (2015) Factors determining obliteration in intracranial arteriovenous malformations and associated complications with stereotactic radiosurgery. Clin Neurol Neurosurg 136:71–72
Kader A, Goodrich JT, Sonstein WJ, Stein BM, Carmel PW, Michelsen WJ (1996) Recurrent cerebral arteriovenous malformations after negative postoperative angiograms. J Neurosurg 85:14–18
Kano H, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Yang HC, Flannery TJ, Awan NR, Niranjan A, Novotny J, Lunsford LD (2012) Stereotactic radiosurgery for arteriovenous malformations, part 2: management of pediatric patients. J Neurosurg Pediatr 9:1–10
Kashiwazaki D, Kobayashi R, Houkin K, Kuroda S (2014) Increased expression of vascular endothelial growth factor and its receptor in enlarging brain arteriovenous malformations—a case report. Br J Neurosurg 28:119–121
Klimo P Jr, Rao G, Brockmeyer D (2007) Pediatric arteriovenous malformations: a 15-year experience with an emphasis on residual and recurrent lesions. Childs Nerv Syst : ChNS : Off J Int Soc Pediatr Neurosurg 23:31–37
Kondziolka D, Kano H, Yang HC, Flickinger JC, Lunsford L (2010) Radiosurgical management of pediatric arteriovenous malformations. Childs Nerv Syst : ChNS : Off J Int Soc Pediatr Neurosurg 26:1359–1366
Levy EI, Niranjan A, Thompson TP, Scarrow AM, Kondziolka D, Flickinger JC, Lunsford LD (2000) Radiosurgery for childhood intracranial arteriovenous malformations. Neurosurgery 47:834–841 discussion 841-832
Menovsky T, van Overbeeke JJ (1997) Cerebral arteriovenous malformations in childhood: state of the art with special reference to treatment. Eur J Pediatr 156:741–746
Monteith SJ, Yen CP, Sheehan JP (2011) Gamma knife surgery for pediatric arteriovenous malformations: a review. Clin Neurosurg 58:126–132
Nicolato A, Gerosa M, Ferraresi P, Piovan E, Pasoli A, Perini S, Mazza C (1997) Stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of arteriovenous malformations in childhood. J Neurosurg Sci 41:359–371
Nicolato A, Lupidi F, Sandri MF, Foroni R, Zampieri P, Mazza C, Pasqualin A, Beltramello A, Gerosa M (2006) Gamma knife radiosurgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations in children/adolescents and adults. Part II: differences in obliteration rates, treatment–obliteration intervals, and prognostic factors. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 64:914–921
Pan DH, Kuo YH, Guo WY, Chung WY, Wu HM, Liu KD, Chang YC, Wang LW, Wong TT (2008) Gamma knife surgery for cerebral arteriovenous malformations in children: a 13-year experience. J Neurosurg Pediatr 1:296–304
Paul L, Casasco A, Kusak ME, Martinez N, Rey G, Martinez R (2014) Results for a series of 697 arteriovenous malformations treated by gamma knife: influence of angiographic features on the obliteration rate. Neurosurgery 75:568–583 dicussion 582-563; quiz 583
Pellettieri L, Svendsen P, Wikholm G, Carlsson CA (1997) Hidden compartments in AVMs—a new concept. Acta Radiol (Stockholm, Sweden : 1987) 38:2–7
Potts MB, Sheth SA, Louie J, Smyth MD, Sneed PK, McDermott MW, Lawton MT, Young WL, Hetts SW, Fullerton HJ, Gupta N (2014) Stereotactic radiosurgery at a low marginal dose for the treatment of pediatric arteriovenous malformations: obliteration, complications, and functional outcomes. J Neurosurg Pediatr 14:1–11
Reyns N, Blond S, Gauvrit JY, Touzet G, Coche B, Pruvo JP, Dhellemmes P (2007) Role of radiosurgery in the management of cerebral arteriovenous malformations in the pediatric age group: data from a 100-patient series. Neurosurgery 60:268–276 discussion 276
Sheth SA, Potts MB, Sneed PK, Young WL, Cooke DL, Gupta N, Hetts SW (2014) Angiographic features help predict outcome after stereotactic radiosurgery for the treatment of pediatric arteriovenous malformations. Childs Nerv Syst : ChNS : Off J Int Soc Pediatr Neurosurg 30:241–247
Sonstein WJ, Kader A, Michelsen WJ, Llena JF, Hirano A, Casper D (1996) Expression of vascular endothelial growth factor in pediatric and adult cerebral arteriovenous malformations: an immunocytochemical study. J Neurosurg 85:838–845
Tanaka T, Kobayashi T, Kida Y, Oyama H, Niwa M (1995) The comparison between adult and pediatric AVMs treated by gamma knife radiosurgery. No Shinkei Geka Neurol Surg 23:773–777
Yen CP, Monteith SJ, Nguyen JH, Rainey J, Schlesinger DJ, Sheehan JP (2010) Gamma knife surgery for arteriovenous malformations in children. J Neurosurg Pediatr 6:426–434
Yeon JY, Shin HJ, Kim JS, Hong SC, Lee JI (2011) Clinico-radiological outcomes following gamma knife radiosurgery for pediatric arteriovenous malformations. Childs Nerv Syst : ChNS : Off J Int Soc Pediatr Neurosurg 27:1109–1119
Zipfel GJ, Bradshaw P, Bova FJ, Friedman WA (2004) Do the morphological characteristics of arteriovenous malformations affect the results of radiosurgery? J Neurosurg 101:393–401
Acknowledgements
The authors thank Dr. Eui Jong Kim for his assistance in cerebral angiography interpretation.
Funding
No funding was received for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The authors have no personal financial or institutional interest in any of the drugs, materials, or devices described in this article.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Presentation at Conference: None
IRB Number: KMC IRB 1523-07
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, C.K., Choi, S.K., Lee, S.H. et al. Clinical outcomes and radiosurgical considerations for pediatric arteriovenous malformation: influence of clinical features on obliteration rate. Childs Nerv Syst 33, 2137–2145 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3579-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-017-3579-7