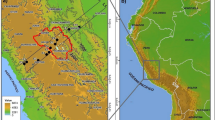
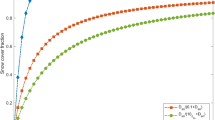
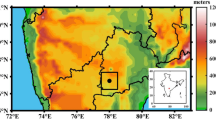
Abstract
The complexity of inhomogeneous surface-atmosphere radiation transfer is one of the foremost problems in the field of atmospheric physics and atmospheric radiation. To date, the influence of surface properties on shortwave radiation has not been well studied. The daily downward surface shortwave radiation of the latest FLASHFlux/CERES (Fast Longwave And Shortwave Fluxes_Time Interpolated and Spatially Averaged/Clouds and the Earth’s Radiant Energy System) satellite data was evaluated against in situ data. The comparison indicated that the differences between the two data sets are unstable and large over rugged terrain compared with relatively flat terrain, and the mean absolute error of the satellite products reaches 31.4 W m−2 (12.3%) over rugged terrain. Based on the SSF (single satellite footprint)/CERES product, the influence of surface properties on the distribution of downward surface shortwave radiation (DSSR) was analyzed. The influence of surface properties on DSSR over the Tibetan Plateau is about twice as large as that in two other regions located at the same latitude (eastern China-western Pacific and subtropical North Pacific). A simulation was carried out with the help of the I3RC (International Intercomparision of Three-Dimensional Radiation Code) Monte Carlo 3D radiative transfer community model. The results showed that DSSR increases as surface albedo increases. Moreover, the impact of surface albedo on DSSR is larger if the spatial distribution of clouds is more non-uniform. It is hoped that these results will contribute to the development of 3D radiative transfer models and the improvement of satellite inversion algorithms.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cahalan, R. F., and Coauthors, 2005: The I3RC: Bringing together the most advanced radiative transfer tools for cloudy atmospheres. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 86(9), 1275–1293.
Cong, Z. Y., S. C. Kang, A. Smirnov, and B. Holben, 2009: Aerosol optical properties at Nam Co, a remote site in central Tibetan Plateau. Atmos. Res., 92(1), 42–48.
Dubayah, R. C., and S. Loechel, 1997: Modeling topographic solar radiation using GOES data. J. Appl. Meteor., 36(2), 141–154.
Dubayah, R. C., and P. M. Rich, 1995: Topographic solar radiation models for GIS. Int. J. Geographical Inform. Syst., 9(4), 405–419.
Evans, K. F., and A. Marshak, 2005: Numerical methods. 3D Radiative Transfer in Cloudy Atmospheres. A. Marshak and A. B. Davis, Eds., Springer, Berlin, 261–274.
Geiger, M., L. Diabate, L. Menard, and L. Wald, 2002: A web service for controlling the quality of measurements of global solar irradiation. Solar Energy, 73(6), 475–480.
Gui, S., S. L. Liang, and L. Li, 2009: Validation of surface radiation data provided by the CERES over the Tibetan Plateau. 2009 17th International Conference on Geoinformatics, Fairfax, VA, 1–6.
Gui, S., S. L. Liang, K. C. Wang, and L. Li, 2010: Assessment of three satellite-estimated land surface downwelling shortwave irradiance data Sets. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett., 7(4), 776–780.
Gupta, S. K., D. P. Kratz, Jr. P. W. Stackhouse, and A. C. Wilber, 2001: The Langley parameterized shortwave algorithm (LPSA) for surface radiation budget studies (version1.0). NASA/TP-2001-211272.
Hayasaka, T., K. Kawamoto, G. Shi, and A. Ohmura, 2006: Importance of aerosols in satellite-derived estimates of surface shortwave irradiance over China. Geophys. Res. Lett., 33, L06802, doi:10.1029/2005GL025093.
Helbig, N., H. Löwe, and M. Lehning, 2009: Radiosity approach for the surface radiation balance in complex terrain. J. Atmos. Sci., 66, 2900–2912.
