Abstract
Purpose
Spinal cord metastasis from rhabdomyosarcoma (RMS) is extremely rare, with three cases reported to date. Herein, we report an aggressive case of RMS of the infratemporal fossa who which developed spinal cord metastases during treatment.
Case presentation
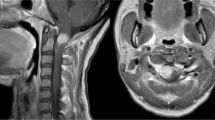
A 6-year-old girl presented with an enlarging painless mass around her right ear for 3 months. An enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) revealed a 5 × x4 × x4.5 5 cm mass on her right infratemporal fossa. A tru-cut biopsy was performed, and histopathologic examination revealed the diagnosis of rhabdomyosarcoma. At the time of the diagnosis, cerebrospinal fluid cytology was negative for malignant cells. The patient underwent induction chemotherapy. There was minimal response to chemotherapy, and the patient underwent curative radiotherapy. However, by 12th fraction of RT, the patient developed a progressive weakness on her lower extremity. Spinal MRI revealed multiple gross masses in different parts of the spinal cord. The local radiotherapy was changed toas craniospinal radiotherapy. However, two 2 weeks after the completion of the RT, the patient developed sepsis and expired because of septic shock.
Conclusion
Parameningeal RMS is a peculiar subgroup of RMS, which needs an aggressive approach. Despite aggressive approach, meningeal spread is the most important cause of the treatment failure. We should keept in mind that during the treatment, there can be meningeal spread towards to either the brain or spinal cord; therefore, we should follow -up the patients closely from this aspect.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okcu MF, Hicks J, Horowitz M. (2016) Rhabdomyosarcoma in childhood and adolescence: Epidemiology, pathology, and molecular pathogenesis. Up to date. Available online: http://www.uptodate.com/contents/rhabdomyosarcoma-in-childhood-and-adolescence-epidemiology-pathology-and-molecularpathogenesis?
Ries LAG, Harkins D, Krapcho M, et al. SEER Cancer Statistics Review, 1975–2003, National Cancer Institute. Bethesda, MD. http://seer.cancer.gov/csr/1975_2003. Accessed 10 June 2011
Pastore G, Peris-Bonet R, Carli M et al (2006) Childhood soft tissue sarcomas incidence and survival in European children (1978-1997): report from the automated childhood cancer information system project. Eur J Cancer 42:2136
Lanzkowsky P (2000) Rhabdomyosarcoma and other soft tissue sarcomas. In: Manual of pediatric hematology and oncology, 3rd ed. New York: Academic Press v. 1. chap. 20
Shields CL, Shields JA, Honavar SG, Demirci H (2001) Primary ophthalmic rhabdomyosarcoma in 33 patients. Trans Am Ophthalmol Soc 99:133–142
Porterfield JF, Zimmerman LE (1962) Rhabdomyosarcoma of the orbit; a clinicopathologic study of 55 cases. Virchows Arch Pathol Anat Physiol Klin Med 335:329–344
Grieman RB, Katsikeris NF, Symington JM (1988) Rhabdomyosarcoma of the maxillary sinus: review of the literature and report of a case. J Oral Maxillofac Surg 46:1090–1096
Makishima K, Iwasaki H, Horie A (1975) Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma of the ethmoid sinus. Laryngoscope 85:400–410
Prat J, Gray GF (1977) Massive neuraxial spread of aural rhabdomyosarcoma. Acta Otolaryngol 103(5):301–303
Raney RB (1978) Spinal cord “drop metastases” from head and neck rhabdomyosarcoma: proceedings of the tumor Board of the Children's Hospital of Philadelphia. Med Pediatr Oncol 4(1):3–9
Keorochana G, Chanplakorn P, Laohacharoensombat W, Larbcharoensub N (2007) Spinal and bilateral breast metastases of embryonal rhabdomyosarcoma. J Med Assoc Thail 90(4):813–818
Sarkar D, Ray S, Saha M, Chakrabarti P (2012) Alveolar rhabdomyosarcoma with multiple distal metastases. A case report and review of literature. BMJ Case Rep. doi: 10.1136/bcr-2012-006523.
Rumboldt Z, Jednacak H, Talan-Hranilović J, Kalousek V (2004) Spinal epidural rhabdomyosarcoma. Acta Neurochir 146(2):195–197
Khalatbari MR, Jalaeikhoo H, Hamidi M, Moharamzad Y (2012) Primary spinal epidural rhabdomyosarcoma: a case report and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst 28(11):1977–1980
Parasuraman S, Langston J, Rao BN, Poquette CA, Jenkins JJ, Merchant T et al (1999) Brain metastases in pediatric Ewing sarcoma and rhabdomyosarcoma: the St. Jude Children's Research Hospital experience. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 21(5):370–377
Gasparini M, Lombardi F, Gianni MC, Massimino M, Gandola L, Fossati-Bellani F (1990) Questionable role of CNS radioprophylaxis in the therapeutic management of childhood rhabdomyosarcoma with meningeal extension. J Clin Oncol 8(11):1854–1857
Karatay S (1949) Rhabdomyosarcoma of the middle ear. Arch Otolaryngol 50:330–334
Hutchinson RT, Raney RB, Littman P (1977) Meningeal extension of head and neck rhabdomyosarcoma. J Pediatr 91:516–517
Tefft M, Fernandez C, Donaldson M et al (1978) Incidence of meningeal involvement by rhabdomyosarcoma of the head and neck in children. Cancer 42:253–258
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Funding source
None
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yavas, G., Karabagli, P., Paksoy, Y. et al. An aggressive parameningeal rhabdomyosarcoma with multiple spinal cord metastases: a case report and review of the literature. Childs Nerv Syst 33, 843–847 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3318-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00381-016-3318-5