Houborg, R., H. Soegaard, W. Emmerich, and S. Moran, 2007: Inferences of all-sky solar irradiance using Terra and Aqua MODIS satellite data. Int. J. Remote Sens., 28(20), 4509–4535.
Huang, J. Y., 2004: Meteorological Statistical Analysis and Forecast Method. China Meteorological Press, Beijing, 298 pp. (in Chinese)
Huo, J., and D. R. L ü, 2012: Cloud amount analysis at Yangbajing of Tibet in 2009–2010 using all-sky images. Climatic and Environmental Research, 17(4), 393–399. (in Chinese)
Kang, S., S. Kim, and D. Lee, 2002: Spatial and temporal patterns of solar radiation based on topography and air temperature. Canadian Journal of Forest Research, 32(3), 487–497.
Kim, H. Y., and S. L. Liang, 2010: Development of a hybrid method for estimating land surface shortwave net radiation from MODIS data. Remote Sens. Environ., 114, 2393–2402.
Kurosaki, Y., and F. Kimura, 2002: Relationship between topography and daytime cloud activity around Tibetan Plateau. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 80(6), 1139–1355.
Kuwagata, T., A. Numaguti, and N. Endo, 2001: Diurnal variation of water vapor over the central Tibetan Plateau during summer. J. Meteor. Soc. Japan, 79, 401–418.
Lee, W. L., K. N. Liou, and C. C. Wang, 2013: Impact of 3-D topography on surface radiation budget over the Tibetan Plateau. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 113, 95–103.
Li, Z., H. G. Leighton, K. Masuda, and T. Takashima, 1993: Estimation of SW flux absorbed at the surface from TOA reflected flux. J. Climate, 6(2), 317–330.
Liou, K. N., 2002: An Introduction to Atmospheric Radiation. 2nd ed., Academic Press, Boston, 583 pp.
Liou, K. N., W. Lee, and A. Hall, 2007: Radiative transfer in mountains: Application to the Tibetan Plateau. Geophys. Res. Lett., 34, L23809, doi: 10.1029/2007GL031762.
Loeb, N. G., N. M. Smith, S. Kato, W. F. Miller, S. K. Gupta, P. Minnis, and B. A. Wielicki, 2003: Angular distribution models for top-of-atmosphere radiative flux estimation from the clouds and the Earth’s radiant energy system instrument on the Tropical Rainfall Measuring Mission satellite. Part I: Methodology. J. Appl. Meteor., 42, 240–265.
Ma, Y., and R. T. Pinker, 2012: Modeling shortwave radiative fluxes from satellites. J. Geophys. Res., 117, D23202, doi: 10.1029/2012JD018332.
Ma, Y., and Coauthors, 2005: Diurnal and inter-monthly variation of land surface heat fluxes over the central Tibetan Plateau area. Theor. Appl. Climatol., 80, 259–273.
Maddux, B., S. A. Ackeman, and S. Platnick, 2010: Viewing geometry dependencies in MODIS cloud products. J. Atmos. Oceanic Technol., 27(9), 1519–1528.
Manners, J., S. B. Vosper, N. Roberts, 2012: Radiative transfer over resolved topographic features for high-resolution weather prediction. Quart. J. Roy. Meteor. Soc., 138, 720–733.
Moeng, C.H., and Coauthors, 1996: Simulation of a stratocumulustopped planetary boundary layer: Intercomparison among different numerical codes. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 77(2), 261–278.
Ohring, G., B. Wielicki, R. Spencer, B. Emery, and R. Datla, 2005: Satellite instrument calibration for measuring global climate change. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 86, 1303–1314.
Pincus, R., and K. F. Evans, 2009: Computational cost and accuracy in calculating three-dimensional radiative transfer: Results for new implementations of Monte Carlo and SHDOM. J. Atmos. Sci., 66, 3131–3146.
Qin, J., K. Yang, S. Liang, and W. Tang, 2012: Estimation of daily mean photosynthetically active radiation under All-Sky conditions based on relative sunshine data. J. Appl. Meteor. Climatol., 51, 150–160.
Ryu, Y., S. Kang, S. K. Moon, and J. Kim, 2008: Evaluation of land surface radiation balance derived from moderate resolution imaging spectroradiometer (MODIS) over complex terrain and heterogeneous landscape on clear sky days. Agric. Forest. Meteorol., 148(10), 1538–1552.
Spencer, J. W., 1971: Fourier series representation of the position of the sun. Search, 2, 172.
Stevens, B., and D. H. Lenschow, 2001: Observations, experiments, and large eddy simulation. Bull. Amer. Meteor. Soc., 82(2), 283–294.
Stöckli, R., 2013: The HelioMont Surface Solar Radiation Processing. Scientific Report MeteoSwiss, No. 93, 122 pp.
Stroeve, J., J. E. Box, F. Gao, S. Liang, A. Nolin, and C. Schaaf, 2005: Accuracy assessment of the MODIS 16-day albedo product for snow: Comparisons with Greenland in suit measurements. Remote Sens. Environ., 94(1), 46–60.
Wang, K. C., X. J. Zhou, J. M. Liu, and M. Sparrow, 2005: Estimating surface solar radiation over complex terrain using moderate-resolution satellite sensor data. Int. J. Remote Sens., 26(1), 47–58.
Wang, L. D., D. R. Lü, and W. X. Zhang, 2013: Study on characteristic of solar radiation at Nam Co and Yangbajain in Qinghai-Xizang Plateau. Plateau Meteorology, 32(2), 315–326. (in Chinese)
Wang, L. D., D. R. Lü, and J. Huo, 2014: Observation and simulation of abnormal transmittance over Yangbajing, Tibet. Atmospheric and Oceanic Sciences Letters, 7, 190–197, doi: 10.3878/j.issn.1674-2834.13.0086.
Wang, S., R. F. Grant, D. L. Verseghy, and T. A. Blac, 2002: Modelling carbon dynamics of boreal forest ecosystems using the Canadian land surface scheme. Climatic Change, 55(4), 451–477.
Yang, K., T. Koike, P. Stackhouse, C. Mikovitz, and S. J. Cox, 2006: An assessment of satellite Surface radiation Products for highlands with Tibet instrumental data. Geophys. Res. Lett., 33, L22403, doi: 10.1029/2006GL027640.
Yang, K., R. T. Pinker, Y. M. Ma, T. Koike, M. M. Wonsick, S. J. Cox, Y. C. Zhang, and P. Stackhouse, 2008: Evaluation of satellite estimates of downward shortwave radiation over the Tibetan Plateau. J. Geophys. Res., 113, D17204, doi: 10.1029/2007JD009736.
Yang, K., J. He, W. J. Tang, J. Qin, and C. C. K. Cheng, 2010: On downward shortwave and longwave radiations over high altitude regions: Observation and modeling in the Tibetan Plateau. Agric. Forest. Meteor., 150(1), 38–46.
Zhang, Y. C., W. B. Rossow, and Jr. P. W. Stackhouse, 2006: Comparison of different global information sources used in surface radiative flux calculation: Radiative properties of the near-surface atmosphere. J. Geophys. Res., 111, D13106, doi: 10.1029/2005JD006873.
Zhang, Y. C., W. B. Rossow, and Jr. P.W. Stackhouse, 2007: Comparison of different global information sources used in surface radiative flux calculation: Radiative properties of the surface. J. Geophys. Res., 112, D01102, doi: 10.1029/2005JD007008.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, L., Lü, D. & He, Q. The impact of surface properties on downward surface shortwave radiation over the Tibetan Plateau. Adv. Atmos. Sci. 32, 759–771 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-014-4131-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00376-014-4131-2